Abstract
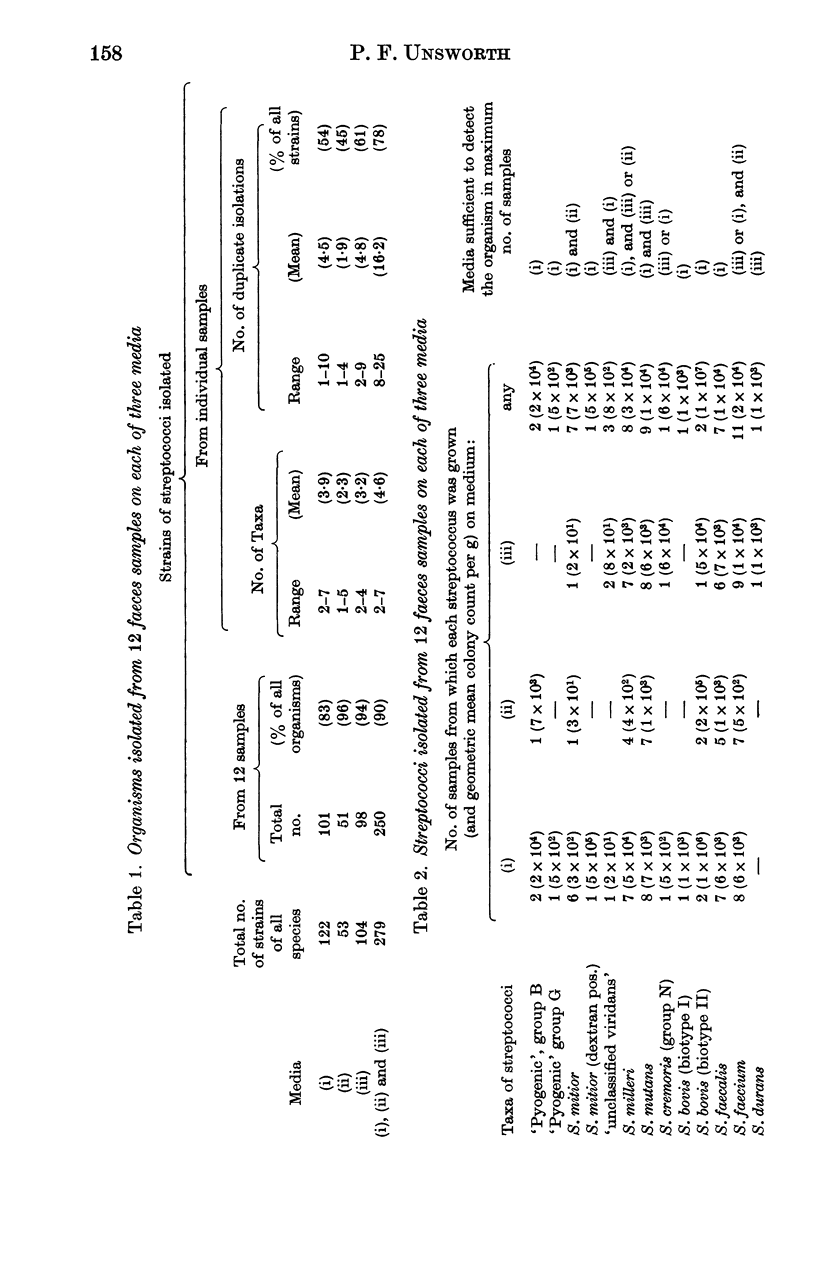
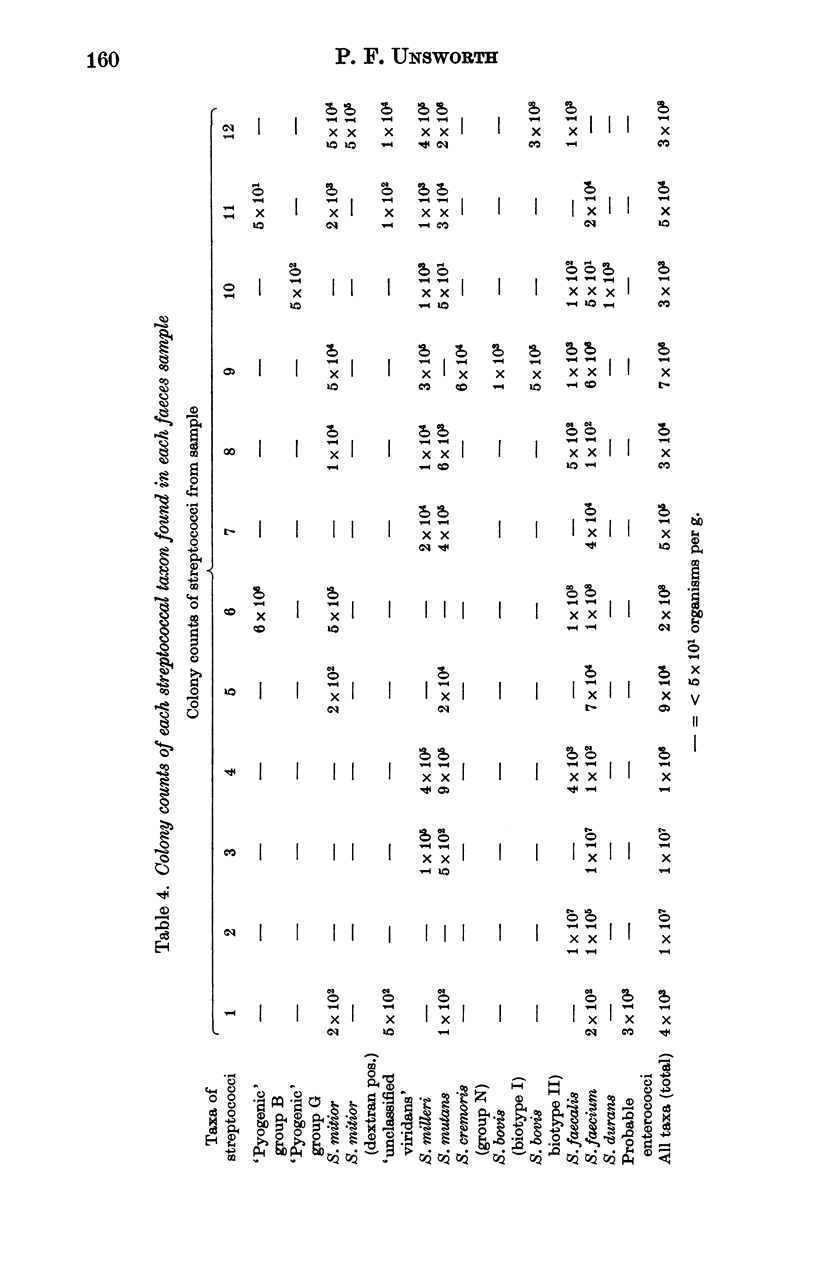
Three selective media were designed for isolation of streptococci from faeces. Samples of faeces from twelve normal adults were suspended and serially diluted in saline or broth saline, and equal volumes of each dilution were spread and incubated on the media. The number of colonies of each different type which developed was counted and one colony of each type was subcultured and identified. Altogether, streptococci of 13 taxa were found. S. faecium, S. mutans, S. milleri, S. faecalis and S. mitior were each found in over half the samples. Lancefield group B and G streptococci, S. bovis II, an atypical strain of S. bovis I, S. cremoris, S. durans and a dextran-positive strain of S. mitior were each present in 1 or 2 samples. Individual samples contained 2-7 (mean 4.6) streptococcal taxa, and total viable counts of streptococci of 3 X 10(3)-3 X 10(8) (geometric mean 7 X 10(5)) per g. The significance of these findings is discussed.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball L. C., Parker M. T. The cultural and biochemical characters of Streptococcus milleri strains isolated from human sources. J Hyg (Lond) 1979 Feb;82(1):63–78. doi: 10.1017/s002217240002547x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J. A medium for isolation of Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol. 1967 Dec;12(12):1657–1658. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(67)90201-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowther J. S. Transport and storage of faeces for bacteriological examination. J Appl Bacteriol. 1971 Jun;34(2):477–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1971.tb02307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott S. D., McCarty M., Lancefield R. C. Teichoic acids of group D streptococci with special reference to strains from pig meningitis (Streptococcus suis). J Exp Med. 1977 Mar 1;145(3):490–499. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.3.490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Nahas L., Lerner P. I., Weinstein L. Studies of intestinal microflora. I. Effects of diet, age, and periodic sampling on numbers of fecal microorganisms in man. Gastroenterology. 1967 Dec;53(6):845–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Islam A. K. Rapid recognition of group-B Streptococci. Lancet. 1977 Jan 29;1(8005):256–257. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91055-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidson A. A new selective medium for Streptococcus pyogenes and other streptococci. J Med Lab Technol. 1967 Jul;24(3):179–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M., Theilade E., Schiott C. R. Isolation of Streptococcus mutans from human faeces. Arch Oral Biol. 1971 May;16(5):553–554. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(71)90201-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. S., Recco R. A., Catalano M. T., Edberg S. C., Casey J. I., Steigbigel N. H. Association of Streptococcus bovis with carcinoma of the colon. N Engl J Med. 1977 Oct 13;297(15):800–802. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197710132971503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melo J. C., Raff M. J. Brain abscess due to Streptococcus MG-intermedius (Streptococcus milleri). J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jun;7(6):529–532. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.6.529-532.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V. Human fecal flora: the normal flora of 20 Japanese-Hawaiians. Appl Microbiol. 1974 May;27(5):961–979. doi: 10.1128/am.27.5.961-979.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble C. J. Carriage of group D streptococci in the human bowel. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Dec;31(12):1182–1186. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.12.1182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OTTENS H., WINKLER K. C. Indifferent and haemolytic streptococci possessing group-antigen F. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Apr;28:181–191. doi: 10.1099/00221287-28-1-181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTERFIELD J. S. Classification of the streptococci of subacute bacterial endocarditis. J Gen Microbiol. 1950 Jan;4(1):92–101. doi: 10.1099/00221287-4-1-92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. T., Ball L. C. Streptococci and aerococci associated with systemic infection in man. J Med Microbiol. 1976 Aug;9(3):275–302. doi: 10.1099/00222615-9-3-275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. T. Neonatal streptococcal infections. Postgrad Med J. 1977 Oct;53(624):598–606. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.53.624.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlova M. T., Brezenski F. T., Litsky W. Evaluation of various media for isolation, enumeration and identification of fecal streptococci from natural sources. Health Lab Sci. 1972 Oct;9(4):289–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips I., Warren C., Harrison J. M., Sharples P., Ball L. C., Parker M. T. Antibiotic susceptibilities of streptococci from the mouth and blood of patients treated with penicillin or lincomycin and clindamycin. J Med Microbiol. 1976 Nov;9(4):393–404. doi: 10.1099/00222615-9-4-393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole P. M., Wilson G. Streptococcus milleri in the appendix. J Clin Pathol. 1977 Oct;30(10):937–942. doi: 10.1136/jcp.30.10.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waitkins S. A., Ball L. C., Fraser C. A. A shortened scheme for the identification of indifferent streptococci. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Jan;33(1):47–52. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waitkins S. A. Use of pyruvate fermentation compared with tetrazolium reduction in the differentiation of group D streptococci. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Jul;31(7):692–695. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.7.692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Louvois J., Gortavai P., Hurley R. Bacteriology of abscesses of the central nervous system: a multicentre prospective study. Br Med J. 1977 Oct 15;2(6093):981–984. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6093.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



