Abstract
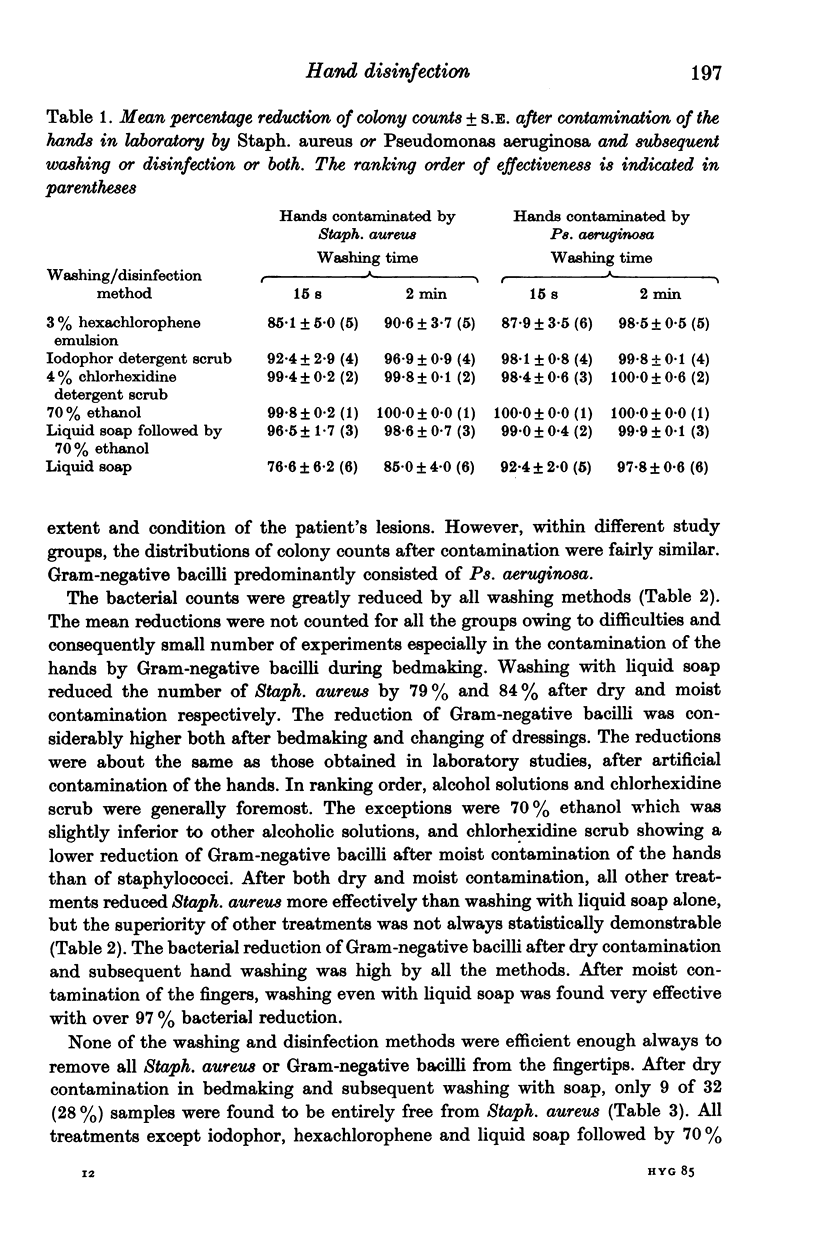
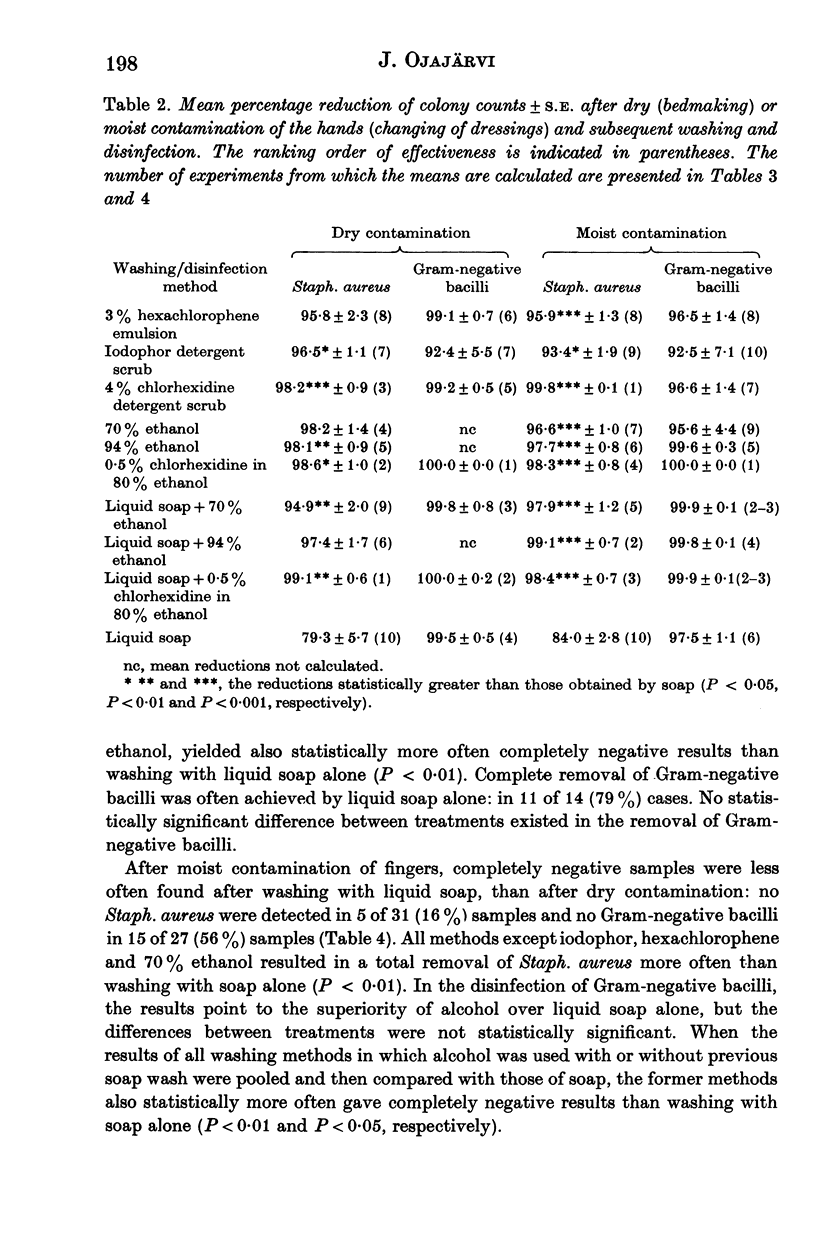
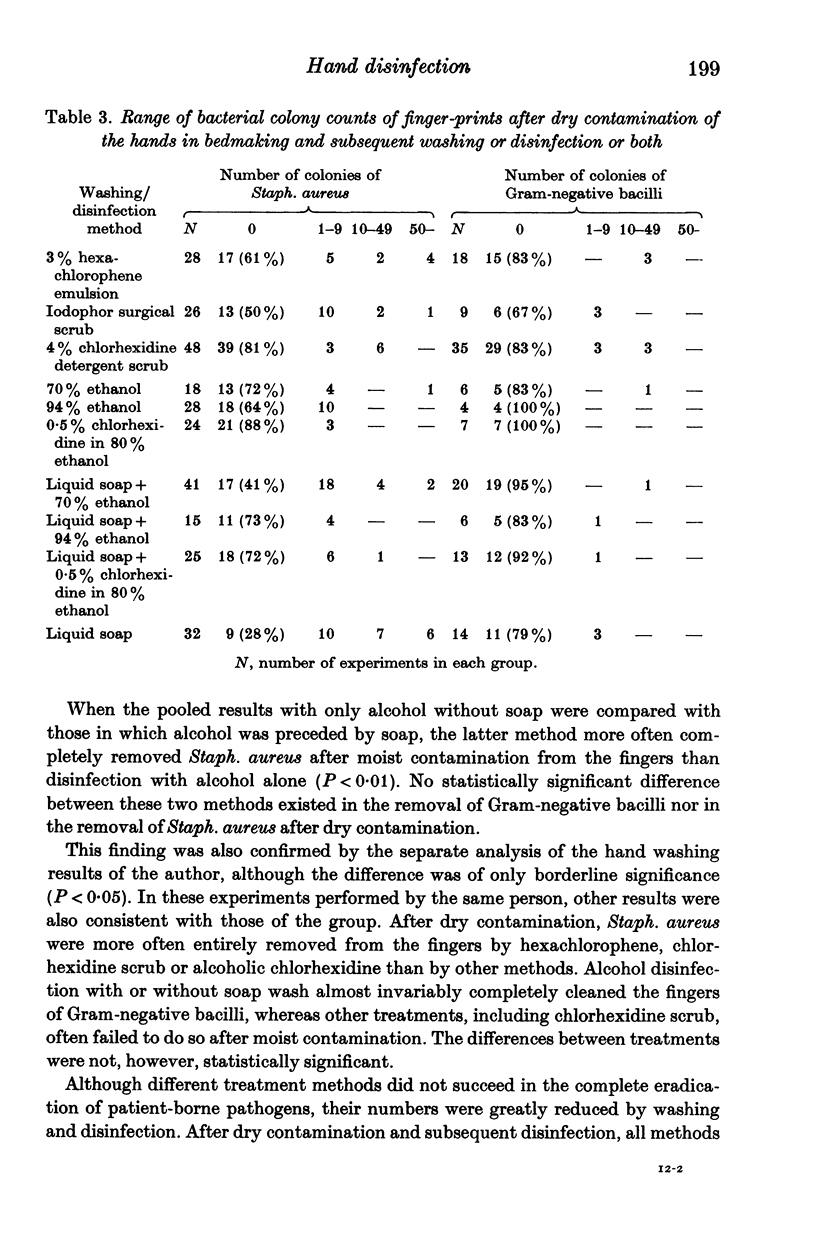
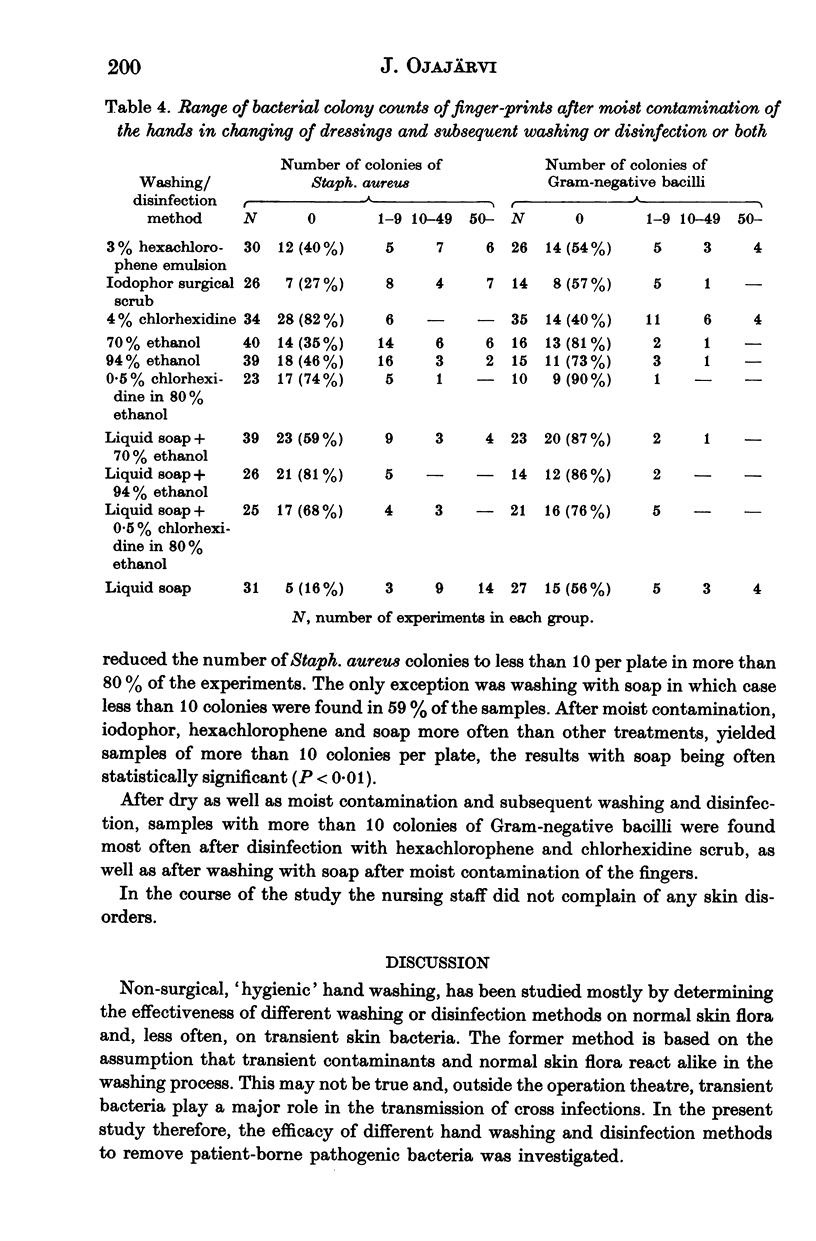
The effectiveness of various hand washing and disinfection methods in removing transient skin bacteria was studied in hospital after dry or moist contamination of the hands when nursing burn patients. The results were compared with those of laboratory tests with volunteers. A fairly good correlation of the bacterial reductions existed between hospital and laboratory tests. All other methods removed Staph. aureus from the hands more effectively than liquid soap. Gram-negative bacilli were more easily removed than staphylococci, even with soap wash alone. In hospital, none of the washing and disinfection methods always removed all patient-borne bacteria from the hands. After dry or moist contamination and subsequent washing with soap only, colonies of Staph. aureus were often detected in finger-print samples. Staphylococci were more often completely removed by a 4% chlorhexidine detergent scrub and alcoholic solutions (either with or without previous soap wash) than by liquid soap, hexachlorophene or iodophor preparations. Gram-negative bacilli were more easily removed by all the washing and disinfection methods. After moist contamination, Gram-negative bacilli were more often completely removed from the hands by ethanol than by other treatments. The results of the present study emphasize the importance of always using gloves when nursing a profuse spreader of bacteria or one who must be protected from infection.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayliffe G. A., Bridges K., Lilly H. A., Lowbury E. J., Varney J., Wilkins M. D. Comparison of two methods for assessing the removal of total organisms and pathogens from the skin. J Hyg (Lond) 1975 Oct;75(2):259–274. doi: 10.1017/s002217240004729x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRODIE J. HAND HYGIENE. Scott Med J. 1965 Mar;10:115–125. doi: 10.1177/003693306501000304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casewell M., Phillips I. Hands as route of transmission for Klebsiella species. Br Med J. 1977 Nov 19;2(6098):1315–1317. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6098.1315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson C., Juhlin I., Willard L. O. Removal of the superficial bacterial flora of the hands--a comparison between different antibacterial preparations and soap. Acta Chir Scand. 1968;134(1):7–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWBURY E. J., LILLY H. A., BULL J. P. DISINFECTION OF HANDS: REMOVAL OF TRANSIENT ORGANISMS. Br Med J. 1964 Jul 25;2(5403):230–233. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5403.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilly H. A., Lowbury E. J. Transient skin flora: their removal by cleansing or disinfection in relation to their mode of deposition. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Oct;31(10):919–922. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.10.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowbury E. J., Lilly H. A., Ayliffe G. A. Preoperative disinfection of surgeons' hands: use of alcoholic solutions and effects of gloves on skin flora. Br Med J. 1974 Nov 16;4(5941):369–372. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5941.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowbury E. J., Lilly H. A. Gloved hand as applicator of antiseptic to operation sites. Lancet. 1975 Jul 26;2(7926):153–156. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90058-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowbury E. J., Lilly H. A. Use of 4 per cent chlorhexidine detergent solution (Hibiscrub) and other methods of skin disinfection. Br Med J. 1973 Mar 3;1(5852):510–515. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5852.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojajärvi J., Mäkelä P., Rantasalo I. Failure of hand disinfection with frequent hand washing: a need for prolonged field studies. J Hyg (Lond) 1977 Aug;79(1):107–119. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400052906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzman T. C., Clark J. J., Klemm L. Hand contamination of personnel as a mechanism of cross-infection in nosocomial infections with antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli and Klebsiella-Aerobacter. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1967;7:97–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprunt K., Redman W., Leidy G. Antibacterial effectiveness of routine hand washing. Pediatrics. 1973 Aug;52(2):264–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


