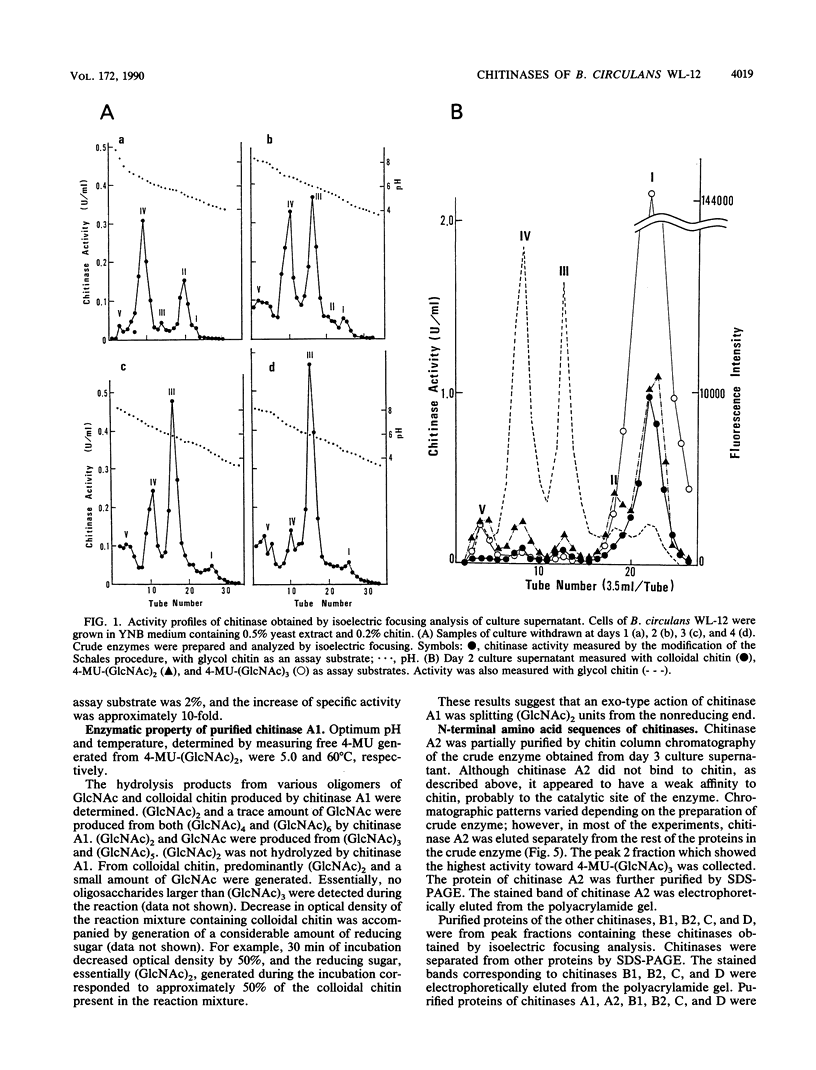
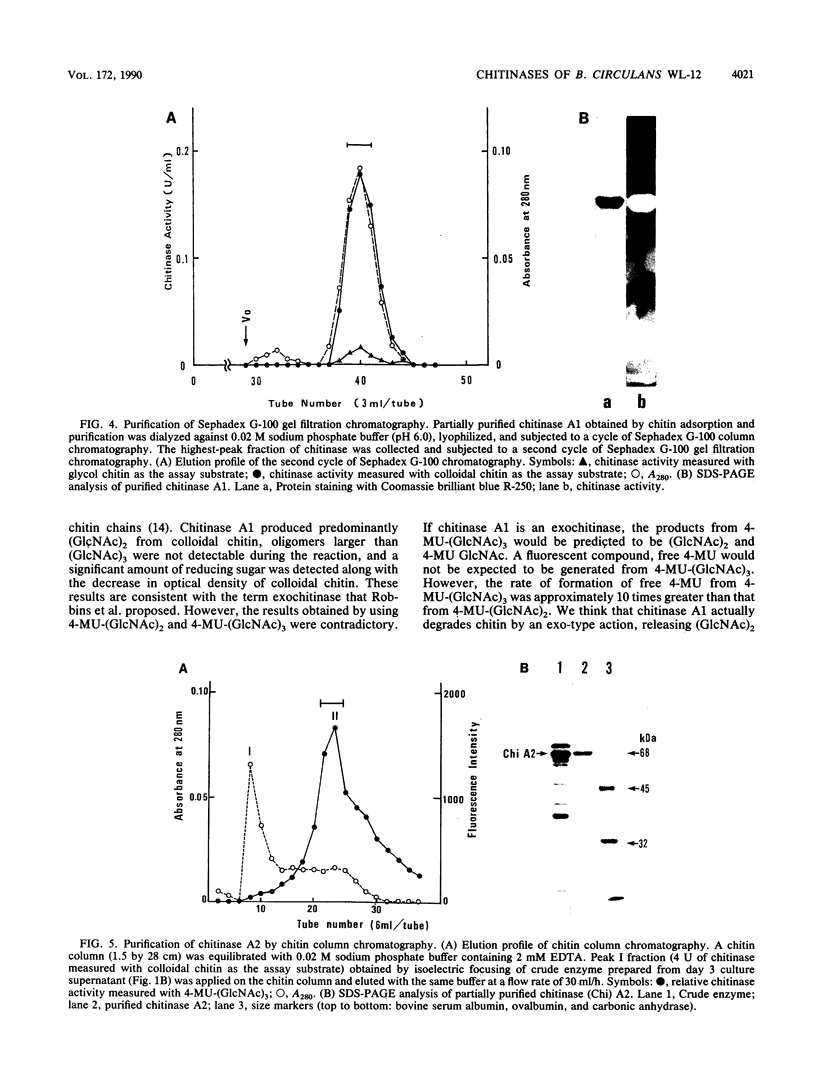
Abstract
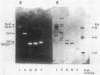
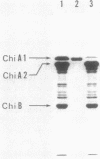
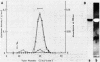
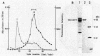
Bacillus circulans WL-12, isolated as a yeast cell wall-lytic bacterium, secretes a variety of polysaccharide-degrading enzymes into culture medium. When chitinases of the bacterium were induced with chitin, six distinct chitinase molecules were detected in the culture supernatant. These chitinases (A1, A2, B1, B2, C, and D) showed the following distinct sizes and isoelectric points: Mr 74,000, pI 4.7 (A1); Mr 69,000, pI 4.5 (A2); Mr 38,000, pI 6.6 (B1); Mr 38,000, pI 5.9 (B2); Mr 39,000, pI 8.5 (C); and Mr 52,000, pI 5.2 (D). Among these chitinases, A1 and A2 had the highest colloidal-chitin-hydrolyzing activities. Chitinase A1 showed a strong affinity to insoluble substrate chitin. Purified chitinase A1 released predominantly chitobiose [(GlcNAc)2] and a trace amount of N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) from colloidal chitin. N-terminal amino acid sequence analysis of chitinases A1 and A2 indicated that chitinase A2 was generated from chitinase A1, presumably by proteolytic removal of a C-terminal portion of chitinase A1. Since chitinase A2 did not have the ability to bind to chitin, the importance of the C-terminal region of chitinase A1 to the strong affinity of chitinase A1 to substrate chitin was suggested. Strong affinity of the chitinase seemed to be required for complete degradation of insoluble substrate chitin. From these results, it was concluded that chitinase A1 is the key enzyme in the chitinase system of this bacterium.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F. Resolution of bacterial proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on slabs. Membrane, soluble, and periplasmic fractions. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):634–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGER L. R., REYNOLDS D. M. The chitinase system of a strain of Streptomyces griseus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Sep;29(3):522–534. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE P. H., TRACEY M. V. The occurrence of chitinase in some bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Feb;14(1):188–196. doi: 10.1099/00221287-14-1-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano S., Ohe Y., Ono H. Selective N-acylation of chitosan. Carbohydr Res. 1976 Apr;47(2):315–320. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)84198-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. C., Lockwood J. L. Powdered chitin agar as a selective medium for enumeration of actinomycetes in water and soil. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Mar;29(3):422–426. doi: 10.1128/am.29.3.422-426.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molano J., Durán A., Cabib E. A rapid and sensitive assay for chitinase using tritiated chitin. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):648–656. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90069-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien M., Colwell R. R. A rapid test for chitinase activity that uses 4-methylumbelliferyl-N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminide. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jul;53(7):1718–1720. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.7.1718-1720.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS D. M. Exocellular chitinase from a Streptomyces sp. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Oct;11(2):150–159. doi: 10.1099/00221287-11-2-150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins P. W., Albright C., Benfield B. Cloning and expression of a Streptomyces plicatus chitinase (chitinase-63) in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):443–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. L., Cabib E. Serratia marcescens chitinase: one-step purification and use for the determination of chitin. Anal Biochem. 1982 Dec;127(2):402–412. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90194-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rombouts F. M., Phaff H. J. Lysis of yeast cell walls. Lytic beta-(1 leads to 6)-glucanase from Bacillus circulans WL-12. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Mar 16;63(1):109–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TANAKA H., PHAFF H. J. ENZYMATIC HYDROLYSIS OF YEAST CELL WALLS. I. ISOLATION OF WALL-DECOMPOSING ORGANISMS AND SEPARATION AND PURIFICATION OF LYTIC ENZYMES. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jun;89:1570–1580. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.6.1570-1580.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yahata N., Watanabe T., Nakamura Y., Yamamoto Y., Kamimiya S., Tanaka H. Structure of the gene encoding beta-1,3-glucanase A1 of Bacillus circulans WL-12. Gene. 1990 Jan 31;86(1):113–117. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90122-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada H., Imoto T. A convenient synthesis of glycolchitin, a substrate of lysozyme. Carbohydr Res. 1981 May 18;92(1):160–162. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)85993-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]