Abstract
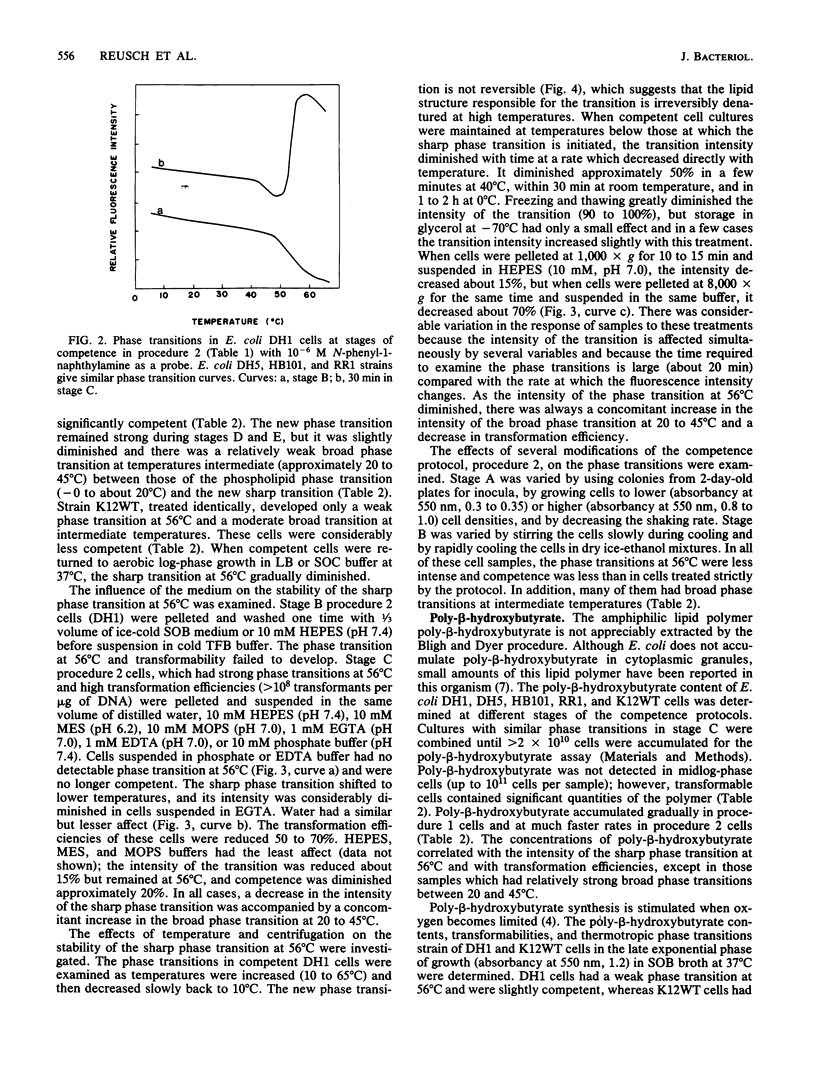
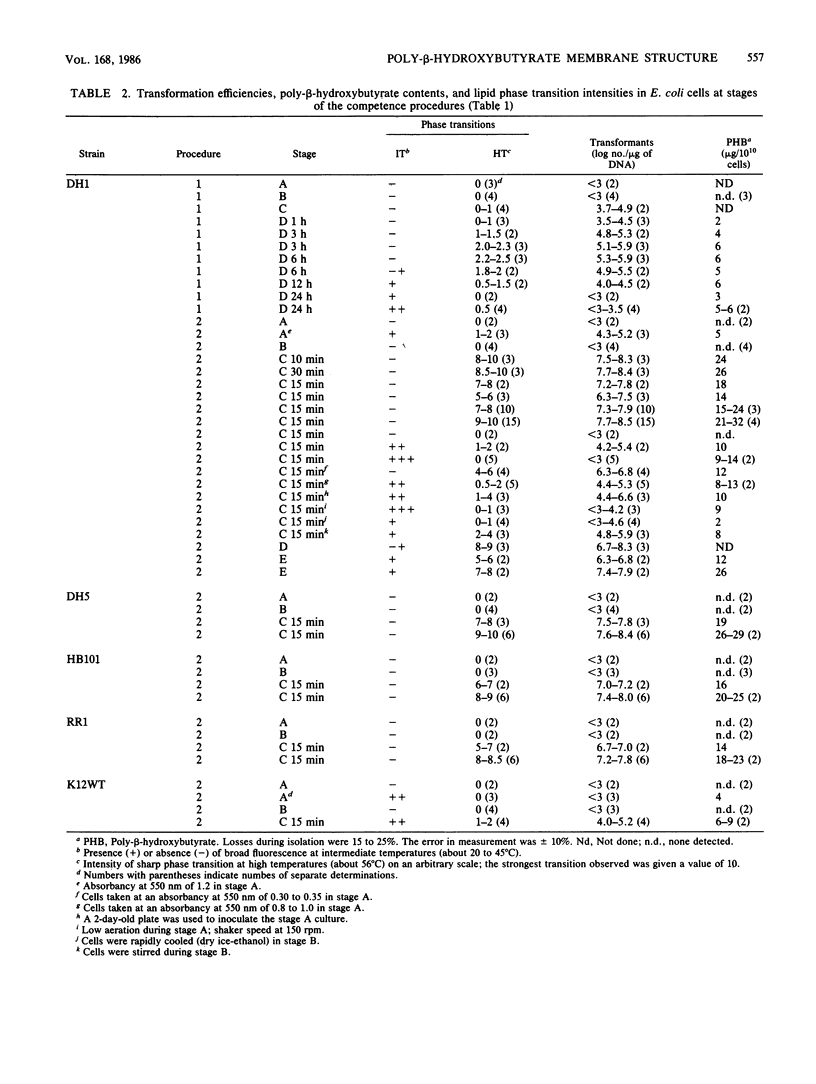
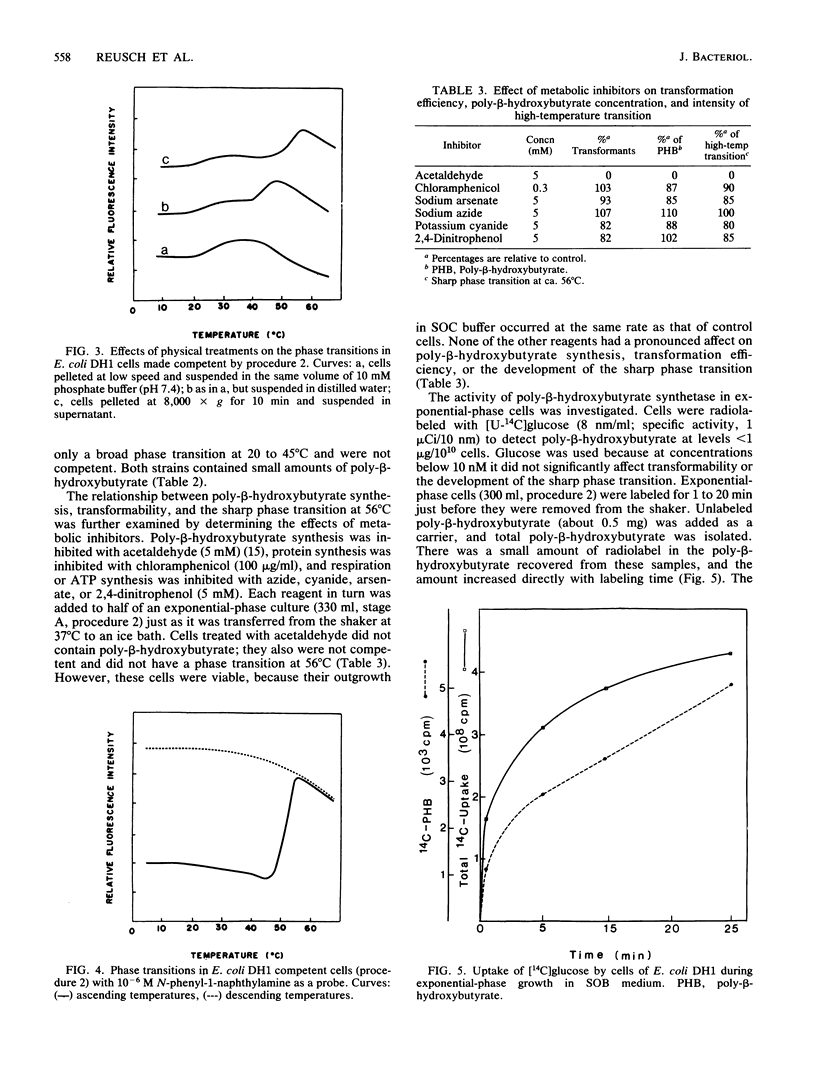
The effects of competence-inducing treatments on the composition and organization of membrane lipids in Escherichia coli K-12, DH1, DH5, HB101, and RR1 were investigated for two widely used protocols in which transformability is developed at low temperatures in Ca2+ buffers. At stages during each procedure, the lipid compositions of the cells were determined, and the thermotropic lipid phase transitions were observed in whole cell culture by fluorescence assay with the hydrophobic probe N-phenyl-1-naphthylamine. Competence was evaluated by determining transformation efficiencies with plasmid pBR322 DNA. The competence-inducing procedures effected only slight changes in phospholipid compositions which did not correlate with transformability. However, the induction of competence was coincident with de novo synthesis and incorporation of poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate into the cytoplasmic membranes and with the appearance of a sharp lipid phase transition above physiological temperatures. Transformation efficiencies correlated with poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate concentrations and with the intensity of the new phase transition. Transformability, poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate synthesis and the new phase transition were not significantly affected by inhibition of protein synthesis with chloramphenicol or inhibition of respiration or ATP synthesis with azide, cyanide, arsenate, or 2,4-dinitrophenol; however, when poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate synthesis was inhibited with acetaldehyde, the new phase transition was not observed, and competence failed to develop. These studies suggest that genetic transformability in E. coli may be physiologically regulated.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullis P. R., de Kruijff B. Lipid polymorphism and the functional roles of lipids in biological membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 20;559(4):399–420. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(79)90012-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes E. A., Senior P. J. The role and regulation of energy reserve polymers in micro-organisms. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;10:135–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60088-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth D. H., Bevers E. M., Verkleij A. J., Op den Kamp J. A., van Deenen L. L. Action of phospholipase A2 and phospholipase C on Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Nov;165(1):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garwin J. L., Cronan J. E., Jr Thermal modulation of fatty acid synthesis in Escherichia coli does not involve de novo enzyme synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Mar;141(3):1457–1459. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.3.1457-1459.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert P., Brown M. R. Effect of R-plasmid RP1 and nutrient depletion on the gross cellular composition of Escherichia coli and its resistance to some uncoupling phenols. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1062–1065. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1062-1065.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griebel R., Smith Z., Merrick J. M. Metabolism of poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate. I. Purification, composition, and properties of native poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate granules from Bacillus megaterium. Biochemistry. 1968 Oct;7(10):3676–3681. doi: 10.1021/bi00850a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlos K., Eibl H. Influence of calcium on phosphatidylglycerol. Two separate lamellar structures. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 4;19(5):895–899. doi: 10.1021/bi00546a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson K., Papahadjopoulos D. Phase transitions and phase separations in phospholipid membranes induced by changes in temperature, pH, and concentration of bivalent cations. Biochemistry. 1975 Jan 14;14(1):152–161. doi: 10.1021/bi00672a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones I. M., Primrose S. B., Robinson A., Ellwood D. C. Effect of growth rate and nutrient limitation on the transformability of Escherichia coli with plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):841–846. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.841-846.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAW J. H., SLEPECKY R. A. Assay of poly-beta-hydroxybutyric acid. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jul;82:33–36. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.1.33-36.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACRAE R. M., WILKINSON J. F. Poly-beta-hyroxybutyrate metabolism in washed suspensions of Bacillus cereus and Bacillus megaterium. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Aug;19(1):210–222. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-1-210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERRICK J. M., DOUDOROFF M. Enzymatic synthesis of poly-beta-hydroxybutyric acid in bacteria. Nature. 1961 Mar 18;189:890–892. doi: 10.1038/189890a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandersloot J. G., Gerritsen W. J., Leunissen-Bijvelt J., van Echteld C. J., Noordam P. C., de Gier J. Ca2+-induced changes in the barrier properties of cardiolipin/phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jan 8;640(1):106–113. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90536-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oeding V., Schlegel H. G. Beta-ketothiolase from Hydrogenomonas eutropha H16 and its significance in the regulation of poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate metabolism. Biochem J. 1973 May;134(1):239–248. doi: 10.1042/bj1340239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overath P., Brenner M., Gulik-Krzywicki T., Shechter E., Letellier L. Lipid phase transitions in cytoplasmic and outer membranes of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 6;389(2):358–369. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90328-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D., Vail W. J., Pangborn W. A., Poste G. Studies on membrane fusion. II. Induction of fusion in pure phospholipid membranes by calcium ions and other divalent metals. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 5;448(2):265–283. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90241-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROUF M. A., STOKES J. L. Isolation and identification of the sudanophilic granules of Sphaerotilus natans. J Bacteriol. 1962 Feb;83:343–347. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.2.343-347.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reusch R. N., Sadoff H. L. 5-n-Alkylresorcinols from encysting Azotobacter vinelandii: isolation and characterization. J Bacteriol. 1979 Aug;139(2):448–453. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.2.448-453.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reusch R. N., Sadoff H. L. D-(-)-poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate in membranes of genetically competent bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):778–788. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.778-788.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie G. A., Senior P. J., Dawes E. A. The purification and characterization of acetoacetyl-coenzyme A reductase from Azotobacter beijerinckii. Biochem J. 1971 Jan;121(2):309–316. doi: 10.1042/bj1210309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scandella C. J., Kornberg A. A membrane-bound phospholipase A1 purified from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov 23;10(24):4447–4456. doi: 10.1021/bi00800a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Protein composition of the cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):890–901. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.890-901.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior P. J., Dawes E. A. Poly- -hydroxybutyrate biosynthesis and the regulation of glucose metabolism in Azotobacter beijerinckii. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(1):55–66. doi: 10.1042/bj1250055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior P. J., Dawes E. A. The regulation of poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate metabolism in Azotobacter beijerinckii. Biochem J. 1973 May;134(1):225–238. doi: 10.1042/bj1340225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimshick E. J., McConnell H. M. Lateral phase separation in phospholipid membranes. Biochemistry. 1973 Jun 5;12(12):2351–2360. doi: 10.1021/bi00736a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit J., Kamio Y., Nikaido H. Outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium: chemical analysis and freeze-fracture studies with lipopolysaccharide mutants. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):942–958. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.942-958.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Danner D. B., Deich R. A. Genetic transformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:41–68. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.000353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Träuble H., Eibl H. Electrostatic effects on lipid phase transitions: membrane structure and ionic environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):214–219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vail W. J., Stollery J. G. Phase changes of cardiolipin vesicles mediated by divalent cations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 20;551(1):74–84. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90354-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasilenko I., De Kruijff B., Verkleij A. J. Polymorphic phase behaviour of cardiolipin from bovine heart and from Bacillus subtilis as detected by 31P-NMR and freeze-fracture techniques. Effects of Ca2+, Mg2+, Ba2+ and temperature. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jan 22;684(2):282–286. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90018-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaskovsky V. E., Kostetsky E. Y. Modified spray for the detection of phospholipids on thin-layer chromatograms. J Lipid Res. 1968 May;9(3):396–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkleij A. J., de Kruyff B., Ververgaert P. H., Tocanne J. F., van Deenen L. L. The influence of pH, Ca2+ and protein on the thermotropic behaviour of the negatively charged phospholipid, phosphatidylglycerol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 29;339(3):432–437. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90171-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSBACH A., HURWITZ J. The formation of 2-keto-3-deoxyheptonic acid in extracts of Escherichia coli B. I. Identification. J Biol Chem. 1959 Apr;234(4):705–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward A. C., Dawes E. A. A disk assay for poly- -hydroxybutyrate. Anal Biochem. 1973 Apr;52(2):607–613. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90067-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitzman P. D., Jones D. Regulation of citrate synthase and microbial taxonomy. Nature. 1968 Jul 20;219(5151):270–272. doi: 10.1038/219270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. A., Lennarz W. J., Schnaitman C. A. Distribution of lipids in the wall and cytoplasmic membrane subfractions of the cell envelope of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):686–690. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.686-690.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C., Frerman F. E. Extraction, characterization, and cellular localization of the lipids of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1854–1867. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1854-1867.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yguerabide J., Foster M. C. Fluorescence spectroscopy of biological membranes. Mol Biol Biochem Biophys. 1981;31:199–269. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-81537-9_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




