Abstract
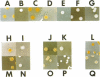
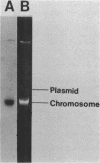
The genes coding for yellow pigment production in Erwinia herbicola Eho10 (ATCC 39368) were cloned and localized to a 12.4-kilobase (kb) chromosomal fragment. A 2.3-kb AvaI deletion in the cloned fragment resulted in the production of a pink-yellow pigment, a possible precursor of the yellow pigment. Production of yellow pigment in both E. herbicola Eho10 and pigmented Escherichia coli clones was inhibited by glucose. When the pigment genes were transformed into a cya (adenylate cyclase) E. coli mutant, no expression was observed unless exogenous cyclic AMP was provided, which suggests that cyclic AMP is involved in the regulation of pigment gene expression. In E. coli minicells, the 12.4-kb fragment specified the synthesis of at least seven polypeptides. The 2.3-kb AvaI deletion resulted in the loss of a 37K polypeptide and the appearance of a polypeptide of 40 kilodaltons (40K polypeptide). The synthesis of the 37K polypeptide, which appears to be required for yellow pigment production, was not repressed by the presence of glucose in the culture medium, as was the synthesis of other polypeptides specified by the 12.4-kb fragment, suggesting that there are at least two types of gene regulation involved in yellow pigment synthesis. DNA hybridization studies indicated that different yellow pigment genes exist among different E. herbicola strains. None of six pigmented plant pathogenic bacteria examined, Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58, Cornyebacterium flaccumfaciens 1D2, Erwinia rubrifaciens 6D364, Pseudomonas syringae ATCC 19310, Xanthomonas campestris 25D11, and "Xanthomonas oryzae" 17D54, exhibited homology with the cloned pigment genes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., Fanning G. R., Steigerwalt A. G. Deoxyribonucleic acid relatedness among species of Erwinia and between Erwinia species and other enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):12–17. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.12-17.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby S., Kotlarz D., Buc H. Deletion mutagenesis of the Escherichia coli galactose operon promoter region. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 25;167(2):259–274. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80335-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee A. K., Gibbins L. N., Carpenter J. A. Some observations on the physiology of Erwinia herbicola and its possible implication as a factor antagonistic to Erwinia amylovora in the "fire-blight" syndrome. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Jun;15(6):640–642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee A. K., Gibbins L. N. Induction of nonpigmented variants of Erwinia herbicola by incubation at supraoptimal temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):107–112. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.107-112.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossart P., Gicquel-Sanzey B. Cloning and sequence of the crp gene of Escherichia coli K 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 25;10(4):1363–1378. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.4.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossart P., Gicquel-Sanzey B. Regulation of expression of the crp gene of Escherichia coli K-12: in vivo study. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):454–457. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.454-457.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN R. N. IN VITRO AND IN VIVO INTERACTIONS BETWEEN COMPONENTS OF MIXED BACTERIAL CULTURES ISOLATED FROM APPLE BUDS. Phytopathology. 1965 Feb;55:217–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gantotti B. V., Beer S. V. Plasmid-borne determinants of pigmentation and thiamine prototrophy in Erwinia herbicola. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1627–1629. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1627-1629.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenbaum P. E., Hall G. A. Transport of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate across Escherichia coli vesicle membranes. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):459–467. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.459-467.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow M., Austin B., Dickinson C. H. Numerical taxonomy of some yellow-pigmented bacteria isolated from plants. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Dec;97(2):219–233. doi: 10.1099/00221287-97-2-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B., Collins J. A small cosmid for efficient cloning of large DNA fragments. Gene. 1980 Nov;11(3-4):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. In vitro packaging of lambda and cosmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:299–309. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAKMAN R. S., SUTHERLAND E. W. ADENOSINE 3',5'-PHOSPHATE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1309–1314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meagher R. B., Tait R. C., Betlach M., Boyer H. W. Protein expression in E. coli minicells by recombinant plasmids. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):521–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. Y., Clegg D. O., Koshland D. E., Jr Molecular cloning and amplification of the adenylate cyclase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4684–4688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]