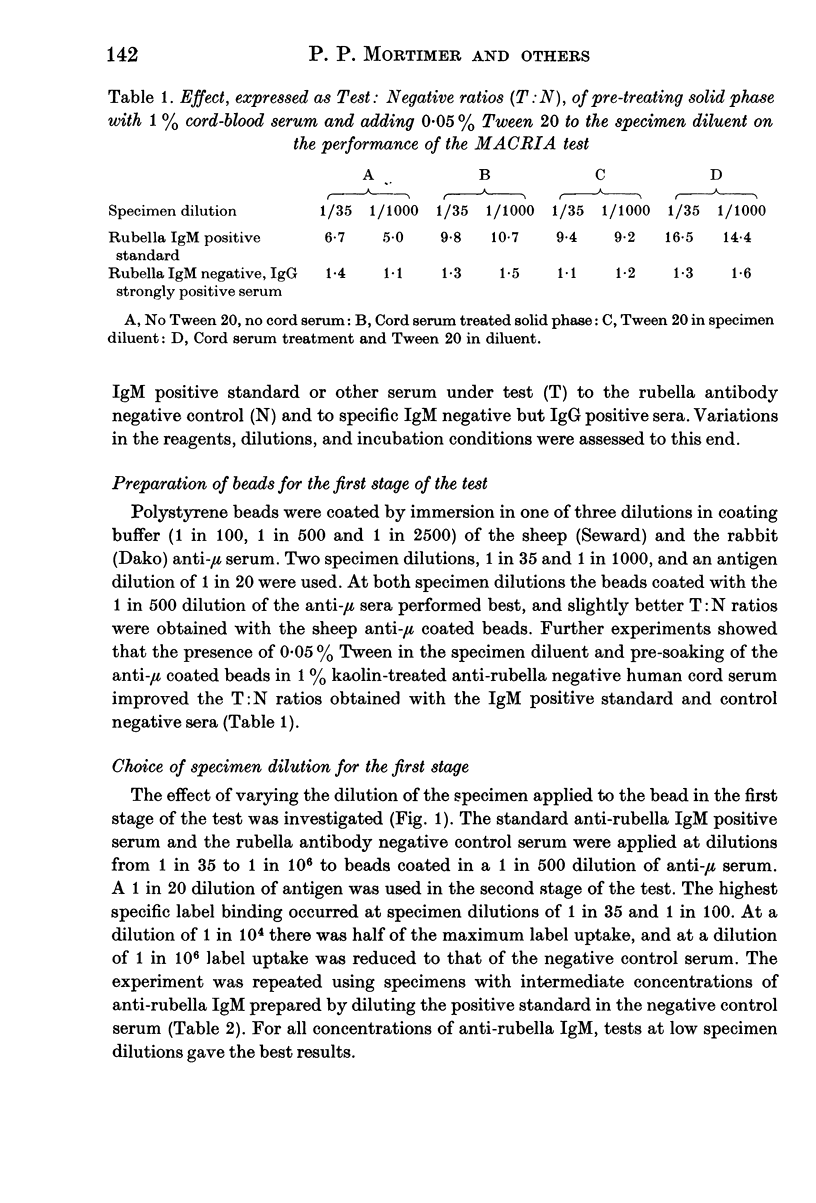
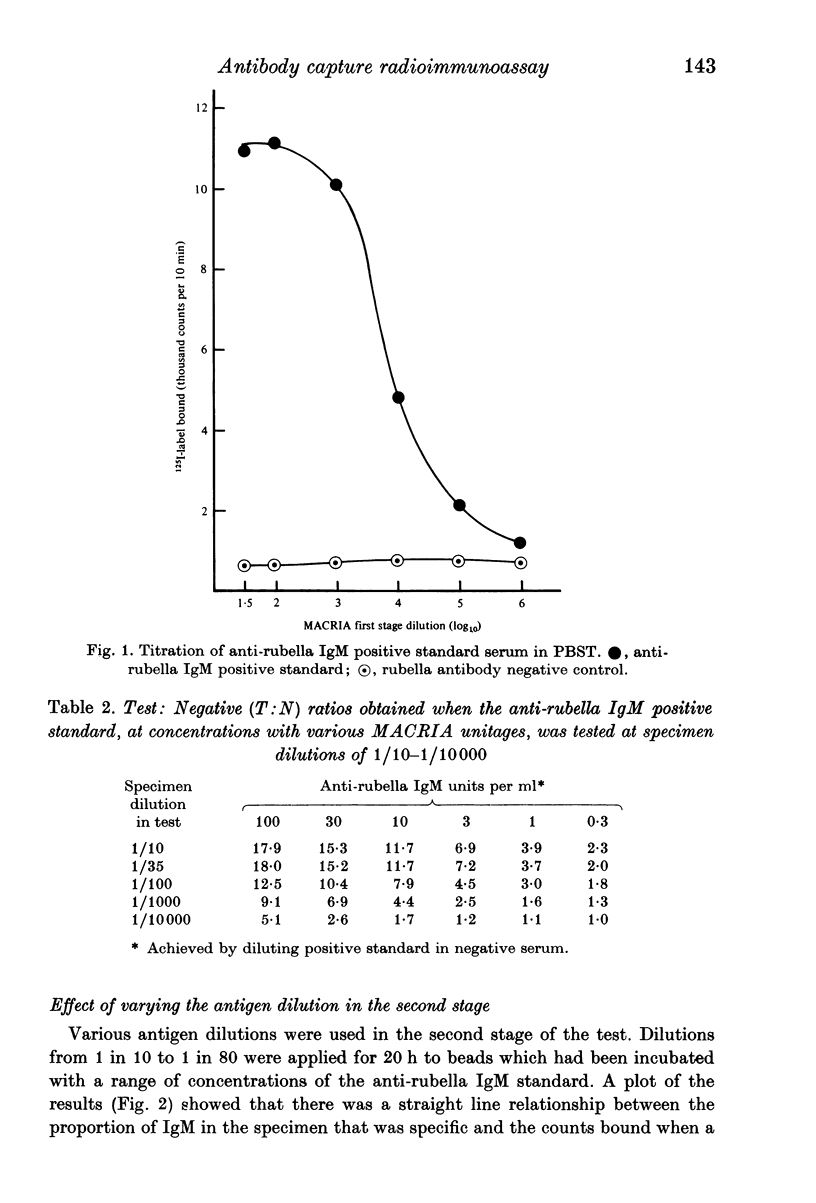
Abstract
An M-antibody capture radioimmunoassay (MACRIA) for anti-rubella IgM was developed. Under optimum conditions positive serum specimens bound up to 20 times as much radioactivity as negative specimens. Positive reactions were expressed in arbitrary units/ml by comparison with a calibration curve derived from results obtained with dilutions of a standard serum. The specificity of the assay was confirmed by testing IgM and IgG rich fractions of positive sera. One hundred and forty specimens from blood donors, patients whose sera contained rheumatoid factor and patients with acute, non-rubella, virus infections were tested by MACRIA. No significant non-specific reactions were detected. Paired sera from acute rubella (25 patients) and individual sera from suspected rubella (69 patients) were tested for anti-rubella IgM by MACRIA and by haemagglutination inhibition following sucrose-density-gradient fractionation. There was close agreement between the two methods. The capture assay was more sensitive and could be used to detect the weak IgM response in women given RA 27/3 vaccine. After the natural infection, the MACRIA was strongly positive for two months and remained weakly so for a further two months. Repeat testing of sera demonstrated good reproducibility of the assay. MACRIA proved a simple, sensitive and specific test for anti-rubella IgM and compared favourably with currently used techniques.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhardt F., Schilt U., Saner H. Virologische Diagnostik der Rötelninfektion. Befunde bei einer Rubella-Epidemie in einer Rekrutenschule. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1980 Apr 12;110(15):555–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cradock-Watson J. E., Ridehalgh M. K., Pattison J. R., Anderson M. J., Kangro H. O. Comparison of immunofluorescence and radioimmunoassay for detecting IgM antibody in infants with the congenital rubella syndrome. J Hyg (Lond) 1979 Dec;83(3):413–423. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400026243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duermeyer W., Wielaard F., van der Veen J. A new principle for the detection of specific IgM antibodies applied in an ELISA for hepatitis A. J Med Virol. 1979;4(1):25–32. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890040104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flehmig B., Ranke M., Berthold H., Gerth H. J. A solid-phase radioimmunoassay for detection of IgM antibodies to hepatitis A virus. J Infect Dis. 1979 Aug;140(2):169–175. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.2.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz J. B., Mortimer P. P., Mortimer P. R., Morgan-Capner P., Shafi M. S., White G. B. Rubella antibody measured by radial haemolysis. Characteristics and performance of a simple screening method for use in diagnostic laboratories. J Hyg (Lond) 1980 Apr;84(2):213–222. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400026711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattison J. R., Mace J. E. The detection of specific IgM antibodies following infection with rubella virus. J Clin Pathol. 1975 May;28(5):377–382. doi: 10.1136/jcp.28.5.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roggendorf M., Frösner G. G., Deinhardt F., Scheid R. Comparison of solid phase test systems for demonstrating antibodies against hepatitis A virus (anti-Hav) of the IgM-class. J Med Virol. 1980;5(1):47–62. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890050107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoop J. W., Zegers B. J., Sander P. C., Ballieux R. E. Serum immunoglobulin levels in healthy children and adults. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Jan;4(1):101–112. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesikari T., Vaheri A. Rubella: a method for rapid diagnosis of a recent infection by demonstration of the IgM antibodies. Br Med J. 1968 Jan 27;1(5586):221–223. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5586.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


