Abstract
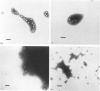
Chlorine dioxide, bromine chloride and iodine were compared with chlorine as virucidal agents. Under optimal conditions all disinfectants were effective at low concentrations, but each disinfectant responded differently to acidity and alkalinity. Disinfection by chlorine was impaired by the presence of ammonia, but the other disinfectants retained much of their potency. Disinfection of poliovirus by iodine resulted in structural changes in the virions as seen by electron micrroscopy, but the other disinfectants were able to inactivate poliovirus without causing any apparent structural changes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvarez M. E., O'Brien R. T. Effects of chlorine concentration on the structure of poliovirus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jan;43(1):237–239. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.1.237-239.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balluz S. A., Butler M., Jones H. H. The behaviour of f2 coliphage in activated sludge treatment. J Hyg (Lond) 1978 Apr;80(2):237–242. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400053584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balluz S. A., Jones H. H., Bulter M. The persistence of poliovirus of poliovirus in activated sludge treatment. J Hyg (Lond) 1977 Apr;78(2):165–173. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400056060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg G., Dahling D. R., Brown G. A., Berman D. Validity of fecal coliforms, total coliforms, and fecal streptococci as indicators of viruses in chlorinated primary sewage effluents. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Dec;36(6):880–884. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.6.880-884.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boublik M., Drzeniek R. Demonstration of a core in poliovirus particles by electron microscopy. J Gen Virol. 1976 Jun;31(3):447–449. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-31-3-447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burleson G. R., Murray T. M., Pollard M. Inactivation of viruses and bacteria by ozone, with and without sonication. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Mar;29(3):340–344. doi: 10.1128/am.29.3.340-344.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer W. N., Kawata K., Krusé C. W. Chlorination and iodination of poliovirus and f2. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1976 Jan;48(1):61–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubra M. S., La Torre J. L., Scodeller E. A., Denoya C. D., Vasquez C. Cores in foot-and-mouth disease virus. Virology. 1982 Jan 15;116(1):349–353. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90426-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajenian H., Butler M. Inactivation of f2 coliphage in municipal effluent by the use of various disinfectants. J Hyg (Lond) 1980 Apr;84(2):247–255. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400026747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. T., Newman J. Structural and compositional changes associated with chlorine inactivation of polioviruses. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Dec;38(6):1034–1039. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.6.1034-1039.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Public Health Weekly Reports for DECEMBER 17, 1943. Public Health Rep. 1943 Dec 17;58(51):1837–1880. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp D. G., Floyd R., Johnson J. D. Nature of the surviving plaque-forming unit of reovirus in water containing bromine. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jan;29(1):94–101. doi: 10.1128/am.29.1.94-101.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDENKOPF S. J. Inactivation of type 1, poliomyelitis virus with chlorine. Virology. 1958 Feb;5(1):56–67. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(58)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]