Abstract
An inorganic pyrophosphatase was purified over 600-fold to homogeneity as judged by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The enzyme is a tetramer of Mr = 84,000, has a sedimentation coefficient of 5.8S, a Stokes radius of 3.5 nm, and an isoelectric point of 5.7. Like the enzyme of Escherichia coli, the pyrophosphatase appears to be made constitutively. The pH and temperature optima are 8.3 and 80 degrees C, respectively. The Km for PPi is 0.6 mM. A divalent cation is essential, with Mg2+ preferred. The enzyme uses only PPi as a substrate.
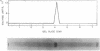
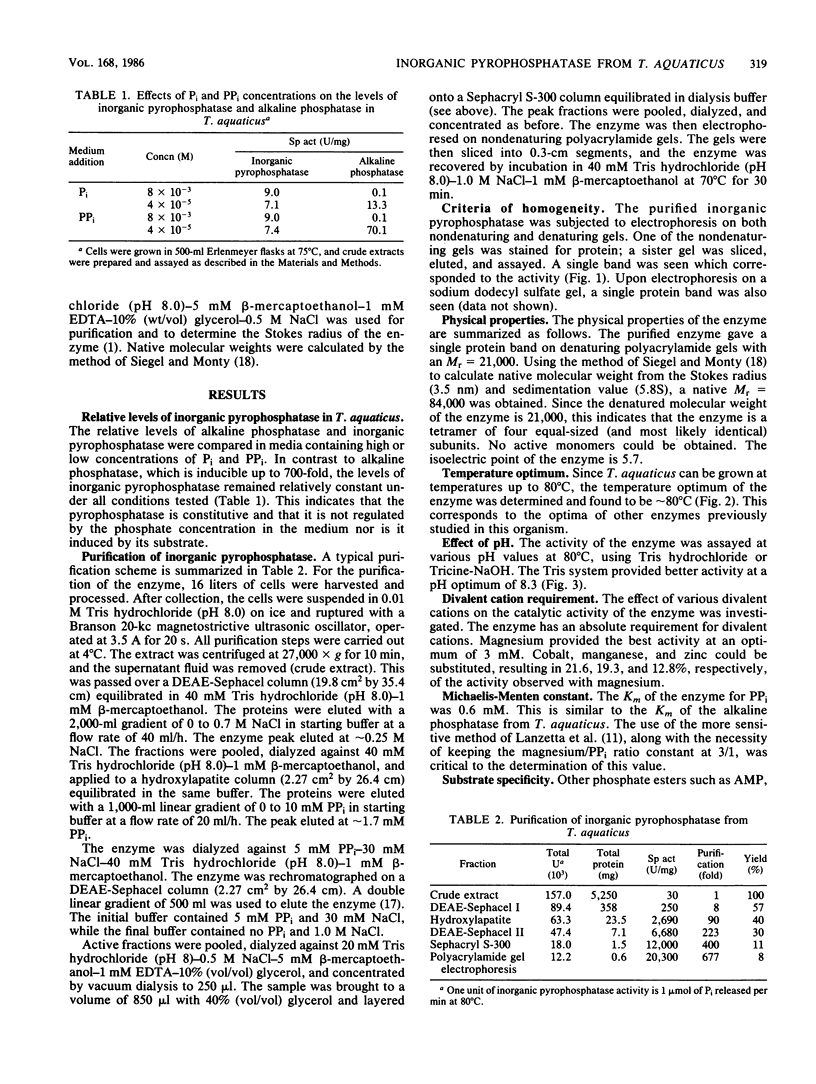
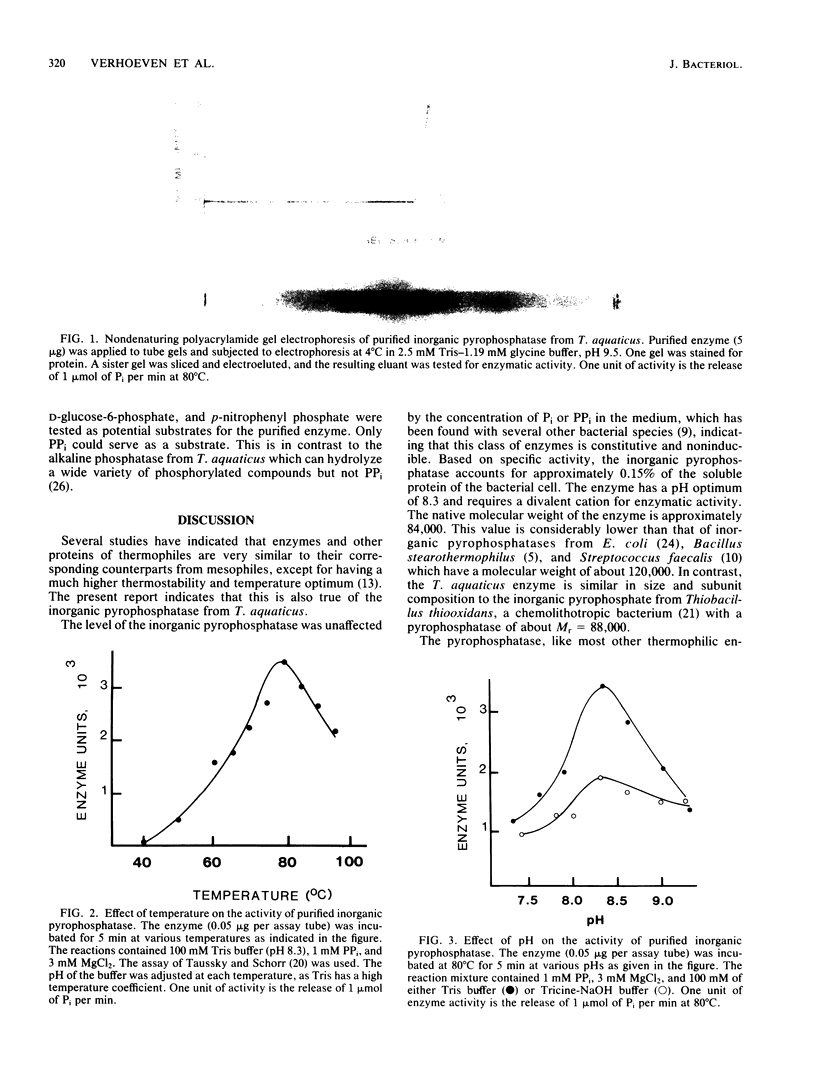
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ACKERS G. K. MOLECULAR EXCLUSION AND RESTRICTED DIFFUSION PROCESSES IN MOLECULAR-SIEVE CHROMATOGRAPHY. Biochemistry. 1964 May;3:723–730. doi: 10.1021/bi00893a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. D., Freeze H. Thermus aquaticus gen. n. and sp. n., a nonsporulating extreme thermophile. J Bacteriol. 1969 Apr;98(1):289–297. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.1.289-297.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Deutscher M. P. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase stimulatory factors and inorganic pyrophosphatase. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 10;18(14):3165–3170. doi: 10.1021/bi00581a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEPPEL L. A., HARKNESS D. R., HILMOE R. J. A study of the substrate specificity and other properties of the alkaline phosphatase of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1962 Mar;237:841–846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hachimori A., Takeda A., Kaibuchi M., Ohkawara N., Samejima T. Purification and characterization of inorganic pyrophosphatase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Biochem. 1975 Jun;77(6):1177–1183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent R. B., Guterman S. K. Pyrophosphate inhibition of rho ATPase: a mechanism of coupling to RNA polymerase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3992–3996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahti R. Microbial inorganic pyrophosphatases. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):169–178. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.169-178.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahti R., Niemi T. Purification and some properties of inorganic pyrophosphatase from Streptococcus faecalis. J Biochem. 1981 Jul;90(1):79–85. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzetta P. A., Alvarez L. J., Reinach P. S., Candia O. A. An improved assay for nanomole amounts of inorganic phosphate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 15;100(1):95–97. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. L., Hart N., Peck H. D., Jr Inorganic pyrophosphate: energy source for sulfate-reducing bacteria of the genus desulfotomaculum. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):363–364. doi: 10.1126/science.217.4557.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungdahl L. G. Physiology of thermophilic bacteria. Adv Microb Physiol. 1979;19:149–243. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60199-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier E., El Samei M. B. Improved procedure of purification of inorganic pyrophosphatase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1979 Mar;13(3):337–340. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1979.tb01889.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Monty K. J. Determination of molecular weights and frictional ratios of proteins in impure systems by use of gel filtration and density gradient centrifugation. Application to crude preparations of sulfite and hydroxylamine reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 7;112(2):346–362. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smile D. H., Donohue M., Yeh M. F., Kenkel T., Trela J. M. Repressible alkaline phosphatase from Thermus aquaticus: associated phosphodiesterase activity. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3399–3401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAUSSKY H. H., SHORR E. A microcolorimetric method for the determination of inorganic phosphorus. J Biol Chem. 1953 Jun;202(2):675–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tominaga N., Mori T. Purificantion and characterization of inorganic pyrophosphatase from Thiobacillus thiooxidans. J Biochem. 1977 Feb;81(2):477–483. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub A., Kaufmann E., Teitz Y. Synthesis of nicontinamide-adenine dinucleotide by NAD pyrophosphorylase on a column of hydroxylapatite. Anal Biochem. 1969 Apr 4;28(1):469–476. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90201-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins A. S. Physiological factors in the regulation of alkaline phosphatase synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):616–623. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.616-623.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. C., Hall D. C., Josse J. Constitutive inorganic pyrophosphatase of Escherichia coli. 3. Molecular weight and physical properties of the enzyme and its subunits. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 10;245(17):4335–4345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood H. G. Some reactions in which inorganic pyrophosphate replaces ATP and serves as a source of energy. Fed Proc. 1977 Aug;36(9):2197–2206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh M. F., Trela J. M. Purification and characterization of a repressible alkaline phosphatase from Thermus aquaticus. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 25;251(10):3134–3139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]