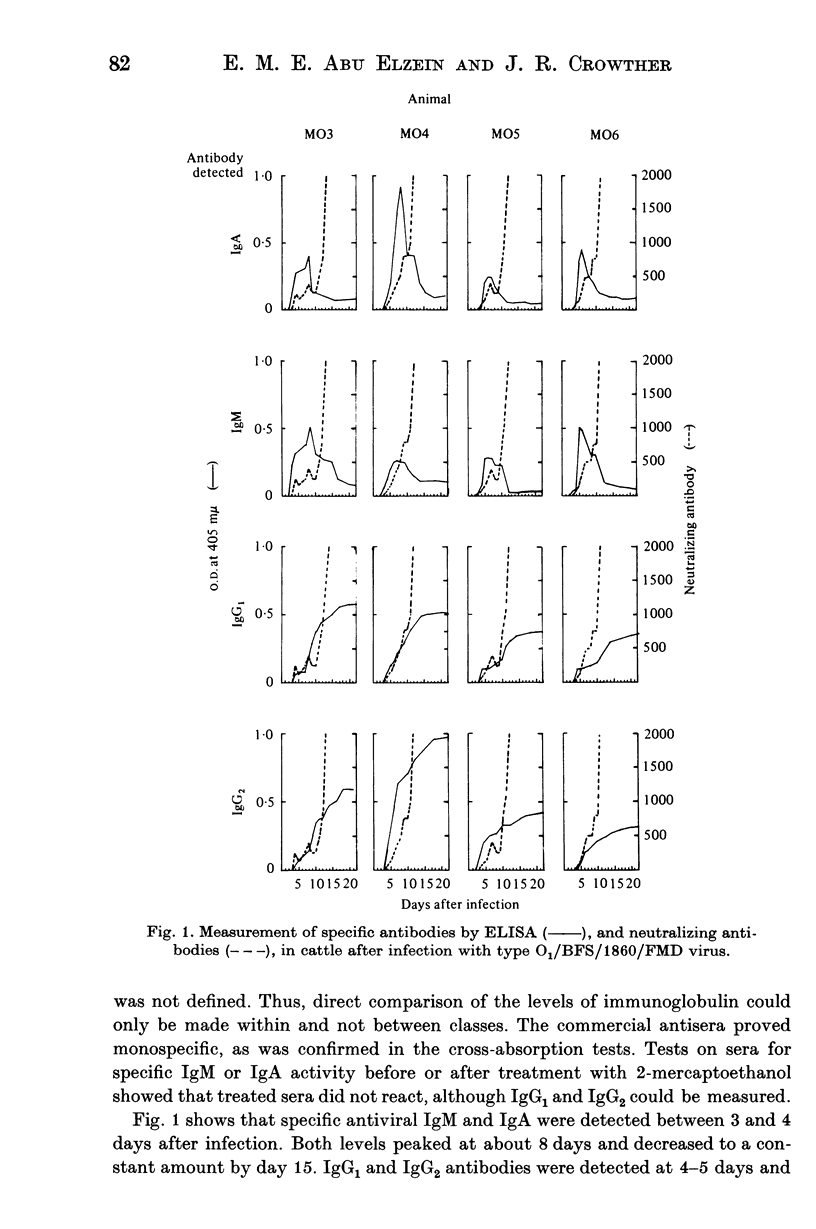
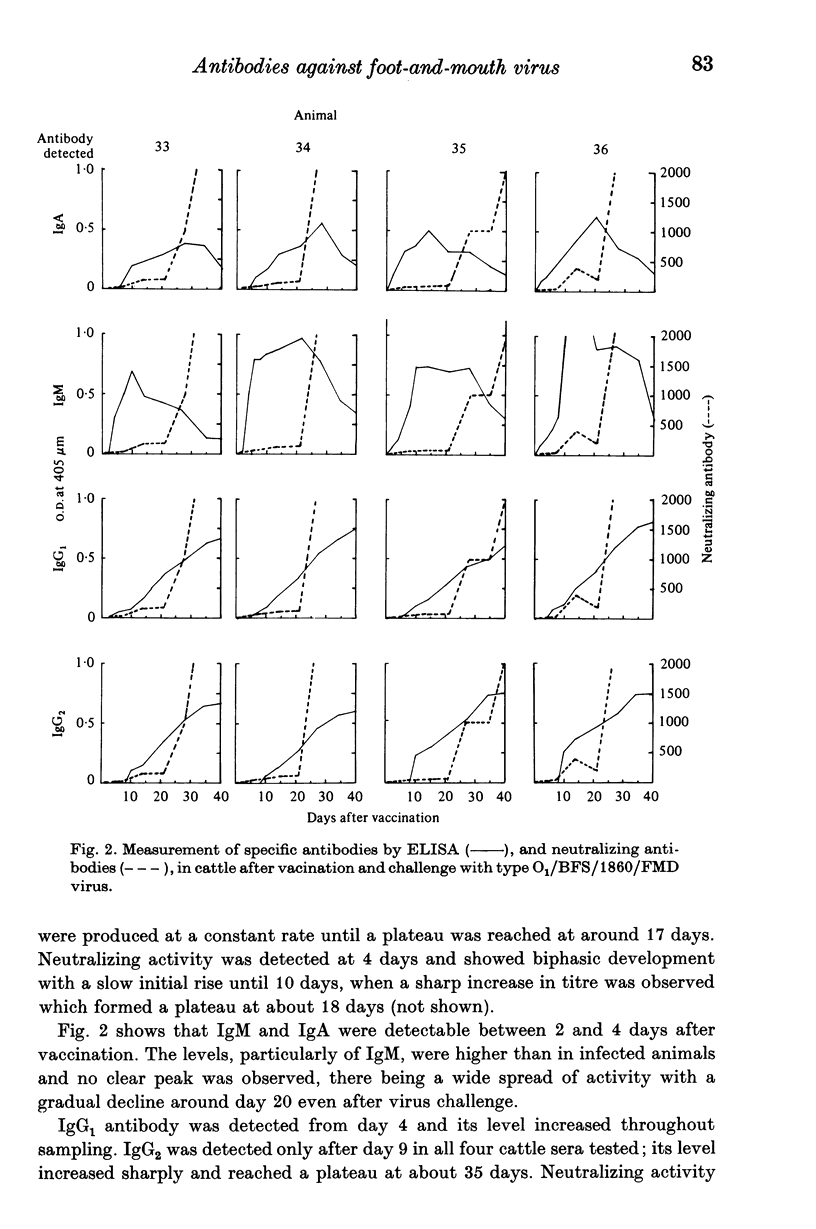
Abstract
A simple solid-phase enzyme immunoassay is described for the detection of antibody classes showing activity against foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) virus in bovine sera. The assay achieves a preliminary separation of the specific class of antibody from other serum proteins through immuno-adsorption to class-specific immunoglobulin-coated wells of micro-titre plates. The specific antibody is reacted with FMD virus, which is then detected by an enzyme-labelled anti virus IgG.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abu Elzein E. M., Crowther J. R. Enzyme-labelled immunosorbent assay techniques in foot-and-mouth disease virus research. J Hyg (Lond) 1978 Jun;80(3):391–399. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400024840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S. Coupling of enzymes to proteins with glutaraldehyde. Use of the conjugates for the detection of antigens and antibodies. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN F., CARTWRIGHT B., NEWMAN J. F. FURTHER STUDIES OF THE EARLY ANTIBODY IN THE SEA OF CATTLE AND GUINEA PIGS INFECTED WITH FOOT-AND-MOUTH DISEASE VIRUS. J Immunol. 1964 Sep;93:397–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN F., CARTWRIGHT B. PURIFICATION OF RADIOACTIVE FOOT-AND-MOUTH DISEASE VIRUS. Nature. 1963 Sep 21;199:1168–1170. doi: 10.1038/1991168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloan G. J., Butler J. E. Evaluation of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for quantitation by subclass for bovine antibodies. Am J Vet Res. 1978 Jun;39(6):935–941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


