Abstract
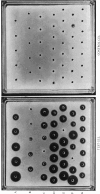
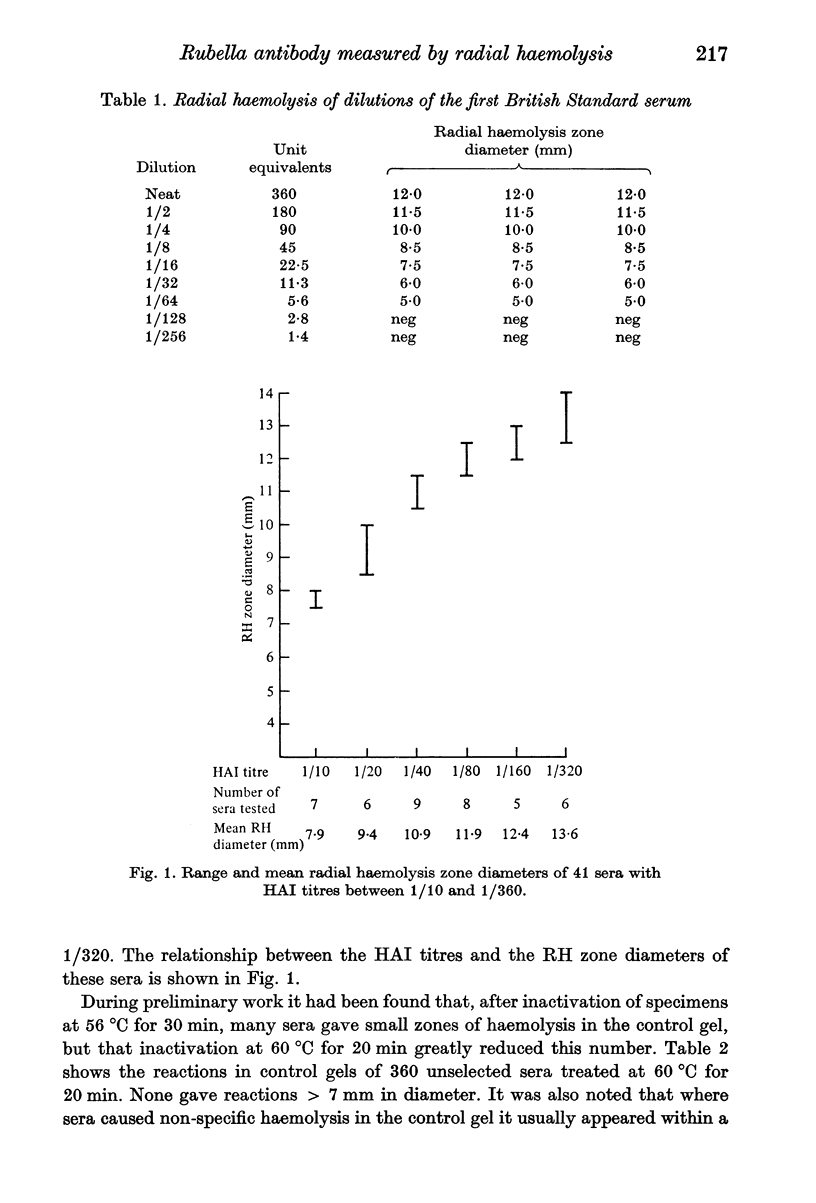
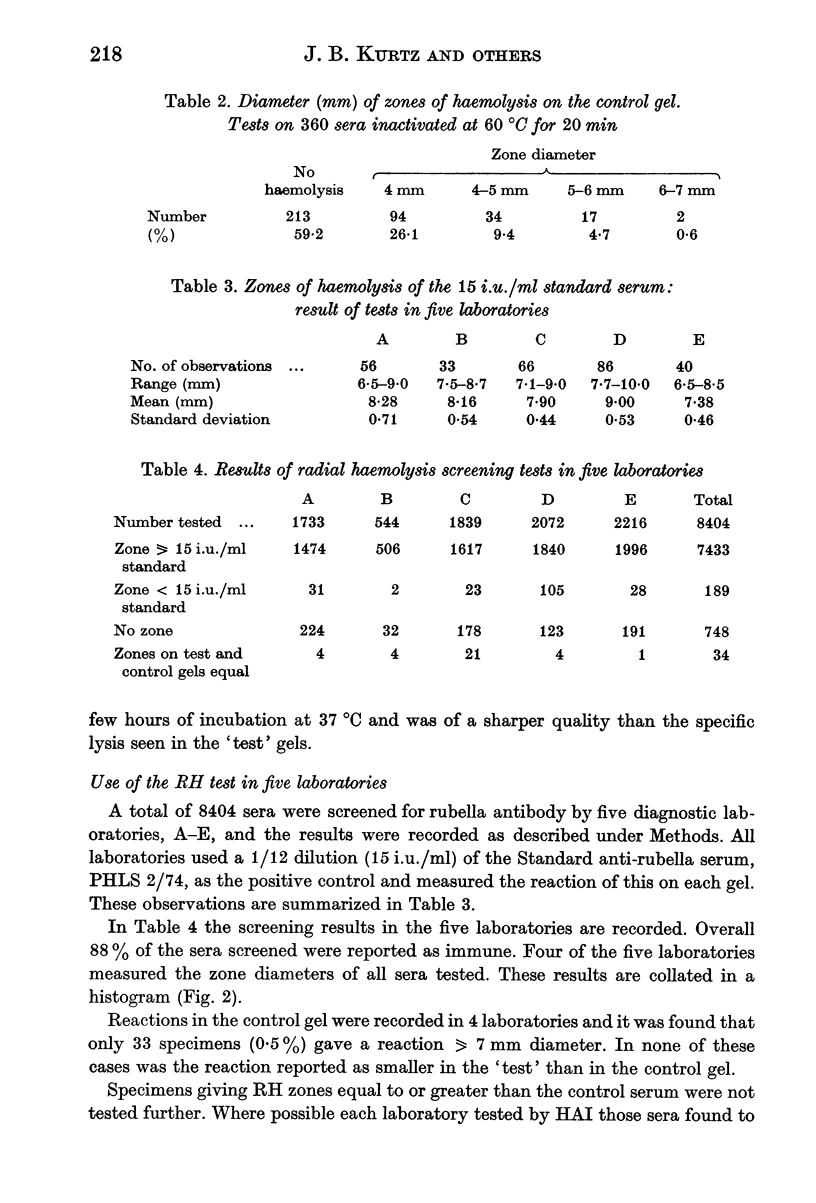
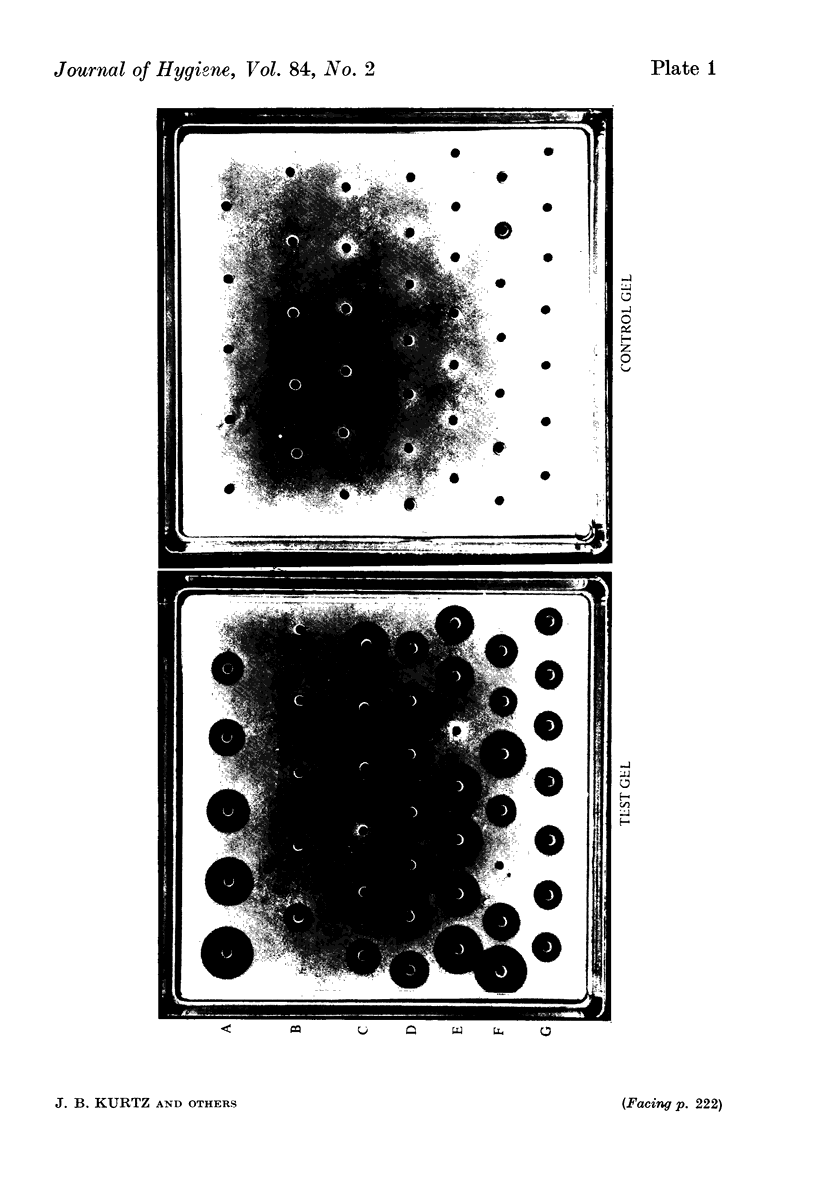
A simple method for preparing radial haemolysis gels for rubella antibody screening is described. In use it gave clear zones of haemolysis when a standard serum was tested at dilutions down to 5.6 i.u./ml rubella antibody. In five laboratories 8404 sera were screened by the method and the results were read by comparing zones of haemolysis with that of a standard serum diluted to contain 15 i.u/ml antibody. A zone greater than or equal to 15 i.u./ml, indicating immunity, was given by 7433 (88.4%) of the sera. No zone indicating susceptibility was seen with 748 (8.9%) sera. Small zones, less than 15 i.u./ml standard, were given by 189 (2.2%) sera, and in only 34 cases (0.4%) did non-specific haemolysis interfere with the test readings. Further testing of the radial haemolysis interfere with the test readings. Further testing of the radial haemolysis negative and low positive sera by the haemagglutination inhibition test gave rise to some discrepant results which are discussed.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradstreet C. M., Kirkwood B., Pattison J. R., Tobin J. O. The derivation of a minimum immune titre of rubella haemagglutination-inhibition (HI) antibody. A Public Health Laboratory Service collaborative survey. J Hyg (Lond) 1978 Dec;81(3):383–388. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400025262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charnley J. Postoperative infection after total hip replacement with special reference to air contamination in the operating room. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1972 Sep;87:167–187. doi: 10.1097/00003086-197209000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grillner L., Blomberg J. Hemolysis-in-gel and neutralization tests for determination of antibodies to mumps virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jul;4(1):11–15. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.1.11-15.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamme C., Lidgren L., Lindberg L., Mårdh P. A. Anaerobic bacteria in late infections after total hip arthroplasty. Scand J Infect Dis. 1974;6(2):161–165. doi: 10.3109/inf.1974.6.issue-2.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble W. C., Habbema J. D., van Furth R., Smith I., de Raay C. Quantitative studies on the dispersal of skin bacteria into the air. J Med Microbiol. 1976 Feb;9(1):53–61. doi: 10.1099/00222615-9-1-53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell S. M., McCahon D., Beare A. S. A single radial haemolysis technique for the measurement of influenza antibody. J Gen Virol. 1975 Apr;27(1):1–10. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-27-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan A., Bengtsson S., Hambraeus A., Laurell G. Airborne contamination and postoperative infection after total hip replacement. Acta Orthop Scand. 1977 May;48(1):86–94. doi: 10.3109/17453677708985116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skaug K., Orstavik I., Ulstrup J. C. Application of the passive haemolysis test for the determination of rubella virus antibodies. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Aug;83(4):367–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strannegård O., Grillner L., Lindberg I. M. Hemolysis-in-gel test for the demonstration of antibodies to rubella virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jun;1(6):491–494. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.6.491-494.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesslén L. Demonstration of antibodies to measles virus by hemolysis-in-gel (HIG) test. Scand J Infect Dis. 1978;10(1):15–20. doi: 10.3109/inf.1978.10.issue-1.04. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White G. B., Tinnion K. H. Letter: A non-specific inhibitor of rubella haemagglutinin. Lancet. 1975 Oct 4;2(7936):664–664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]