Abstract
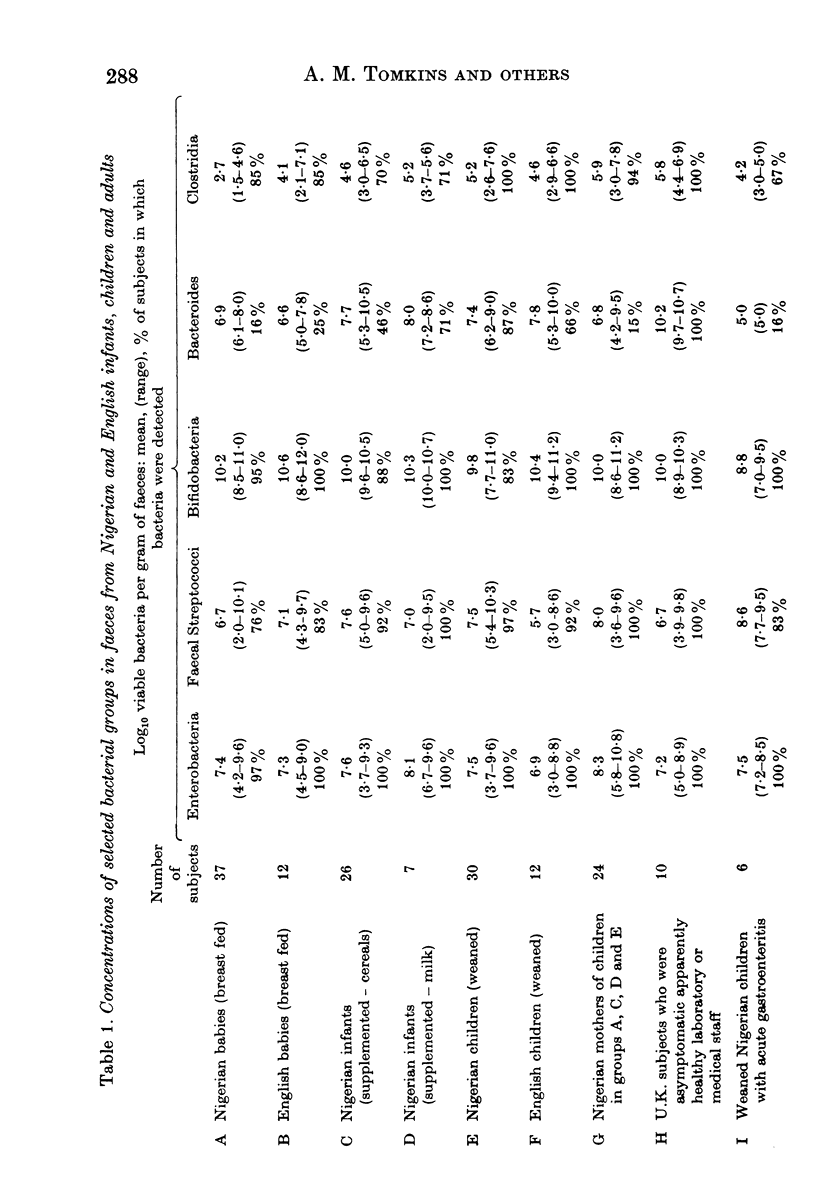
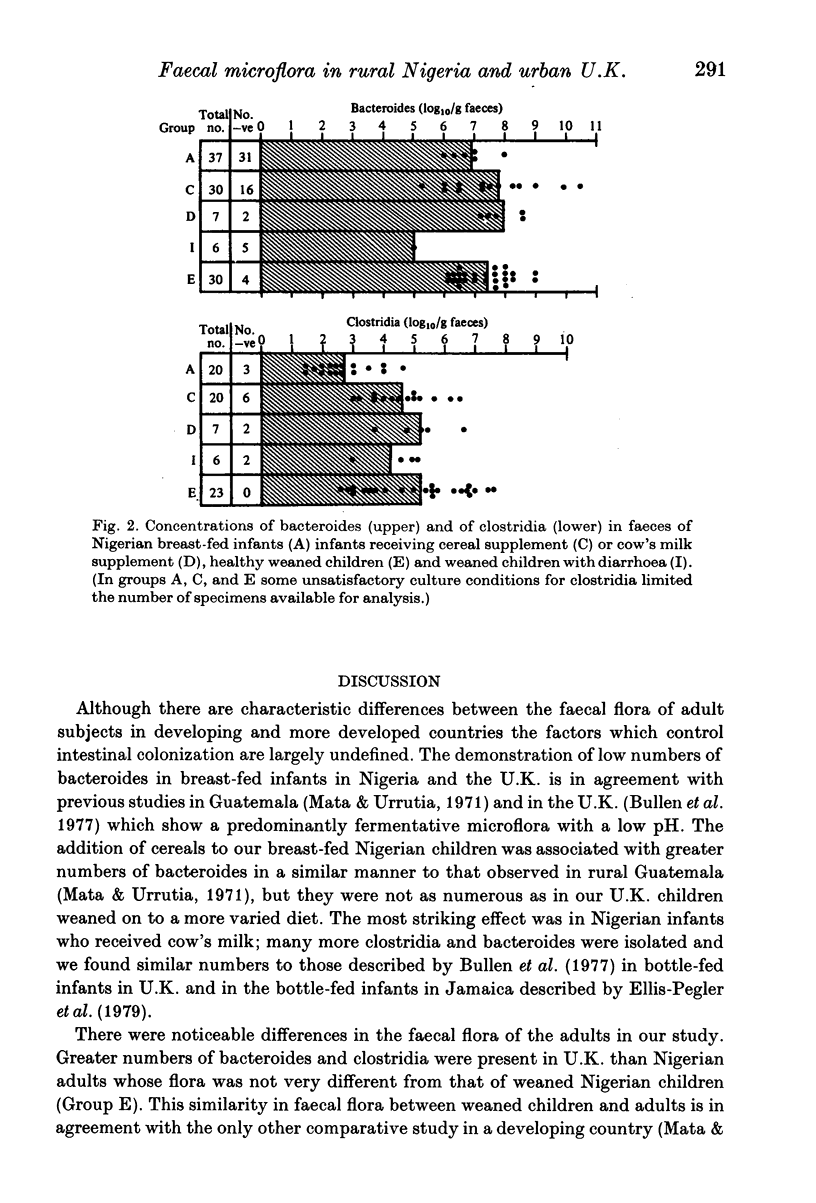
The faecal microflora of breast-fed infants, weaned children and adults has been examined in rural Nigeria and urban U.K. Breast-fed infants had a similar anaerobic flora dominated by bifidobacteria but bacteroides were isolated in less than a quarter of either community. Weaned children in both communities had greater numbers of bacteroides and clostridia than breast-fed infants. Even higher numbers of bacteroides and clostridia were present in U.K. adults but not in Nigerian adults. Numbers of bacteroides and clostridia were greater in a group of Nigerian infants drinking cow's milk than those receiving breast milk alone and lower in a group of weaned children with diarrhoea compared with uninfected subjects.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aries V. C., Crowther J. S., Drasar B. S., Hill M. J., Ellis F. R. The effect of a strict vegetarian diet on the faecal flora and faecal steroid concentration. J Pathol. 1971 Jan;103(1):54–56. doi: 10.1002/path.1711030108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aries V., Crowther J. S., Drasar B. S., Hill M. J., Williams R. E. Bacteria and the aetiology of cancer of the large bowel. Gut. 1969 May;10(5):334–335. doi: 10.1136/gut.10.5.334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen C. L., Tearle P. V., Stewart M. G. The effect of "humanised" milks and supplemented breast feeding on the faecal flora of infants. J Med Microbiol. 1977 Nov;10(4):403–413. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-4-403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowther J. S. Transport and storage of faeces for bacteriological examination. J Appl Bacteriol. 1971 Jun;34(2):477–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1971.tb02307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings J. H., Wiggins H. S., Jenkins D. J., Houston H., Jivraj T., Drasar B. S., Hill M. J. Influence of diets high and low in animal fat on bowel habit, gastrointestinal transit time, fecal microflora, bile acid, and fat excretion. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):953–963. doi: 10.1172/JCI109020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drasar B. S., Jenkins D. J., Cummings J. H. The influence of a diet rich in wheat fibre on the human faecal flora. J Med Microbiol. 1976 Nov;9(4):423–431. doi: 10.1099/00222615-9-4-423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis-Pegler R. B., Crabtree C., Lambert H. P. The faecal flora of children in the United Kingdom. J Hyg (Lond) 1975 Aug;75(1):135–142. doi: 10.1017/s002217240004715x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis-Pegler R. B., Higgs R., Lambert H. P. Gastroenteritis in London and Jamaica: a clinical and bacteriological study. J Hyg (Lond) 1979 Feb;82(1):101–114. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400025523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floch M. H., Gorbach S. L., Luckey T. D. Intestinal microflora. Introduction. Am J Clin Nutr. 1970 Nov;23(11):1425–1426. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/23.11.1425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Neale G., Levitan R., Hepner G. W. Alterations in human intestinal microflora during experimental diarrhoea. Gut. 1970 Jan;11(1):1–6. doi: 10.1136/gut.11.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAEDLER R. W., DUBOS R., COSTELLO R. THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE BACTERIAL FLORA IN THE GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT OF MICE. J Exp Med. 1965 Jul 1;122:59–66. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe A. N., Kilsby D. C. A rapid, inexpensive bacterial count technique using agar droplets. J Appl Bacteriol. 1971 Jun;34(2):435–440. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1971.tb02303.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkins A. M., Drasar B. S., Bradley A. K., Williamson W. A. Water supply and nutritional status in rural northern Nigeria. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(3):239–243. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90201-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis A. T., Bullen C. L., Williams K., Fagg C. G., Bourne A., Vignon M. Breast milk substitute: a bacteriological study. Br Med J. 1973 Oct 13;4(5884):67–72. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5884.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


