Abstract
An immunosorbent assay using solid-phase attachment of red cells (SPARC) was used for the detection of rubella-specific IgM. The method is described and the results compared with those obtained by the IgM antibody capture radioimmunoassay (MACRIA). One hundred and ninety-nine sera were investigated for the presence of rubella-specific IgM and only one discrepant result occurred, namely a false positive obtained by MACRIA in a patient with infectious mononucleosis. Rheumatoid factor, heterophile antibody, and rubella-specific IgG did not interfere with the results obtained by the SPARC technique. Advantages of the SPARC technique include the case and lack of expense of testing large numbers of sera, the small volume of sample required and the fact that pretreatment of serum is not necessary.
Full text
PDF




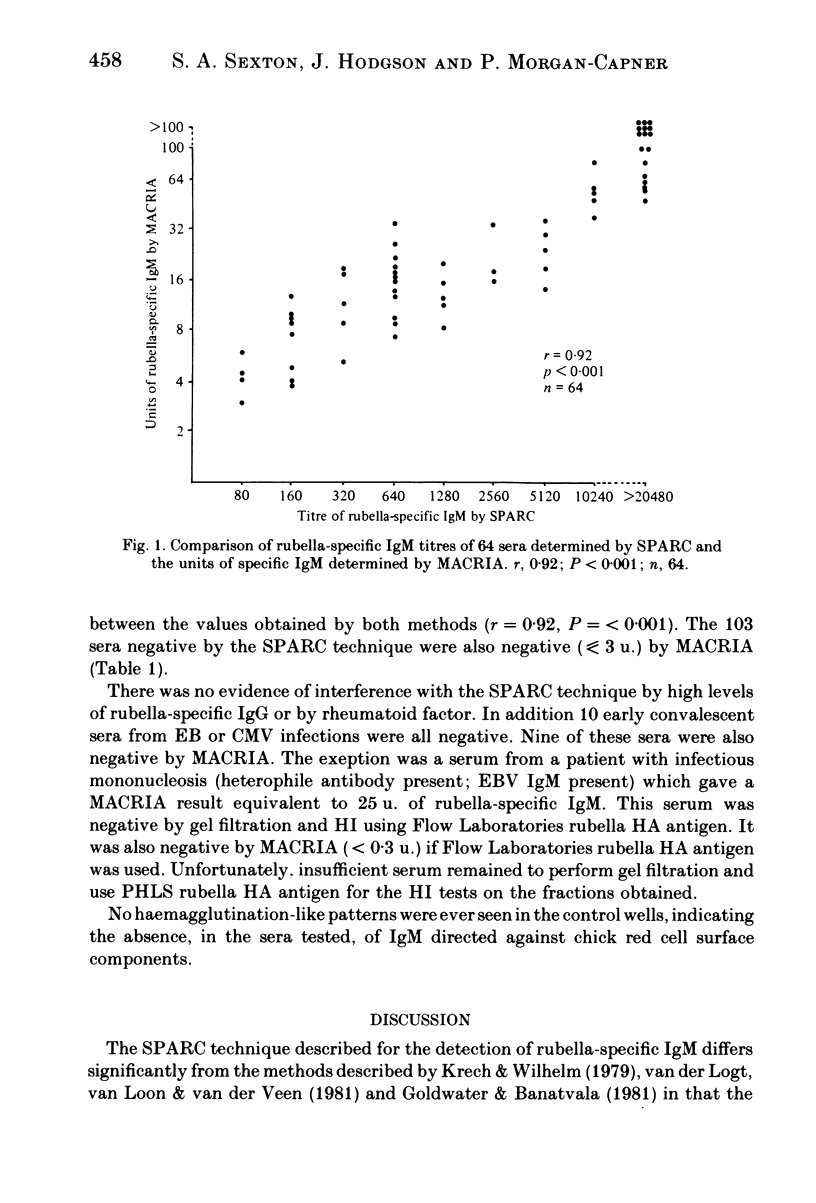



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Best J. M., Banatvala J. E., Watson D. Serum IgM and IgG responses in postnatally acquired rubella. Lancet. 1969 Jul 12;2(7611):65–68. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92386-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cradock-Watson J. E., Ridehalgh M. K., Anderson M. J., Pattison J. R. Outcome of asymptomatic infection with rubella virus during pregnancy. J Hyg (Lond) 1981 Oct;87(2):147–154. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400069345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denoyel G. A., Gaspar A., Peyramond D. Diagnosis of recent rubella virus infection by demonstration of specific immunoglobulin M antibodies: comparison of solid-phase reverse immunosorbent test with sucrose density gradient centrifugation. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Apr;13(4):698–704. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.4.698-704.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldwater P. N., Banatvala J. E. Solid-phase immunosorbent haemadsorption (SPIHAd): a new, rapid and simple test for rubella-specific IgM. J Virol Methods. 1981 Jun;2(6):341–347. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(81)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krech U., Wilhelm J. A. A solid-phase immunosorbent technique for the rapid detection of rubella IgM by haemagglutination inhibition. J Gen Virol. 1979 Aug;44(2):281–286. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-2-281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz J. B., Malic A. Rubella-specific IgM detected by an antibody capture assay/ELISA technique. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Dec;34(12):1392–1395. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.12.1392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz J. B., Mortimer P. P., Mortimer P. R., Morgan-Capner P., Shafi M. S., White G. B. Rubella antibody measured by radial haemolysis. Characteristics and performance of a simple screening method for use in diagnostic laboratories. J Hyg (Lond) 1980 Apr;84(2):213–222. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400026711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinikki P. O., Shekarchi I., Dorsett P., Sever J. L. Determination of virus-specific IgM antibodies by using ELISA: elimination of false-positive results with protein A-Sepharose absorption and subsequent IgM antibody assay. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Dec;92(6):849–857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meurman O. H., Viljanen M. K., Granfors K. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay of rubella virus immunoglobulin M antibodies: comparison with sucrose density gradient centrifugation test. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Mar;5(3):257–262. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.3.257-262.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meurman O. H., Ziola B. R. IgM-class rheumatoid factor interference in the solid-phase radioimmunoassay of rubella-specific IgM antibodies. J Clin Pathol. 1978 May;31(5):483–487. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.5.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan-Capner P., Davies E., Pattison J. R. Rubella-specific IgM detection using Sephacryl S-300 gel filtration. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Nov;33(11):1082–1085. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.11.1082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer P. P., Tedder R. S., Hamblig M. H., Shafi M. S., Burkhardt F., Schilt U. Antibody capture radioimmunoassay for anti-rubella IgM. J Hyg (Lond) 1981 Apr;86(2):139–153. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400068856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash A. A. Separation of lymphocyte sub-populations using antibodies attached to staphylococcal protein A-coated surfaces. J Immunol Methods. 1976;12(1-2):149–161. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90105-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Logt J. T., van Loon A. M., van der Veen J. Hemadsorption immunosorbent technique for determination of rubella immunoglobulin M antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Mar;13(3):410–415. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.3.410-415.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]