Abstract
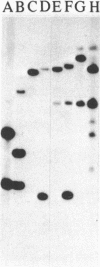
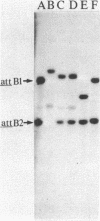
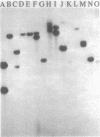
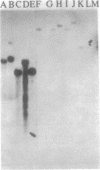
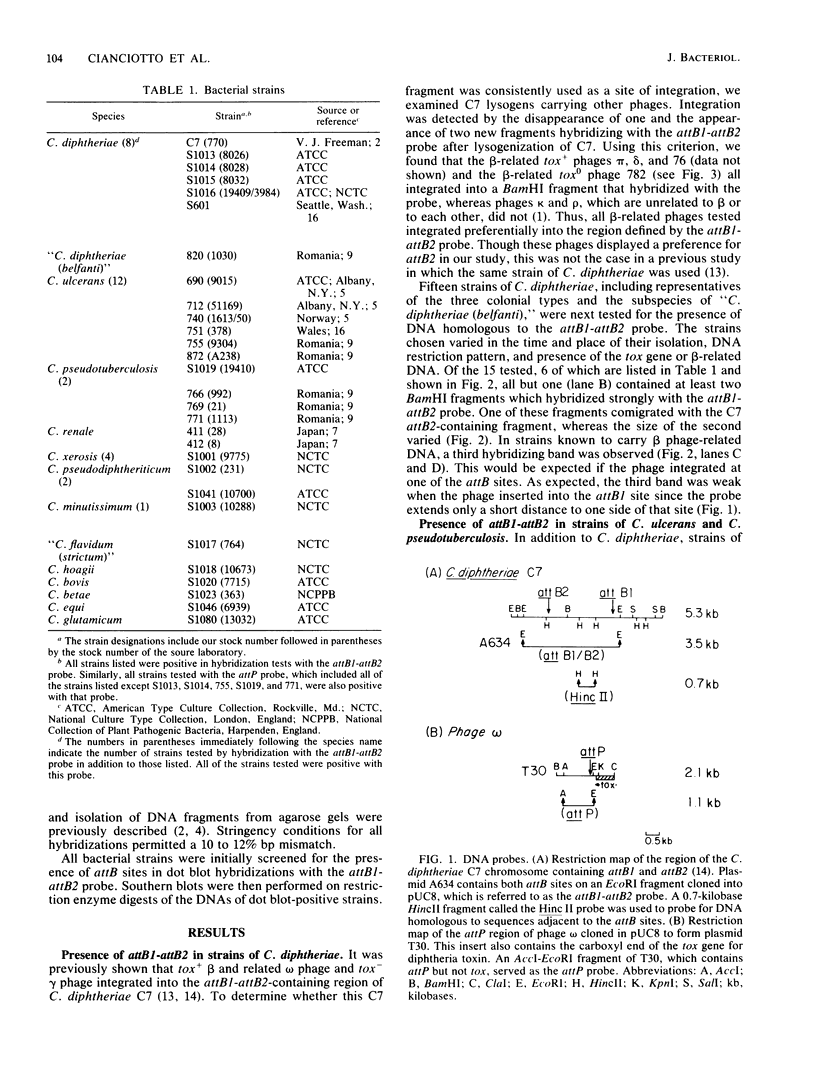
In toxigenic conversion of Corynebacterium diphtheriae C7, beta bacteriophage DNA integrates into either of two chromosomal attachment sites, attB1 or attB2. These attB sites share a 96-base-pair sequence with the attP sites of beta-related phages. The distribution of attB-related sites in other species of Corynebacterium was assessed by hybridization with a DNA probe containing both attB sites of the C7 strain and a second DNA probe containing the attP site of a beta-related phage. All but one of the 15 C. diphtheriae strains tested, regardless of origin or colonial type, contained at least two BamHI fragments that hybridized strongly to both of these probes under conditions of high stringency. Strains of C. ulcerans and C. pseudotuberculosis, species in which conversion to toxinogeny has also been demonstrated, also had one or two hybridizing BamHI fragments. The functionality of these sites as integration sites was demonstrated by isolating lysogens of all three species following single infection with one or more beta-related phages. As predicted, following lysogenization one of the DNA fragments that had exhibited homology with the attB1-attB2 probe was replaced by two hybridizing fragments. Other species of Corynebacterium, including pathogens and nonpathogens from animals, plant pathogens, and soil isolates also carried at least one BamHI fragment that hybridized with the attB1-attB2 and attP probes. The data indicate that sequences homologous to the beta phage integration sites in C. diphtheriae have been conserved in members of the genus Corynebacterium.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buck G. A., Cross R. E., Wong T. P., Loera J., Groman N. DNA relationships among some tox-bearing corynebacteriophages. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):679–684. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.679-684.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck G. A., Groman N. B. Physical mapping of beta-converting and gamma-nonconverting corynebacteriophage genomes. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):131–142. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.131-142.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cianciotto N., Groman N. A beta-related corynebacteriophage which lacks a tox allele but can acquire it by recombination with converting phage. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):32–35. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.32-35.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groman N. B. Conversion by corynephages and its role in the natural history of diphtheria. J Hyg (Lond) 1984 Dec;93(3):405–417. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400065001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groman N., Cianciotto N., Bjorn M., Rabin M. Detection and expression of DNA homologous to the tox gene in nontoxinogenic isolates of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):48–56. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.48-56.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groman N., Schiller J., Russell J. Corynebacterium ulcerans and Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis responses to DNA probes derived from corynephage beta and Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):511–517. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.511-517.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Yanagawa R. Generalized transduction in Corynebacterium renale. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):1086–1087. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.1086-1087.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird W., Groman N. Prophage map of converting corynebacteriophage beta. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):208–219. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.208-219.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maximescu P., Oprişan A., Pop A., Potorac E. Further studies on Corynebacterium species capable of producing diphtheria toxin (C. diphtheriae, C. ulcerans, C. ovis). J Gen Microbiol. 1974 May;82(1):49–56. doi: 10.1099/00221287-82-1-49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel J. L., Rappuoli R., Murphy J. R., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Restriction endonuclease map of the nontoxigenic corynephage gamma c and its relationship to the toxigenic corynephage beta c. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):510–518. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.510-518.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappuoli R. Isolation and characterization of Corynebacterium diphtheriae nontandem double lysogens hyperproducing CRM197. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Sep;46(3):560–564. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.3.560-564.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappuoli R., Michel J. L., Murphy J. R. Integration of corynebacteriophages beta tox+, omega tox+, and gamma tox- into two attachment sites on the Corynebacterium diphtheriae chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1202–1210. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1202-1210.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappuoli R., Michel J. L., Murphy J. R. Restriction endonuclease map of corynebacteriophage omega ctox+ isolated from the Park-Williams no. 8 strain of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):524–530. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.524-530.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappuoli R., Ratti G. Physical map of the chromosomal region of Corynebacterium diphtheriae containing corynephage attachment sites attB1 and attB2. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):325–330. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.325-330.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller J., Groman N., Coyle M. Plasmids in Corynebacterium diphtheriae and diphtheroids mediating erythromycin resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):814–821. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]