Abstract
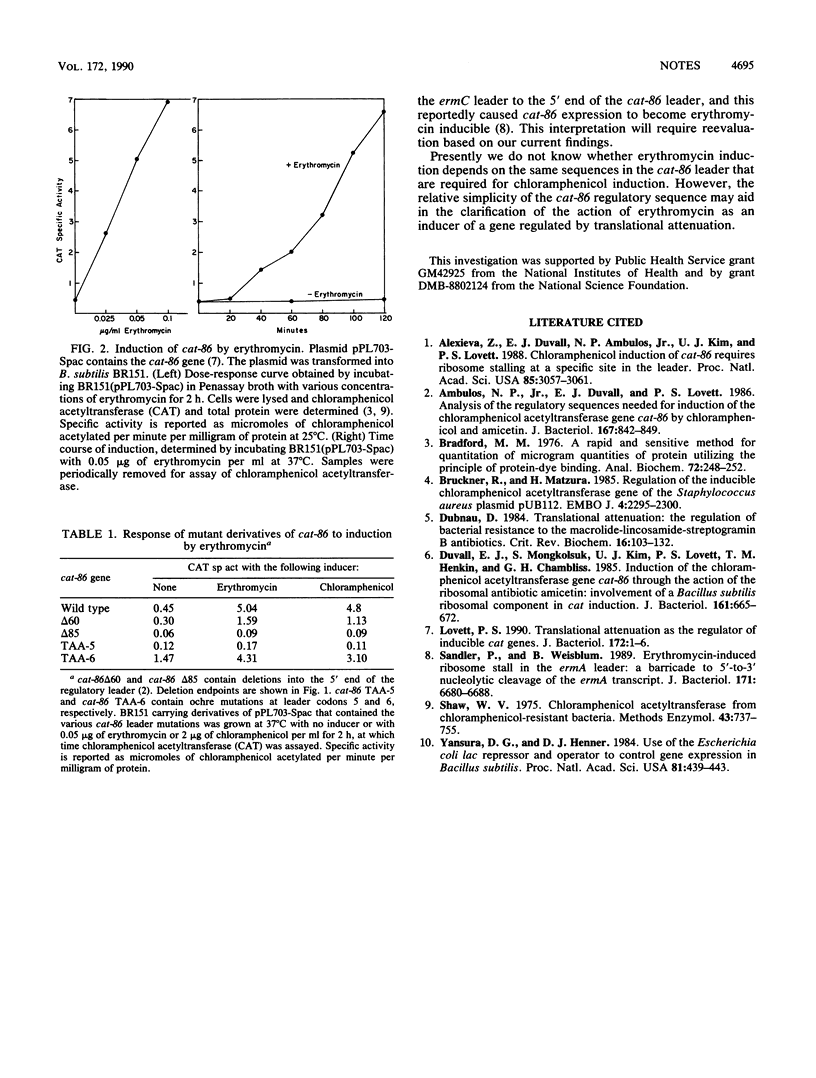
The plasmid gene cat-86 specifies chloramphenicol-inducible chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in Bacillus subtilis. This gene, like the erythromycin-inducible erm genes, is regulated by translational attenuation. Here we show that cat-86 is also inducibly regulated by erythromycin. cat-86 does not confer resistance to erythromycin.
Full text
PDF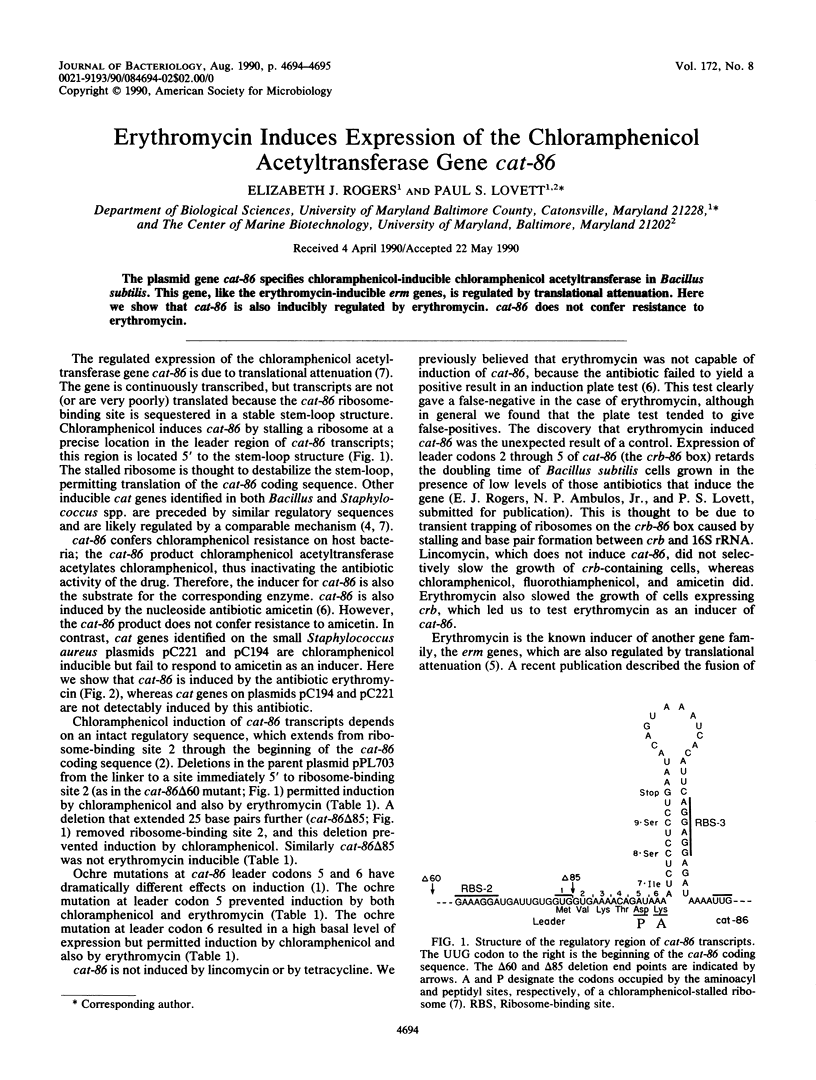
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexieva Z., Duvall E. J., Ambulos N. P., Jr, Kim U. J., Lovett P. S. Chloramphenicol induction of cat-86 requires ribosome stalling at a specific site in the leader. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3057–3061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambulos N. P., Jr, Duvall E. J., Lovett P. S. Analysis of the regulatory sequences needed for induction of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene cat-86 by chloramphenicol and amicetin. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):842–849. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.842-849.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brückner R., Matzura H. Regulation of the inducible chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene of the Staphylococcus aureus plasmid pUB112. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2295–2300. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03929.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D. Translational attenuation: the regulation of bacterial resistance to the macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B antibiotics. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1984;16(2):103–132. doi: 10.3109/10409238409102300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duvall E. J., Mongkolsuk S., Kim U. J., Lovett P. S., Henkin T. M., Chambliss G. H. Induction of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene cat-86 through the action of the ribosomal antibiotic amicetin: involvement of a Bacillus subtilis ribosomal component in cat induction. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):665–672. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.665-672.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett P. S. Translational attenuation as the regulator of inducible cat genes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.1-6.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandler P., Weisblum B. Erythromycin-induced ribosome stall in the ermA leader: a barricade to 5'-to-3' nucleolytic cleavage of the ermA transcript. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6680–6688. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6680-6688.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V. Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase from chloramphenicol-resistant bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:737–755. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43141-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yansura D. G., Henner D. J. Use of the Escherichia coli lac repressor and operator to control gene expression in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):439–443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



