Abstract
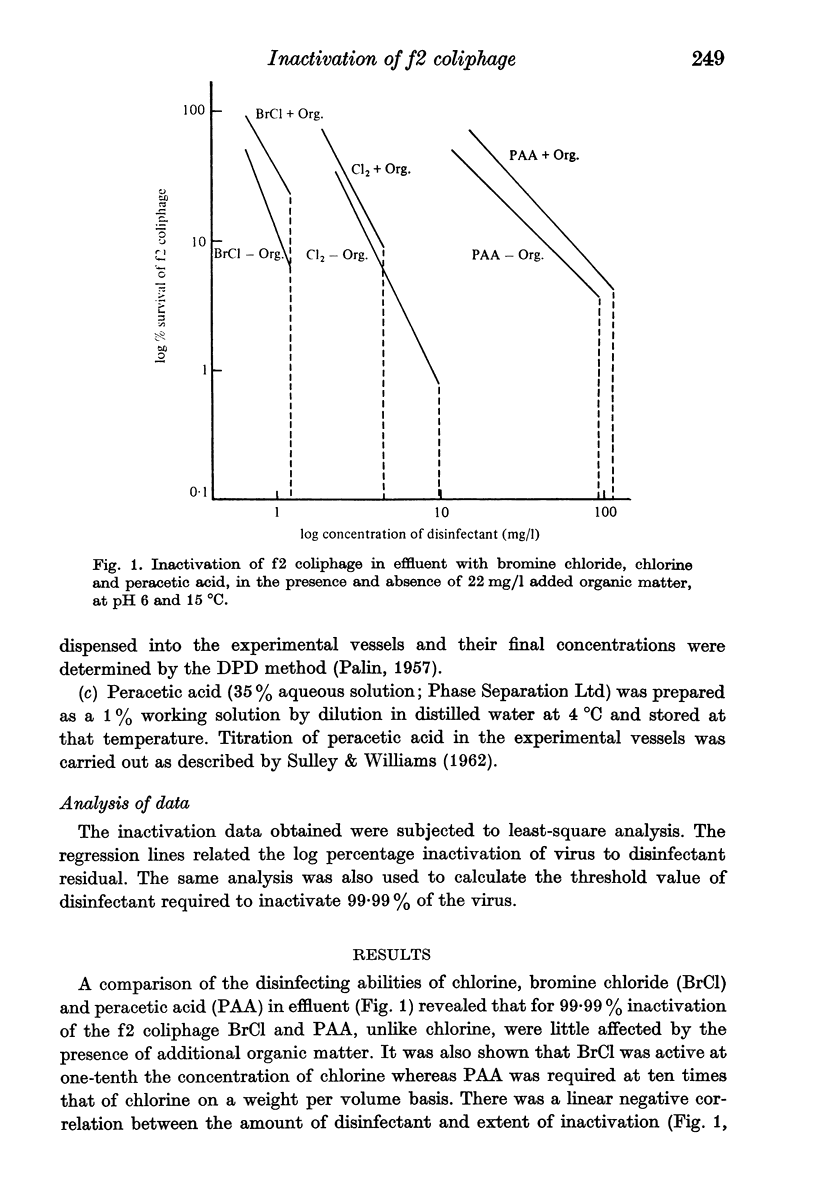
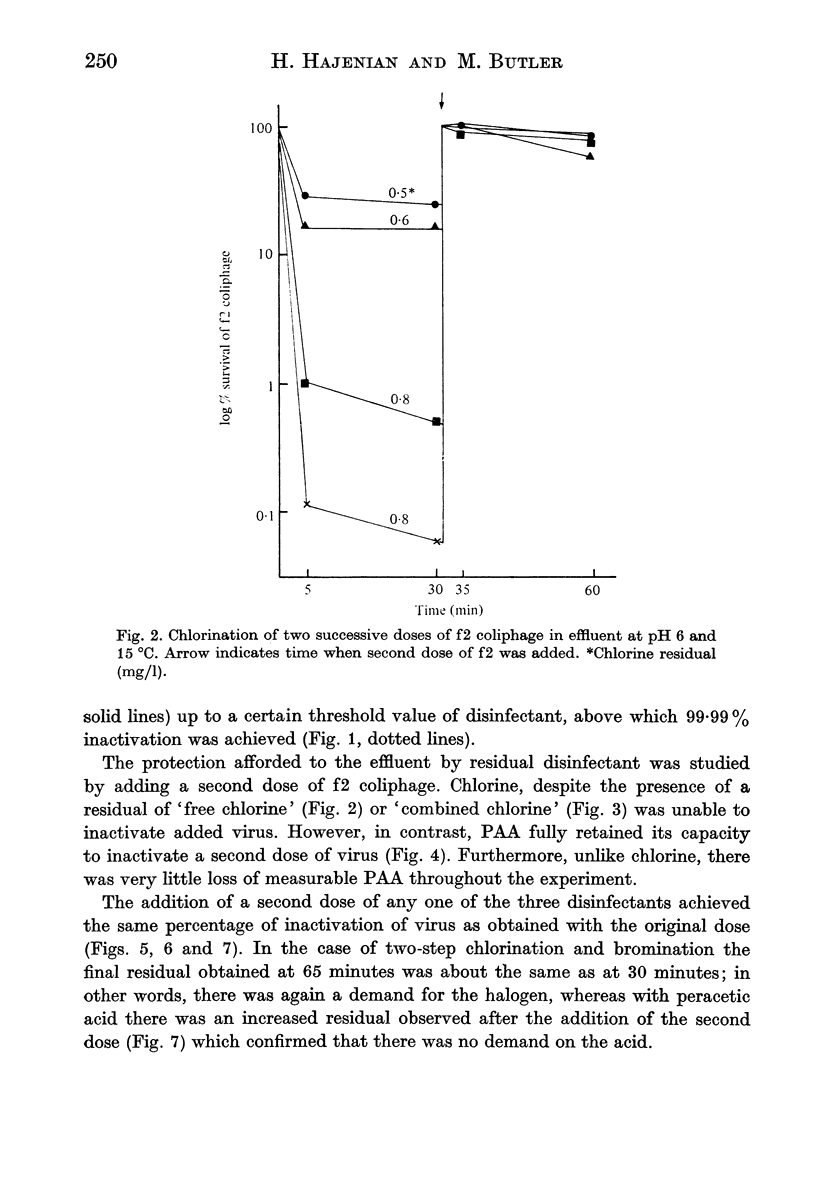
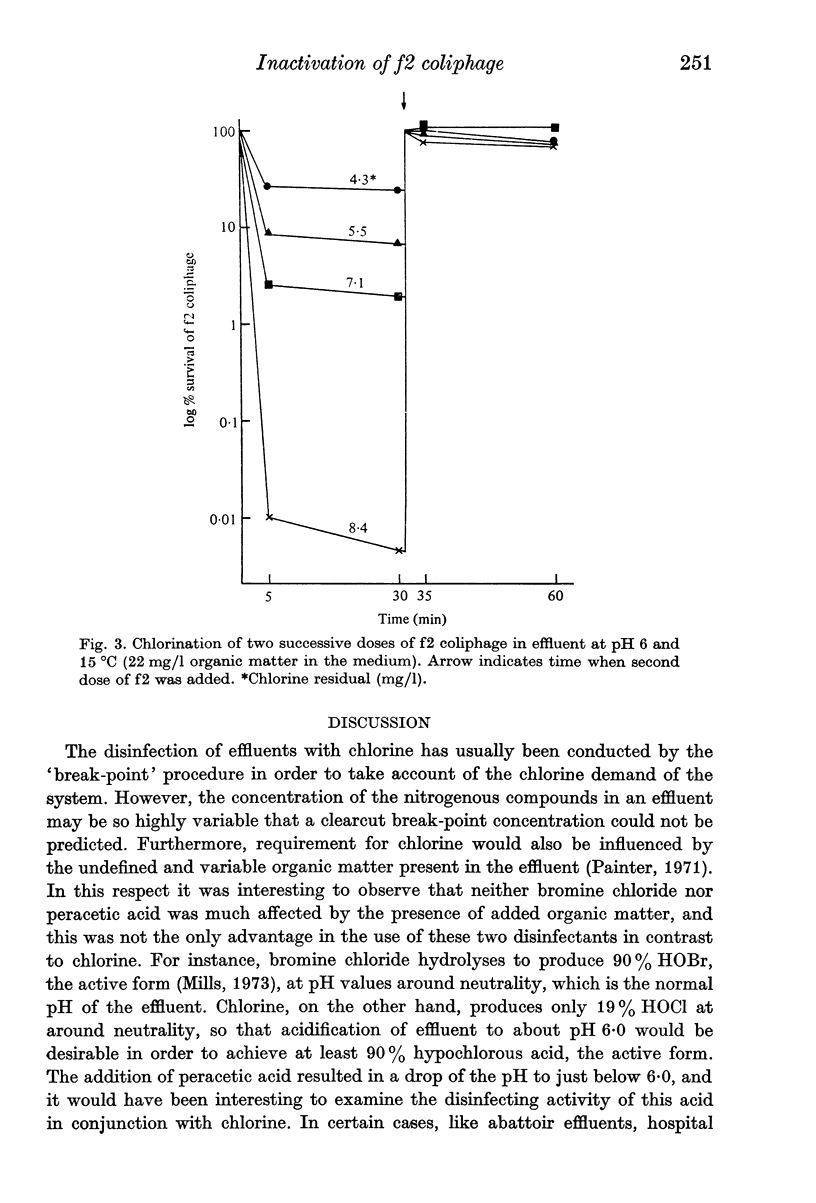
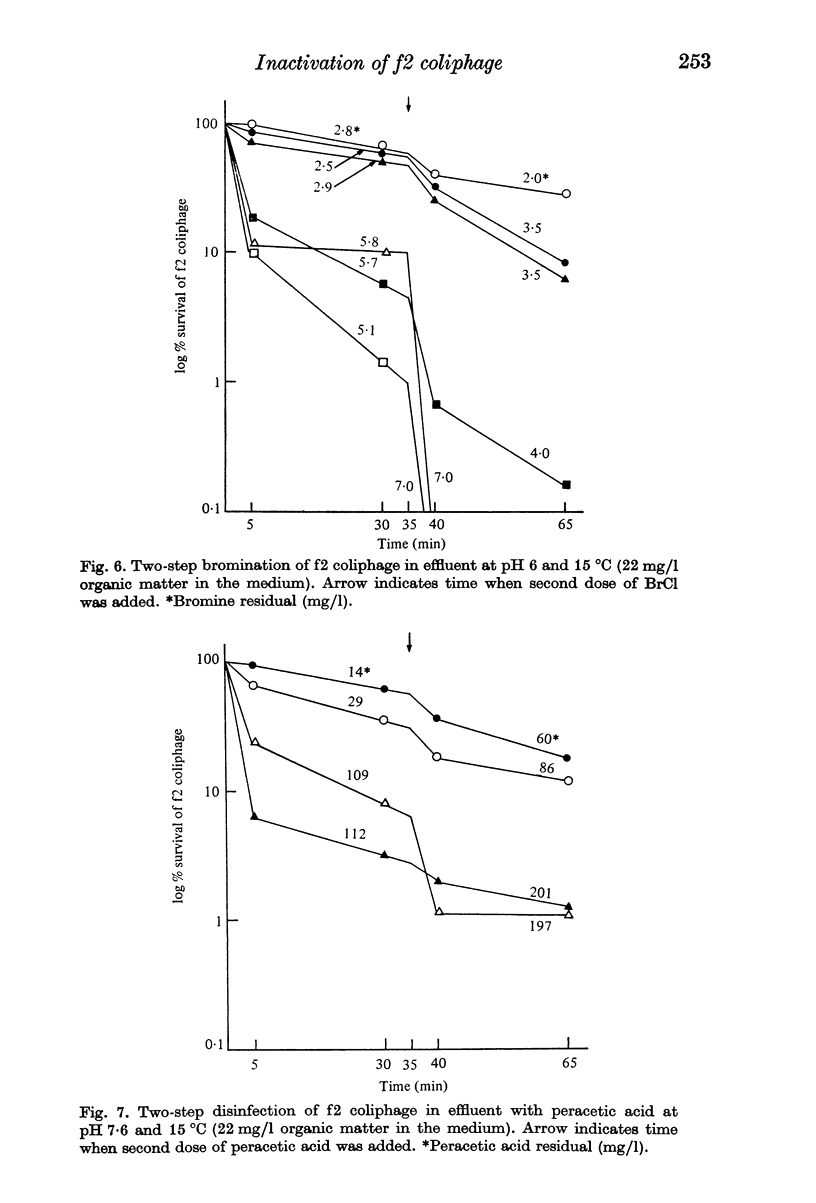
Bromine chloride, chlorine and peracetic acid inactivated f2 coliphages in effluent but in order to achieve 99.99% inactivation the three disinfectants were required at about 1, 10 and 100 mg/l respectively. The activity of chlorine was halved by the presence of added organic matter, whereas bromine chloride and peracetic acid were very little affected. When a second successive dose of virus was added to the reaction mixture, the virus was inactivated only by peracetic acid despite the fact that in the chlorine-treated effluent residual chlorine was detected. The addition of a second dose of disinfectant inactivated residual virus in the same way as the first dose.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balluz S. A., Butler M., Jones H. H. The behaviour of f2 coliphage in activated sludge treatment. J Hyg (Lond) 1978 Apr;80(2):237–242. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400053584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COIN L., HANNOUN C., GOMELLA C. INACTIVATION PAR L'OZONE DU VIRUS DE LA POLIOMY'ELITE PR'ESENT DANS LES EAUX. Presse Med. 1964 Sep 12;72:2153–2156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajenian H. G., Butler M. Inactivation of viruses in municipal effluent by chlorine. J Hyg (Lond) 1980 Feb;84(1):63–69. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400026528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLINE L. B., HULL R. N. The virucidal properties of peracetic acid. Am J Clin Pathol. 1960 Jan;33:30–33. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/33.1.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lothrop T. L., Sproul O. J. High-level inactivation of viruses in wastewater by chlorination. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1969 Apr;41(4):567–575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tifft E. C., Moffa P. E., Richardson S. L., Field R. I. Enhancement of high-rate disinfection by sequential addition of chlorine and chlorine dioxide. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1977 Jul;49(7):1652–1658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt T. D., Wilson T. S. A bacteriological investigation of two leisure centre swimming pools disinfected with ozone. J Hyg (Lond) 1979 Jun;82(3):425–441. doi: 10.1017/s002217240005395x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


