Abstract
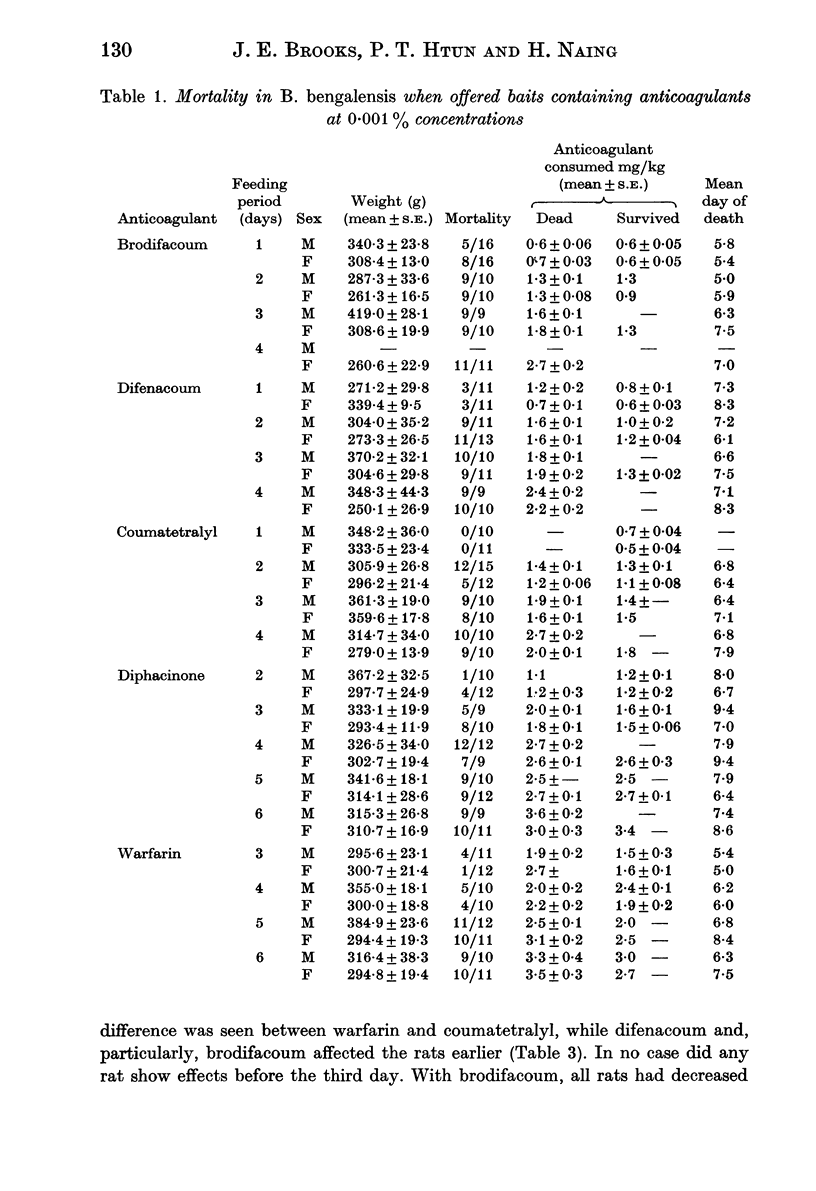
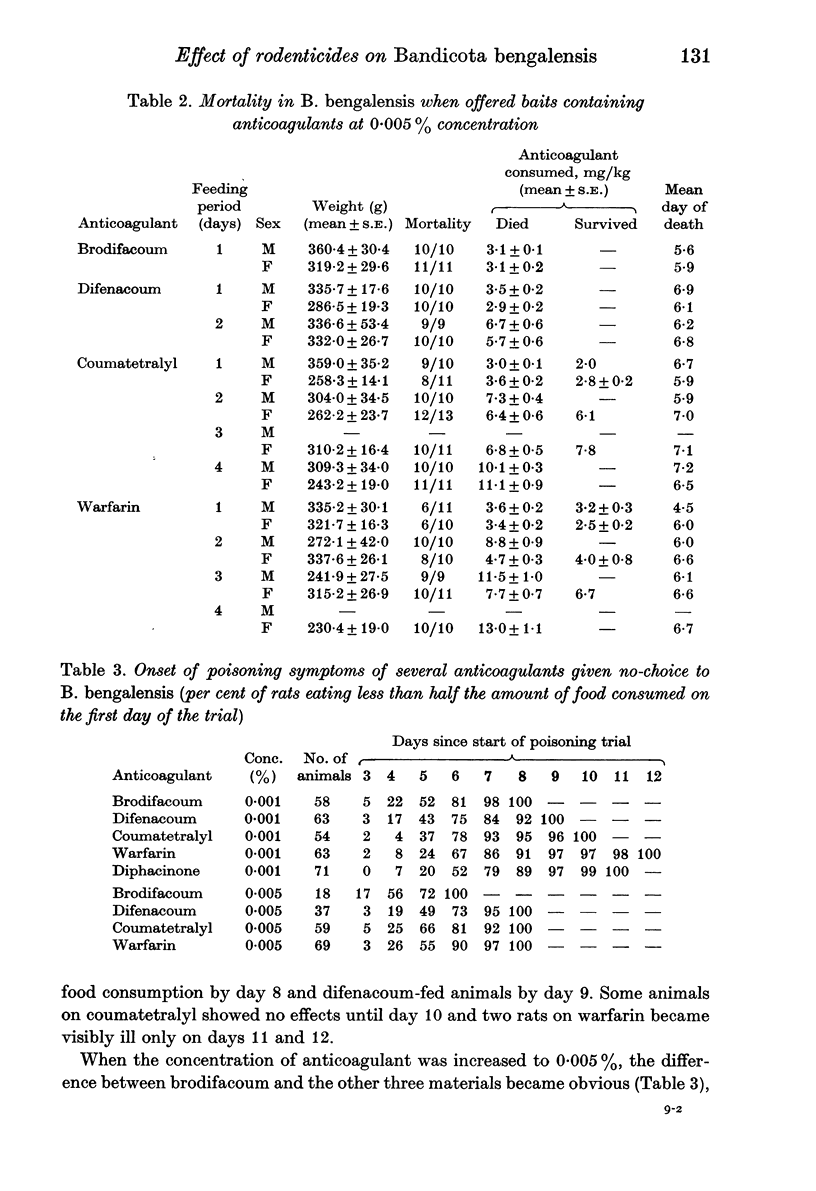
The baseline susceptibility of the lesser bandicoot rat, Bandicota bengalensis, from Rangoon, Burma, to five anticoagulant rodenticides was established with no-choice feeding in the laboratory. The susceptibility of lesser bandicoots to the several poisons (brodifacoum, difenacoum, diphacinone, coumatetralyl, and warfarin) was such that they were offered at a 0.001% concentration. B. bengalensis was most susceptible to brodifacoum, and in descending order, difenacoum, coumatetralyl, diphacinone and warfarin. In comparison with Rattus norvegicus on warfarin at 0.005%, B. bengalensis proved more susceptible. Feeding tests at 0.005% concentration indicated that a 1-day feeding on brodifacoum and difenacoum would result in complete mortality, whereas coumatetralyl and warfarin would require 4 days feeding to a 100% kill. Brodifacoum and difenacoum are recommended at 0.002-0.005% bait concentrations and coumatetralyl at 0.005--0.01% concentrations for the control of B. bengalensis in the field in Rangoon. The use of any anticoagulant material in rat control should be alternated with acute toxicants to retard the possible development of anticoagulant resistance.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brooks J. E., Bowerman A. M. An analysis of the susceptibilities of several populations of Rattus norvegicus to warfarin. J Hyg (Lond) 1974 Dec;73(3):401–407. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400042753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. E., Naing U. H., Walton D. W., Myint D. S., Tun U. M., Thaung U., Kyi D. O. Plague in small mammals and humans in Rangoon, Burma. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1977 Sep;8(3):335–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. E., Pe Than Htun Laboratory evaluation of pyriminyl used as a rodenticide against the lesser bandicoot rat, Bandicota bengalensis. J Hyg (Lond) 1978 Jun;80(3):401–408. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400024852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadler M. R., Redfern R., Rowe F. P. Laboratory evaluation of difenacoum as a rodenticide. J Hyg (Lond) 1975 Jun;74(3):441–448. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400046957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadler M. R., Shadbolt R. S. Novel 4-hydroxycoumarin anticoagulants active against resistant rats. Nature. 1975 Jan 24;253(5489):275–277. doi: 10.1038/253275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfern R., Gill J. E., Hadler M. R. Laboratory evaluation of WBA 8119 as a rodenticide for use against warfarin-resistant and non-resistant rats and mice. J Hyg (Lond) 1976 Dec;77(3):419–426. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400055807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton D. W., Maung Tun U. M. Fleas of small mammals from Rangoon, Burma. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1978 Sep;9(3):369–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


