Abstract
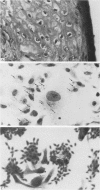
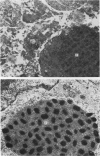
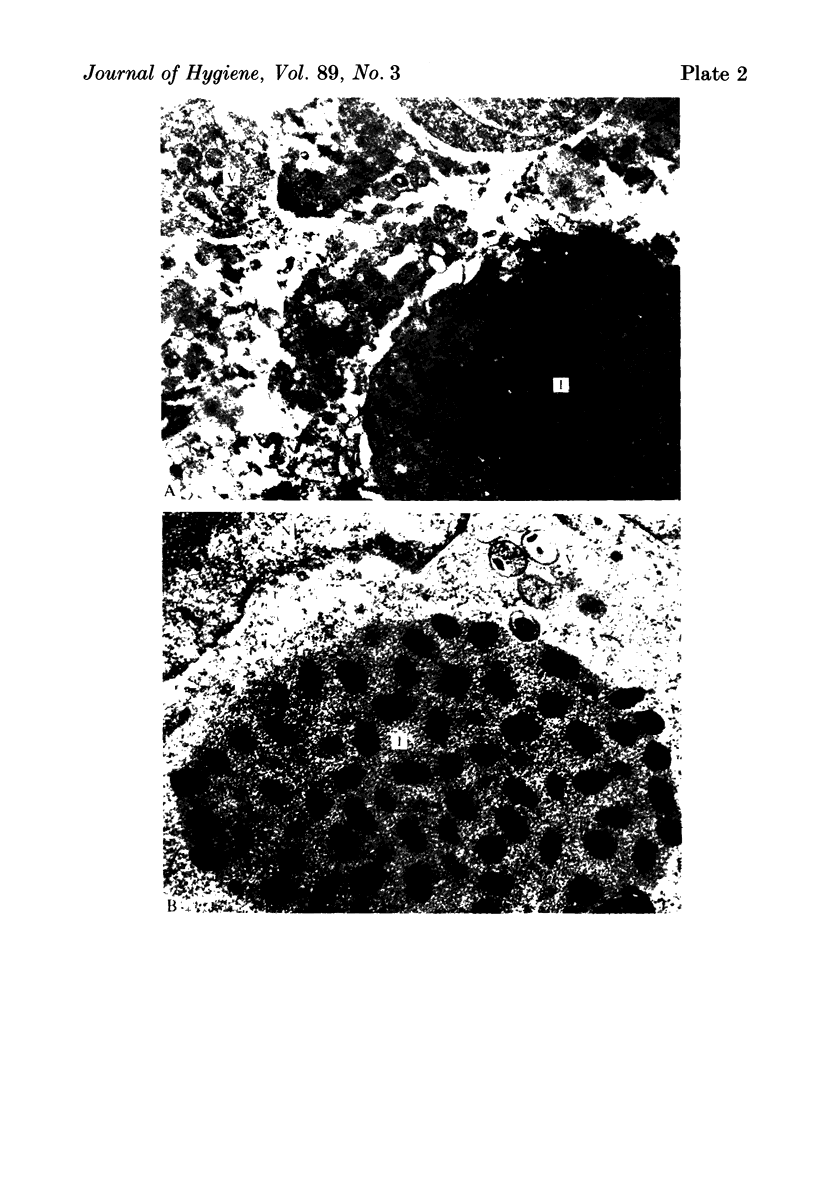
This paper describes virological and epidemiological features of an infection which killed two of three affected cheetahs at Whipsnade Park in 1977. Two animals had profuse skin lesions and the third had an acute haemorrhagic pneumonia. The outbreak was shown to be caused by cowpox virus. Cowpox virus is believed to circulate in small wild animals, but the source of infection was not traced despite virological and serological tests on 93 captive and 102 wild animals. Sub-clinical infections did not occur in susceptible contact cheetahs. Immune globulin did not influence the outcome and smallpox vaccine does not take in cheetahs. Management of any future outbreak will rely on prompt diagnosis and segregation of infected animals.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOULTER E. A. The titration of vaccinial neutralizing antibody on chorio-allantoic membranes. J Hyg (Lond) 1957 Dec;55(4):502–512. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400037414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxby D., Ghaboosi B. Laboratory characteristics of poxviruses isolated from captive elephants in Germany. J Gen Virol. 1977 Nov;37(2):407–414. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-37-2-407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxby D. Identification and interrelationships of the variola/vaccinia subgroup of poxviruses. Prog Med Virol. 1975;19:215–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxby D. Is cowpox misnamed? A review of 10 human cases. Br Med J. 1977 May 28;1(6073):1379–1381. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6073.1379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxby D., Shackleton W. B., Wheeler J., Turner A. Comparison of cowpox-like viruses isolated from European zoos. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1979;61(4):337–340. doi: 10.1007/BF01315021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan C., Healing T. D., Evans N., Healing L., Prior A. Evidence of infection by viruses in small British field rodents. J Hyg (Lond) 1980 Apr;84(2):285–294. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400026784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marennikova S. S., Maltseva N. N., Korneeva V. I., Garanina N. Outbreak of pox disease among carnivora (felidae) and edentata. J Infect Dis. 1977 Mar;135(3):358–366. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.3.358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marennikova S. S., Shelukhina E. M. White rats as source of pox infection in carnivora of the family Felidae. Acta Virol. 1976 Oct;20(5):442–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsett L. R., Baxby D., Denham E. M. Cowpox in the domestic cat. Vet Rec. 1978 Dec 16;103(25):567–567. doi: 10.1136/vr.103.25.567-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwart P., Gispen R., Peters J. C. Cowpox in okapis Okapia johnstoni at Rotterdam zoo. Br Vet J. 1971 Jan;127(1):20–24. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)37783-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]