Abstract
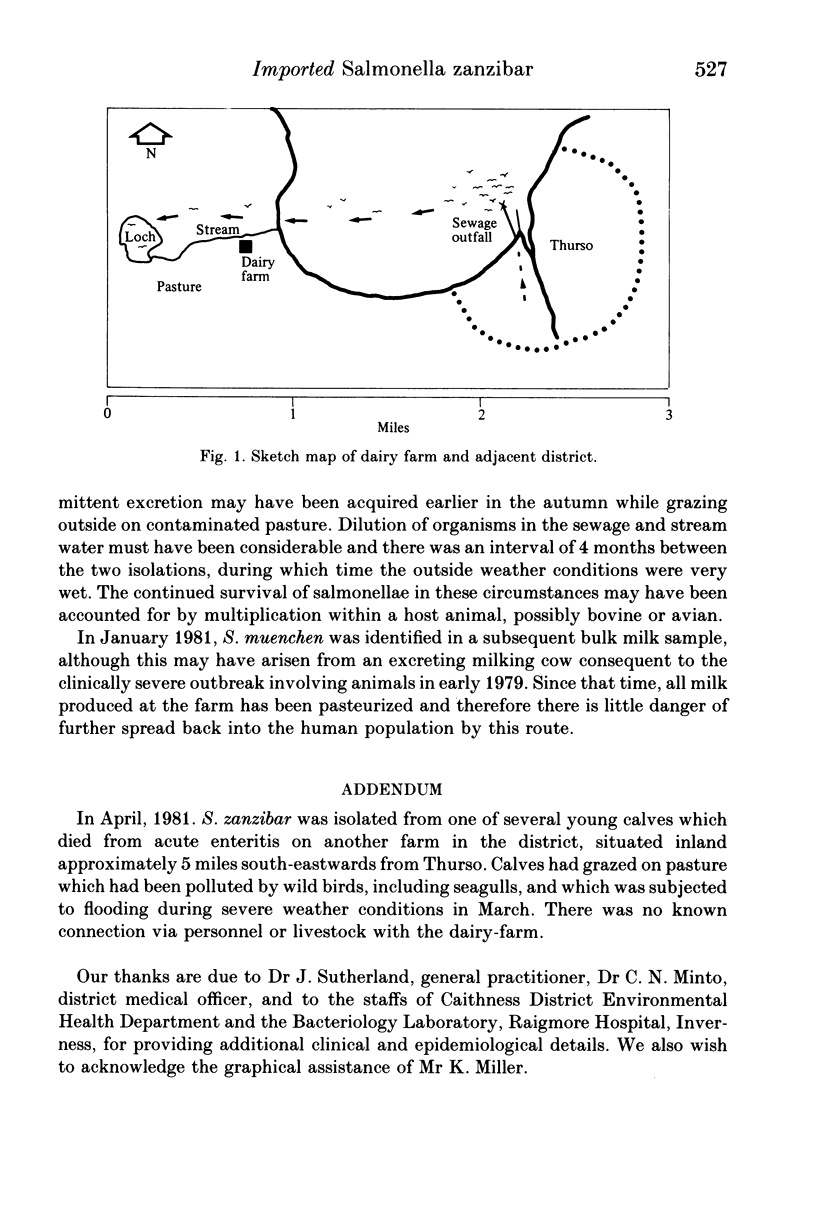
In August, 1980 a rare serotype S. zanzibar was isolated in the North of Scotland from a man home on leave from Malaysia, whence he returned in November having been bacteriologically negative 2 months previously. In December however, S. zanzibar was isolated from a bulk milk sample taken at a nearby dairy farm. No illness occurred among milking cows which had been brought inside from pasture in mid-October. Since 1972 a variety of different salmonella serotypes had been identified in cattle, milk and other samples at this farm, with seagulls being implicated as the vector transmitting infection from the sewage of a local town on to farmland and an adjacent loch. Although water from this source has not been used in recent years for drinking by cattle, it is utilized for washing floors within the dairy premises. Since 1979, following an outbreak affecting consumers, all milk produced at the farm has been pasteurized.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fenlon D. R. Seagulls (Larus spp.) as vectors of salmonellae: an investigation into the range of serotypes and numbers of salmonellae in gull faeces. J Hyg (Lond) 1981 Apr;86(2):195–202. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400068911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston W. S., MacLachlan G. K., Hopkins G. F. The possible involvement of seagulls (Larus sp) in the transmission of salmonella in dairy cattle. Vet Rec. 1979 Dec 8;105(23):526–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. M., Richards D. W., Stephens D. P., Griffiths T. The transmission of S livingstone to cattle by the herring gull (Larus argentatus). Vet Rec. 1977 May 21;100(21):450–451. doi: 10.1136/vr.100.21.450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



