Abstract
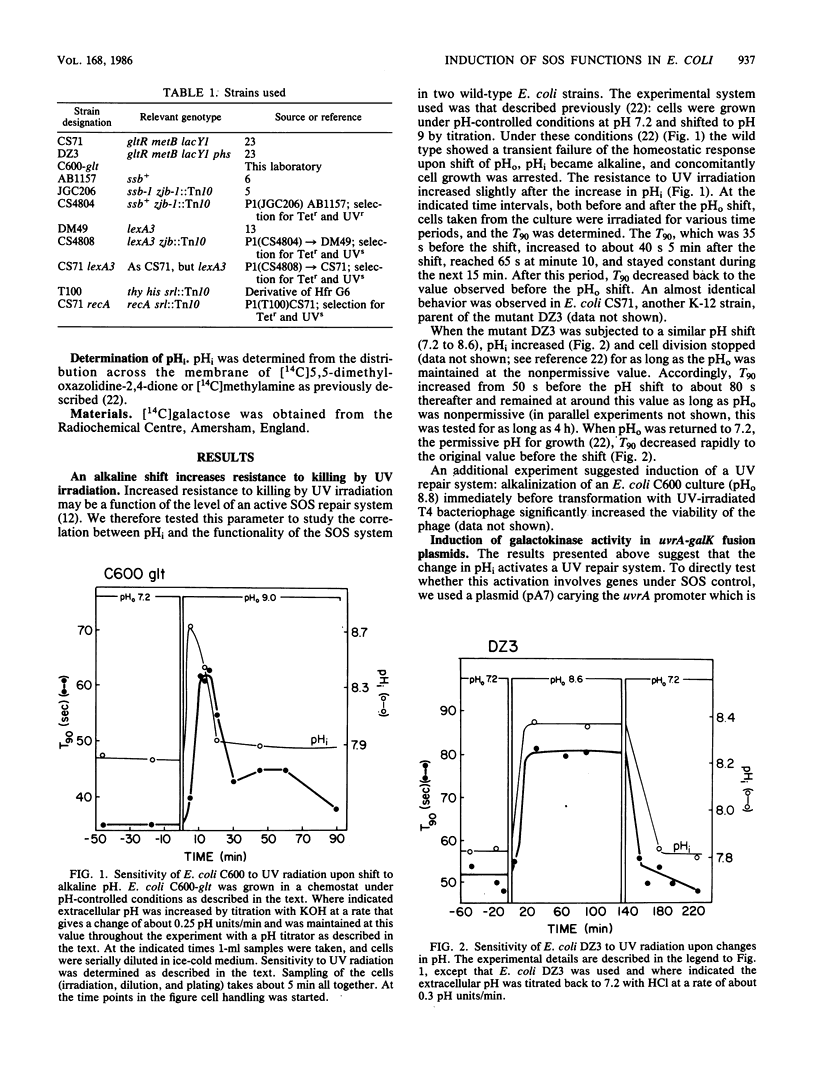
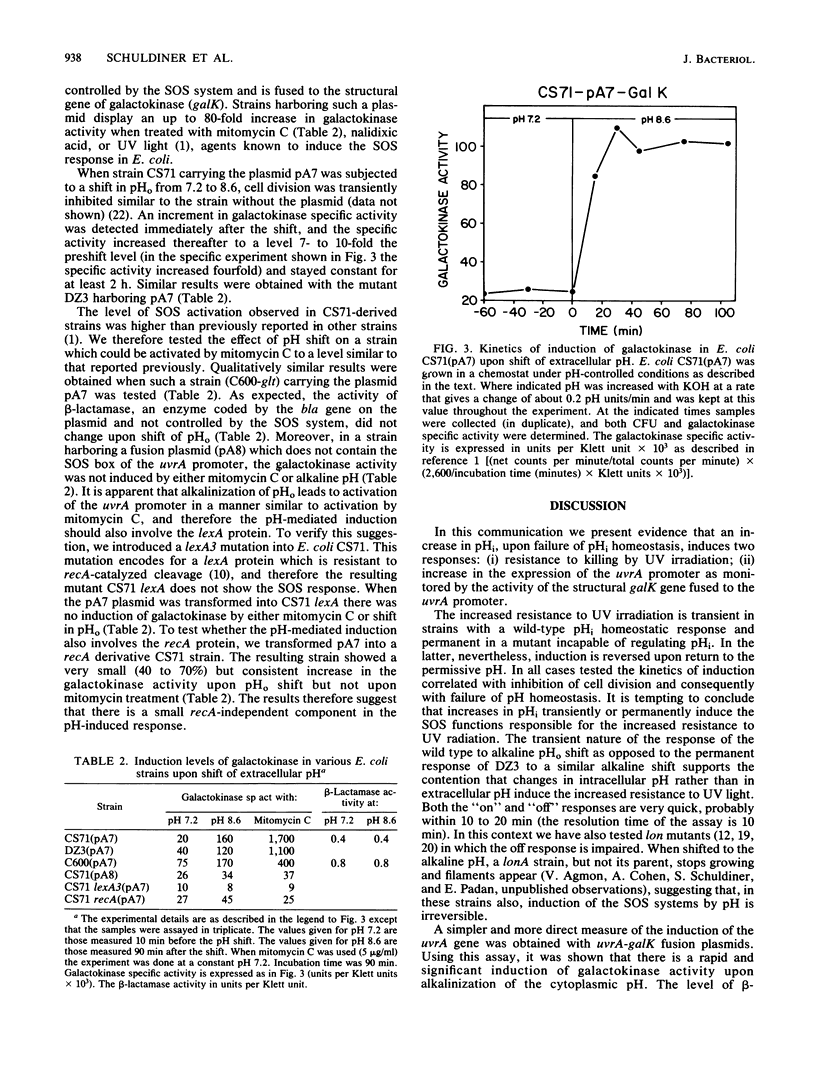
Alkalinization of intracellular pH (pHi) causes an increase in UV resistance in wild-type and pH-sensitive mutant (DZ3) cells of Escherichia coli. Utilizing cells transformed with a plasmid (pA7) which bears the uvrA promoter fused to galK galactokinase structural gene, it was shown that alkaline pHi leads to an increase in the specific activity of galactokinase. This effect was not displayed in a mutant bearing a recA-insensitive lexA gene, nor in cells harboring a plasmid (pA8) in which the galK is fused to a lexA-insensitive uvrA promoter. Hence, the effects of pHi on cells functions may involve the lexA product of the SOS system.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Backendorf C., Brandsma J. A., Kartasova T., van de Putte P. In vivo regulation of the uvrA gene: role of the "-10" and "-35" promoter regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 10;11(17):5795–5810. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.17.5795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth I. R., Kroll R. G. Regulation of cytoplasmic pH (pH1) in bacteria and its relationship to metabolism. Biochem Soc Trans. 1983 Jan;11(1):70–72. doi: 10.1042/bst0110070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citri N., Kalkstein A., Samuni A., Zyk N. Conformational adaptation of RTEM beta-lactamase to cefoxitin. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Oct 15;144(2):333–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08468.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glassberg J., Meyer R. R., Kornberg A. Mutant single-strand binding protein of Escherichia coli: genetic and physiological characterization. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):14–19. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.14-19.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWARD-FLANDERS P., THERIOT L. A method for selecting radiation-sensitive mutants of Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1962 Sep;47:1219–1224. doi: 10.1093/genetics/47.9.1219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. D., Epel D. Intracellular pH and activation of sea urchin eggs after fertilisation. Nature. 1976 Aug 19;262(5570):661–664. doi: 10.1038/262661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihara M., Macnab R. M. Cytoplasmic pH mediates pH taxis and weak-acid repellent taxis of bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1209–1221. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1209-1221.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A., Guffanti A. A. Physiology of acidophilic and alkalophilic bacteria. Adv Microb Physiol. 1983;24:173–214. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60386-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W. Autodigestion of lexA and phage lambda repressors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1375–1379. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Mount D. W. The SOS regulatory system of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W. The SOS regulatory system: control of its state by the level of RecA protease. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 15;167(4):791–808. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80111-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount D. W., Low K. B., Edmiston S. J. Dominant mutations (lex) in Escherichia coli K-12 which affect radiation sensitivity and frequency of ultraviolet lght-induced mutations. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):886–893. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.886-893.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Zilberstein D., Rottenberg H. The proton electrochemical gradient in Escherichia coli cells. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Apr 1;63(2):533–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10257.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Zilberstein D., Schuldiner S. pH homeostasis in bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec;650(2-3):151–166. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(81)90004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuldiner S., Rozengurt E. Na+/H+ antiport in Swiss 3T3 cells: mitogenic stimulation leads to cytoplasmic alkalinization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7778–7782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow B., Setlow P. Measurements of the pH within dormant and germinated bacterial spores. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2474–2476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C. Mutagenesis and inducible responses to deoxyribonucleic acid damage in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Mar;48(1):60–93. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.1.60-93.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. Ultraviolet mutagenesis and inducible DNA repair in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):869–907. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.869-907.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein D., Agmon V., Schuldiner S., Padan E. Escherichia coli intracellular pH, membrane potential, and cell growth. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):246–252. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.246-252.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein D., Agmon V., Schuldiner S., Padan E. The sodium/proton antiporter is part of the pH homeostasis mechanism in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3687–3691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein D., Padan E., Schuldiner S. A single locus in Escherichia coli governs growth in alkaline pH and on carbon sources whose transport is sodium dependent. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jul 28;116(2):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80637-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



