Abstract
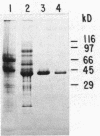
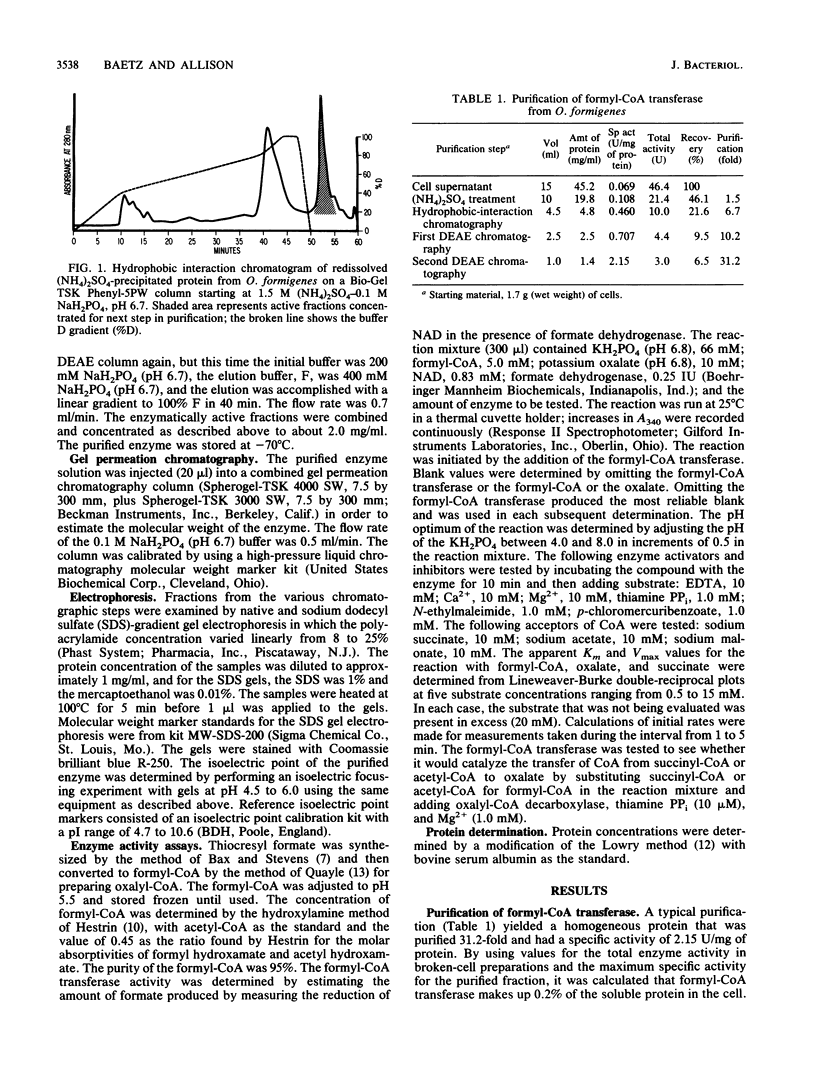
Formyl-coenzyme A (formyl-CoA) transferase was purified from Oxalobacter formigenes by high-pressure liquid chromatography with hydrophobic interaction chromatography and by DEAE anion-exchange chromatography. The enzyme was a single entity on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and gel permeation chromatography (Mr, 44,000). It had an isoelectric point of 4.7. The enzyme catalyzed the transfer of CoA from formyl-CoA to either oxalate or succinate. Apparent Km and Vmax values, respectively, were 3.0 mM and 29.6 mumols/min per mg for formyl-CoA with an excess of succinate. The maximum specific activity was 2.15 mumols of CoA transferred from formyl-CoA to oxalate per min per mg of protein.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison M. J., Cook H. M. Oxalate degradation by microbes of the large bowel of herbivores: the effect of dietary oxalate. Science. 1981 May 8;212(4495):675–676. doi: 10.1126/science.7221555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison M. J., Dawson K. A., Mayberry W. R., Foss J. G. Oxalobacter formigenes gen. nov., sp. nov.: oxalate-degrading anaerobes that inhabit the gastrointestinal tract. Arch Microbiol. 1985 Feb;141(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00446731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison M. J., Littledike E. T., James L. F. Changes in ruminal oxalate degradation rates associated with adaptation to oxalate ingestion. J Anim Sci. 1977 Nov;45(5):1173–1179. doi: 10.2527/jas1977.4551173x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anantharam V., Allison M. J., Maloney P. C. Oxalate:formate exchange. The basis for energy coupling in Oxalobacter. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7244–7250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baetz A. L., Allison M. J. Purification and characterization of oxalyl-coenzyme A decarboxylase from Oxalobacter formigenes. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2605–2608. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2605-2608.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson K. A., Allison M. J., Hartman P. A. Isolation and some characteristics of anaerobic oxalate-degrading bacteria from the rumen. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Oct;40(4):833–839. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.4.833-839.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James L. F., Butcher J. E. Halogeton poisoning of sheep: effect of high level oxalate intake. J Anim Sci. 1972 Dec;35(6):1233–1238. doi: 10.2527/jas1972.3561233x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUAYLE J. R. CARBON ASSIMILATION BY PSEUDOMONAS OXALATICUS (OX1). 7. DECARBOXYLATION OF OXALYL-COENZYME A TO FORMYL-COENZYME A. Biochem J. 1963 Dec;89:492–503. doi: 10.1042/bj0890492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUAYLE J. R. Chemical synthesis of oxalyl-coenzyme A and its enzymic reduction to glyxylate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Feb 26;57:398–400. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)91142-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLY W. S., STADTMAN E. R. FORMATE METABOLISM. I. FORMYL COENZYME A, AN INTERMEDIATE IN THE FORMATE-DEPENDENT DECOMPOSITION OF ACETYL PHOSPHATE IN CLOSTRIDIUM KLUYVERI. J Biol Chem. 1963 Aug;238:2632–2638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sramek S. J., Frerman F. E. Escherichia coli coenzyme A-transferase: kinetics, catalytic pathway and structure. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Nov;171(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sramek S. J., Frerman F. E. Purification and properties of Escherichia coli coenzyme A-transferase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Nov;171(1):14–26. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]