Abstract
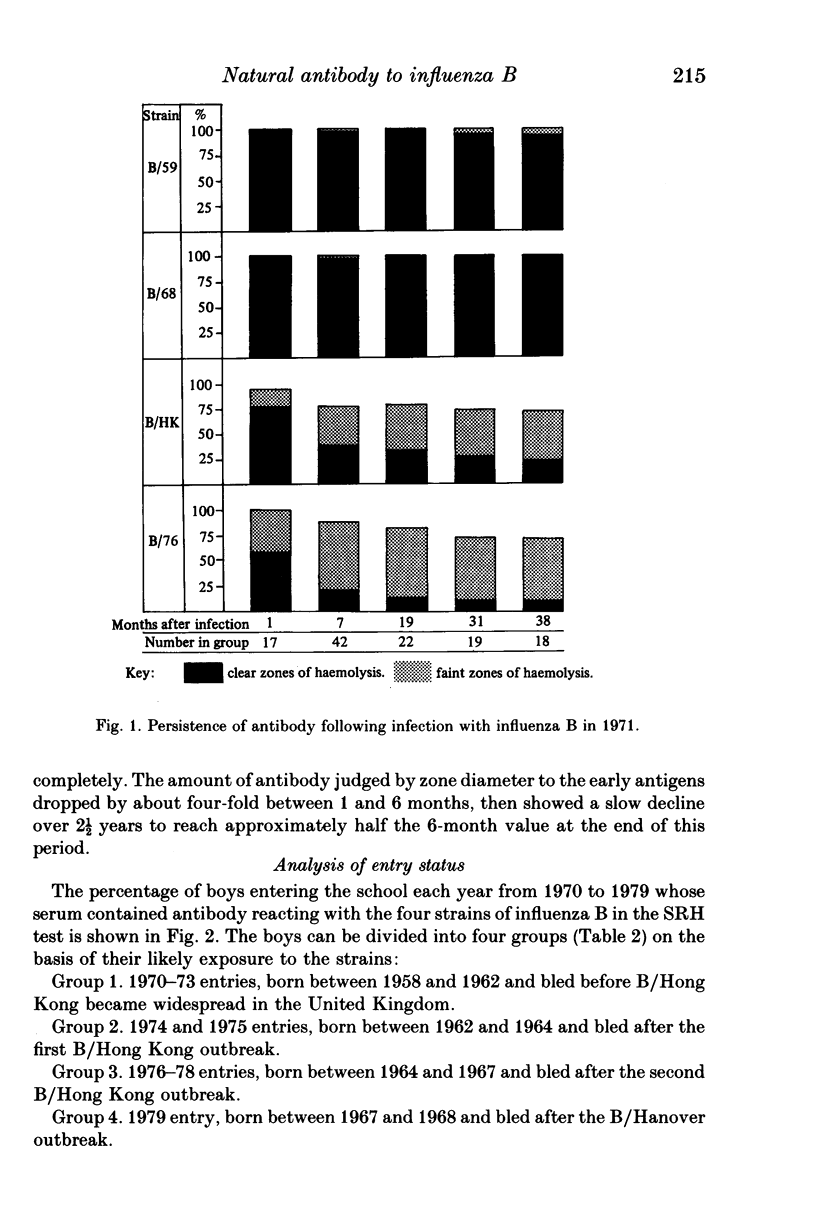
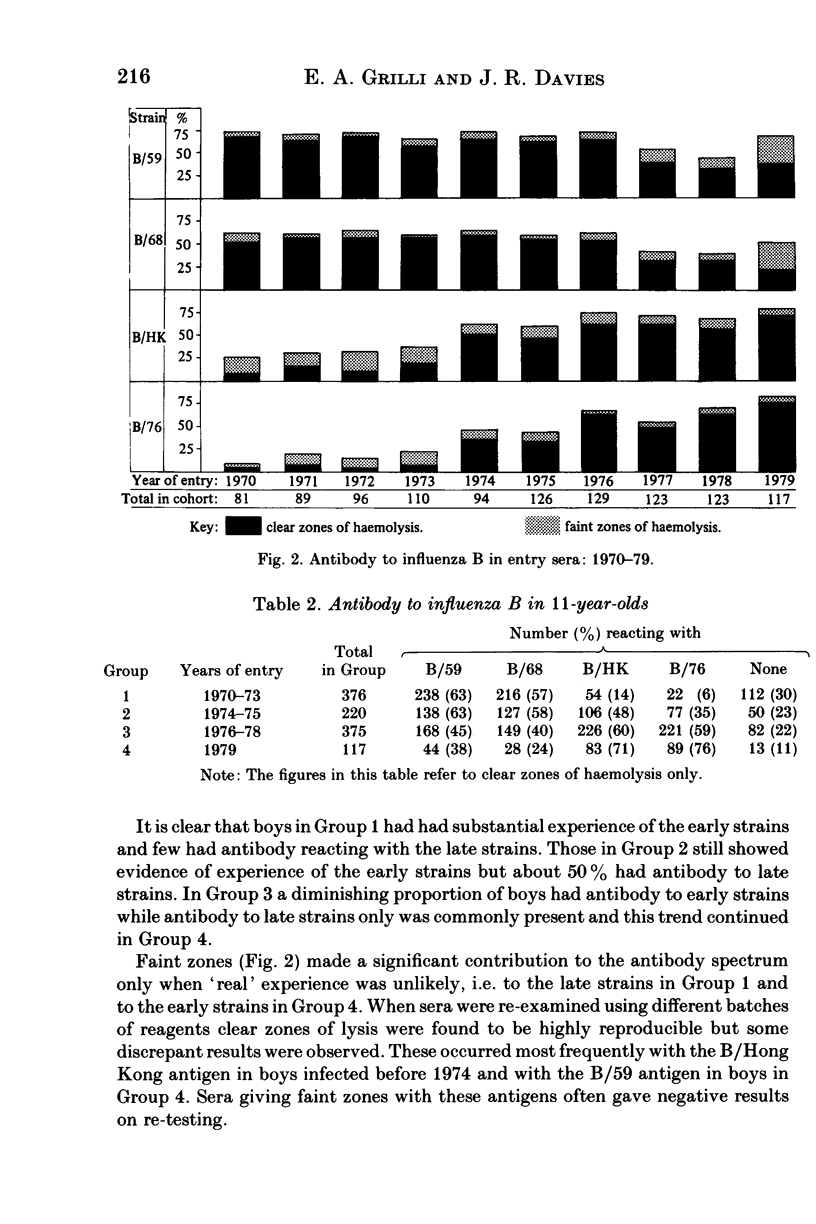
The technique of radial haemolysis (SRH) was used to assess the response to infection with different strains of influenza B virus, to determine the persistence of antibody following such infection and to examine sera from boys entering school at age 11 years. The technique detected 95% of infections and in primary infection the antibody response was mainly to the infecting strain. Re-infections resulted in a broad response, both to the homotypic strain and to strains more distantly related. Antibody to the homotypic strain persisted for at least 3 years but in some individuals the reaction with heterotypic strains tended to become weaker--resulting in zones of incomplete lysis--or was lost. Examination of the sera collected on entry to the school showed that about 60% of the boys bled before B/Hong Kong became widespread in the United Kingdom had antibody to strains representative of those isolated in the 1960s and few boys had antibody to B/Hong Kong. After 1974 antibody to B/Hong Kong and later strains became more common while antibody to earlier strains was less frequently detected. The significance of the results as an estimate of past experience is discussed.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Callow K. A., Beare A. S. Measurement of antibody to influenza virus neuraminidase by single radial hemolysis in agarose gels. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.1-8.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraverty P. Antigenic relationship between influenza B viruses. Bull World Health Organ. 1971;45(6):755–766. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraverty P. Comparison of haemagglutination-inhibition and single-radial-haemolysis techniques for detection of antibodies to influenza B virus. Arch Virol. 1980;63(3-4):285–289. doi: 10.1007/BF01315034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxford J. S., Schild G. C., Potter C. W., Jennings R. The specificity of the anti-haemagglutinin antibody response induced in man by inactivated influenza vaccines and by natural infection. J Hyg (Lond) 1979 Feb;82(1):51–61. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400025468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira M., Assaad F. A., Delon P. J. Influenza surveillance. Bull World Health Organ. 1978;56(2):192–203. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schild G. C., Pereira M. S., Chakraverty P., Coleman M. T., Dowdle W. R., Chang W. K. Antigenic variants of influenza B virus. Br Med J. 1973 Oct 20;4(5885):127–131. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5885.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schild G. C., Pereira M. S., Chakraverty P. Single-radial-hemolysis: a new method for the assay of antibody to influenza haemagglutinin. Applications for diagnosis and seroepidemiologic surveillance of influenza. Bull World Health Organ. 1975;52(1):43–50. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. J., Davies J. R. Natural infection with influenza A (H3N2). The development, persistance and effect of antibodies to the surface antigens. J Hyg (Lond) 1976 Oct;77(2):271–282. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400024712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


