Abstract
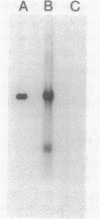
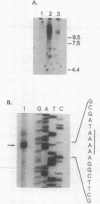
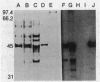
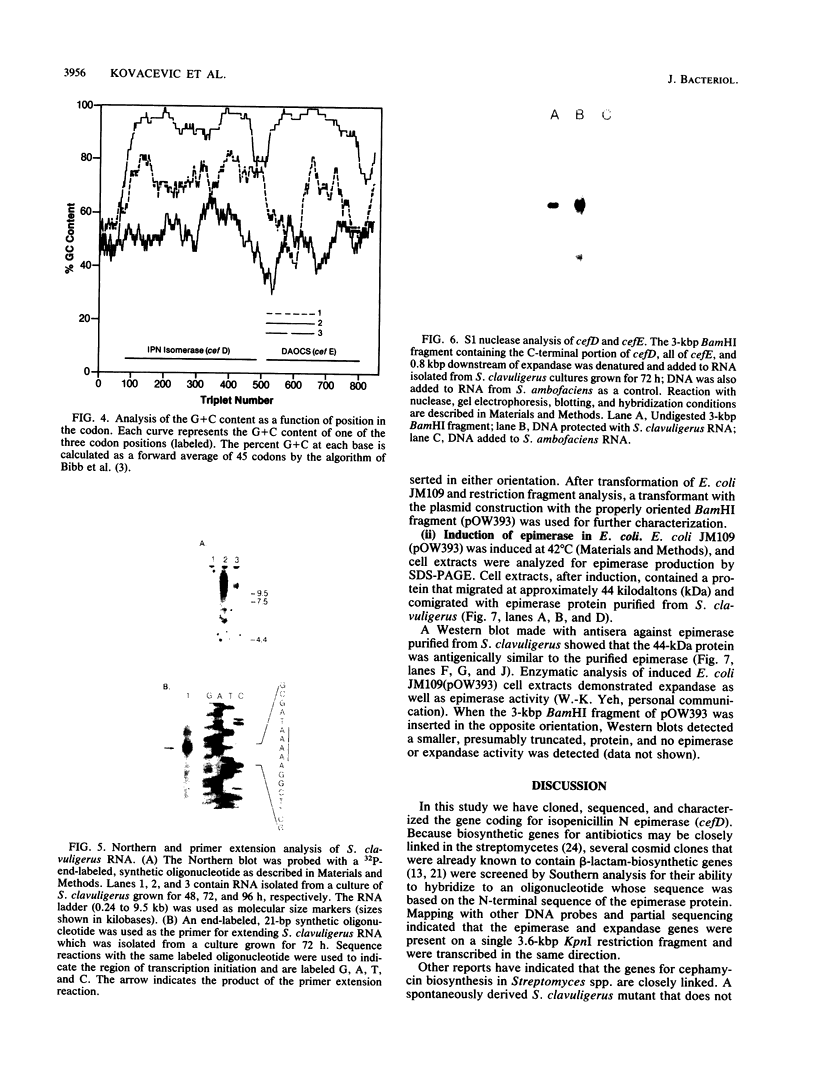
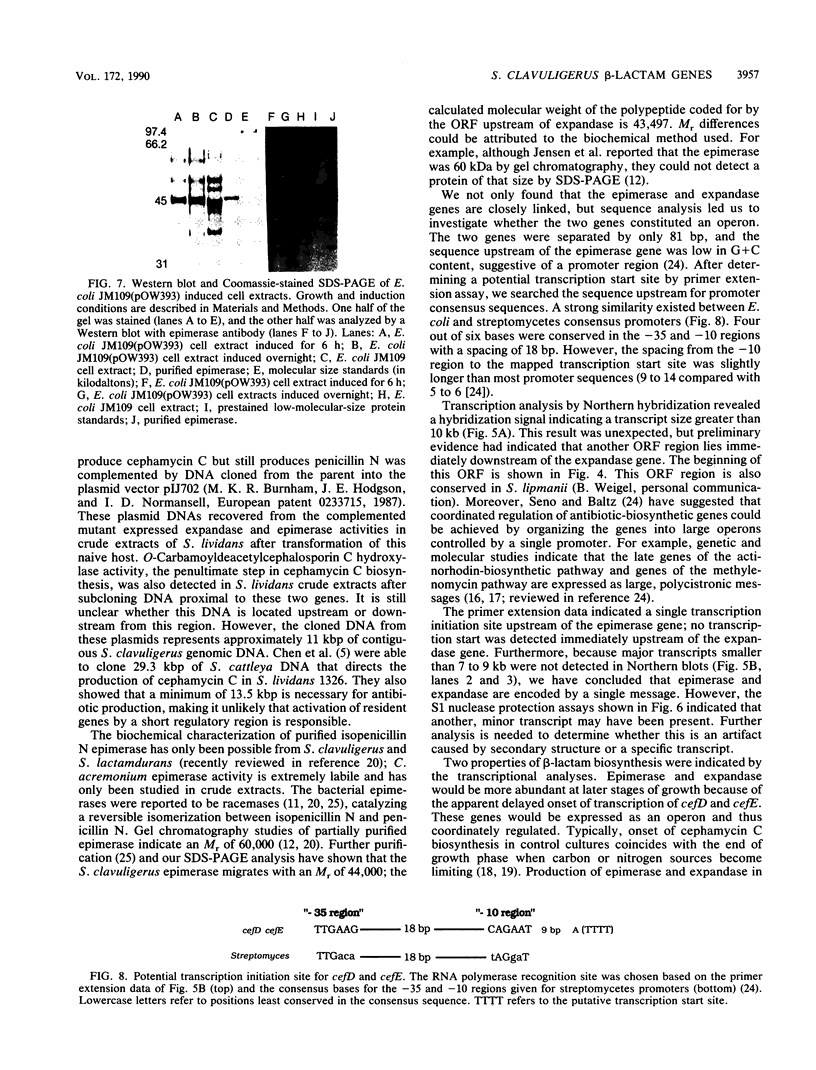
Isopenicillin N isomerase (epimerase) has been purified from Streptomyces clavuligerus, and the amino acid sequence of the N-terminus has been determined. By using single oligonucleotide probes based on high GC codon bias ("guessmers"), the translation start codons were determined for two successive genes in the beta-lactam-biosynthetic pathway and mapped within a 3.6-kilobase-pair KpnI restriction fragment. The epimerase gene (cefD) was located immediately upstream of the deacetoxycephalosporin C synthetase (expandase) gene (cefE) that was characterized previously. cefD was sequenced and expressed in Escherichia coli; the resulting cell extracts contained epimerase activity. Western immunoblots demonstrated that a protein comigrated with purified S. clavuligerus epimerase at 44 kilodaltons. cefD and cefE were separated by an 81-base-pair segment. The DNA sequence upstream of the epimerase gene had a high AT content, suggestive of a promoter region. Primer extension analysis of S. clavuligerus mRNA showed that the start of transcription occurred approximately 130 base pairs upstream of the epimerase translation start site; Northern (RNA blot) analysis revealed a hybridization signal large enough to code for both epimerase and expandase, and nuclease S1 protection assays showed that a single message may code for epimerase, expandase, and another unknown protein. When cefD and cefE were placed in an expression vector, concomitant synthesis of both epimerase and expandase occurred in E. coli.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aharonowitz Y., Demain A. L. Carbon catabolite regulation of cephalosporin production in Streptomyces clavuligerus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Aug;14(2):159–164. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.2.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aharonowitz Y., Demain A. L. Nitrogen nutrition and regulation of cephalosporin production in Streptomyces clavuligerus. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Jan;25(1):61–67. doi: 10.1139/m79-010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Findlay P. R., Johnson M. W. The relationship between base composition and codon usage in bacterial genes and its use for the simple and reliable identification of protein-coding sequences. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortés J., Liras P., Castro J. M., Martín J. F. Glucose regulation of cephamycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces lactamdurans is exerted on the formation of alpha-aminoadipyl-cysteinyl-valine and deacetoxycephalosporin C synthase. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Jul;132(7):1805–1814. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-7-1805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher S. H., Wray L. V., Jr Regulation of glutamine synthetase in Streptomyces coelicolor. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2378–2383. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2378-2383.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingolia T. D., Queener S. W. Beta-lactam biosynthetic genes. Med Res Rev. 1989 Apr-Jun;9(2):245–264. doi: 10.1002/med.2610090206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayatilake G. S., Huddleston J. A., Abraham E. P. Conversion of isopenicillin N into penicillin N in cell-free extracts of Cephalosporium acremonium. Biochem J. 1981 Feb 15;194(2):645–647. doi: 10.1042/bj1940645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen S. E., Westlake D. W., Wolfe S. Partial purification and characterization of isopenicillin N epimerase activity from Streptomyces clavuligerus. Can J Microbiol. 1983 Nov;29(11):1526–1531. doi: 10.1139/m83-234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacevic S., Weigel B. J., Tobin M. B., Ingolia T. D., Miller J. R. Cloning, characterization, and expression in Escherichia coli of the Streptomyces clavuligerus gene encoding deacetoxycephalosporin C synthetase. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):754–760. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.754-760.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leskiw B. K., Aharonowitz Y., Mevarech M., Wolfe S., Vining L. C., Westlake D. W., Jensen S. E. Cloning and nucleotide sequence determination of the isopenicillin N synthetase gene from Streptomyces clavuligerus. Gene. 1988;62(2):187–196. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90557-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lübbe C., Wolfe S., Demain A. L. Repression and inhibition of cephalosporin synthetases in Streptomyces clavuligerus by inorganic phosphate. Arch Microbiol. 1985 Jan;140(4):317–320. doi: 10.1007/BF00446970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malpartida F., Hopwood D. A. Molecular cloning of the whole biosynthetic pathway of a Streptomyces antibiotic and its expression in a heterologous host. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):462–464. doi: 10.1038/309462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malpartida F., Hopwood D. A. Physical and genetic characterisation of the gene cluster for the antibiotic actinorhodin in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Oct;205(1):66–73. doi: 10.1007/BF02428033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martín J. F., Liras P. Enzymes involved in penicillin, cephalosporin and cephamycin biosynthesis. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 1989;39:153–187. doi: 10.1007/BFb0051954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usui S., Yu C. A. Purification and properties of isopenicillin N epimerase from Streptomyces clavuligerus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Nov 9;999(1):78–85. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(89)90033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]