Abstract
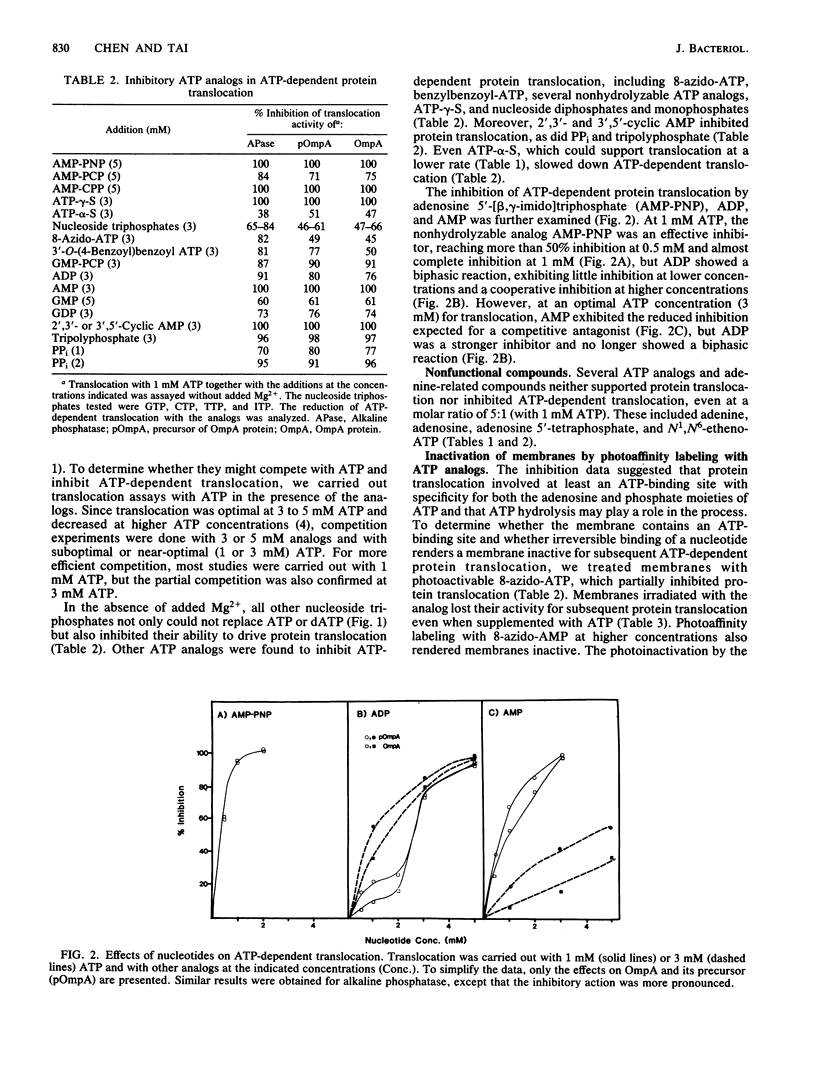
We have shown previously that Escherichia coli can translocate the same protein either co- or posttranslationally and that ATP hydrolysis is essential for the posttranslational translocation of the precursors of alkaline phosphatase and OmpA protein into inverted E. coli membrane vesicles. ATP-dependent protein translocation has now been further characterized. In the absence of exogenous Mg2+, dATP, formycin A-5'-triphosphate, ATP-alpha-S, and N1-oxide-ATP could replace ATP, but many other nucleotides were not only ineffective but inhibited ATP-dependent translocation. The inhibitors included nonhydrolyzable ATP analogs, ATP-gamma-S, 8-azido-ATP, AMP, ADP, cyclic AMP, PPi, and tripolyphosphate. On the other hand, adenosine, adenosine 5'-tetraphosphate, and N1,N6-etheno-ATP neither supported nor inhibited translocation. Moreover, photoaffinity labeling of azido-adenine nucleotides rendered membranes inactive for subsequent ATP-dependent protein translocation. These results suggest that protein translocation involves at least an ATP-binding site in the membrane and hydrolysis of ATP and that both the adenosine and phosphate moieties of ATP play a role.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker E. P., Randall L. L. The requirement for energy during export of beta-lactamase in Escherichia coli is fulfilled by the total protonmotive force. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):895–900. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01902.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. L., Tai P. C. Roles of H+-ATPase and proton motive force in ATP-dependent protein translocation in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):389–392. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.389-392.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., Rhoads D., Tai P. C. Alkaline phosphatase and OmpA protein can be translocated posttranslationally into membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):973–980. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.973-980.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., Tai P. C. ATP is essential for protein translocation into Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4384–4388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway C. J., Dean G. E., Marsh M., Rudnick G., Mellman I. Acidification of macrophage and fibroblast endocytic vesicles in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3334–3338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginther C. L., Ingraham J. L. Nucleoside diphosphokinase of Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3406–3411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen W., Garcia P. D., Walter P. In vitro protein translocation across the yeast endoplasmic reticulum: ATP-dependent posttranslational translocation of the prepro-alpha-factor. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90325-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. I. Signal recognition particle (SRP) does not mediate a translational arrest of nascent secretory proteins in mammalian cell-free systems. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2031–2033. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03888.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueckler M., Lodish H. F. The human glucose transporter can insert posttranslationally into microsomes. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):629–637. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90272-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Blobel G. In vitro translocation of bacterial proteins across the plasma membrane of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7421–7425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perara E., Rothman R. E., Lingappa V. R. Uncoupling translocation from translation: implications for transport of proteins across membranes. Science. 1986 Apr 18;232(4748):348–352. doi: 10.1126/science.3961485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. B., Tai P. C., Davis B. D. Energy-requiring translocation of the OmpA protein and alkaline phosphatase of Escherichia coli into inner membrane vesicles. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):63–70. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.63-70.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Translocation of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum III. Signal recognition protein (SRP) causes signal sequence-dependent and site-specific arrest of chain elongation that is released by microsomal membranes. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):557–561. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters M. G., Blobel G. Secretory protein translocation in a yeast cell-free system can occur posttranslationally and requires ATP hydrolysis. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1543–1550. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams N., Coleman P. S. Exploring the adenine nucleotide binding sites on mitochondrial F1-ATPase with a new photoaffinity probe, 3'-O-(4-benzoyl)benzoyl adenosine 5'-triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2834–2841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]