Abstract
Upon antigen contact, epidermal Langerhans cells (LC) and dendritic cells (DC) leave peripheral organs and home to lymph nodes via the afferent lymphatic vessels and then assemble in the paracortical T cell zone and present antigen to T lymphocytes. Since splice variants of CD44 promote metastasis of certain tumors to lymph nodes, we explored the expression of CD44 proteins on migrating LC and DC. We show that upon antigen contact, LC and DC upregulate pan CD44 epitopes and epitopes encoded by variant exons v4, v5, v6, and v9. Antibodies against CD44 epitopes inhibit the emigration of LC from the epidermis, prevent binding of activated LC and DC to the T cell zones of lymph nodes, and severely inhibit their capacity to induce a delayed type hypersensitivity reaction to a skin hapten in vivo. Our results demonstrate that CD44 splice variant expression is obligatory for the migration and function of LC and DC.
Epidermal Langerhans cells (LC)1 belong to the dendritic cell (DC) family and are potent antigen-presenting cells located in the suprabasal layers of the epidermis (3, 30, 36). After antigen uptake, LC leave the epidermis and migrate into dermis, where they travel via afferent lymphatics into the regional lymph nodes to present antigen to T cells (9, 26). The mechanisms that govern their migration, entry, and movement in lymphatic vessels and subsequent homing and adhesion to distinct areas within secondary lymphatic tissues remain unidentified.
CD44 is a heterogeneous multifunctional molecule expressed by cells of different origin including immunocompetent cells (15). CD44 is encoded by a total of 20 exons, seven of which form the invariant extracellular region of the so-called standard form (CD44s). By alternative splicing, up to 10 variant exons (CD44v1–v10) can be inserted within this invariant extracellular region (37). In humans, exon v1 seems to be nonfunctional because of a stop codon (17). CD44 is involved in a variety of cellular functions. Among them are lymphocyte homing to skin and to lymph nodes (23, 33), lymphopoesis (29), and lymphocyte activation (10, 20, 39). As a major cell surface receptor for the extracellular matrix (ECM)-component hyaluronate (HA), CD44 has been shown to regulate cell migration on HA-coated substrates (2, 48, 49). Furthermore, CD44 isoforms containing variant exon v6 play a crucial role during the early phases of metastasis of rat pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells to peripheral lymph nodes (LN) (14, 38). Taken together, these findings suggest that CD44 is of central importance for physiological or pathological cell migration and cell adhesion to lymphatic tissues.
It remains unknown which CD44 isoforms are expressed on LC and which functional properties are attributed to their expression. In this study we show that CD44 isoforms are differentially modulated during the activation and migration of LC, and participate in their migration out of skin, their adhesion to the paracortical T cell zones of peripheral LN, and the LC-dependent sensitization phase of contact hypersensitivity.
Materials and Methods
Media and Chemicals
Complete-RPMI 1640 (c-RPMI) (Gibco, Eggenstein, Germany) was supplemented with 10% heat inactivated FCS (Gibco), 25 mM Hepes (Sigma Chemical Co., München, Germany), 1 mM nonessential amino acids (Gibco), 2 mM l-glutamine (Gibco), 1 nM 2-mercaptoethanol (Sigma Chemical Co.), 4 μg penicillin, and 45 μg streptomycin (Gibco). Minimal essential medium (MEM) (Gibco) was supplemented with 1.3 U/ml DNAse I (Boehringer Mannheim, Ingelheim, Germany), 10% FCS, 45 μg penicillin, and 45 μg streptomycin (both from Gibco). Organ culture medium comprised 75% DME, 25% HAMS-F12, 45 μg penicillin, 45 μg streptomycin, 10% FCS (all from Gibco).
LC and DC Isolation
Epidermal cell suspensions were generated by limited trypsinization of human skin obtained during plastic surgery (51), and from trunk skin of female C57/BL6 mice (40) (Harlan Winkelmann, Boechen, Germany). LC were enriched by density gradient centrifugation on Lymphoprep (Gibco) to 5–20% LC. Both fresh LC and LC cultured in supplemented RPMI for 48 or 72 h were analyzed by FACS®. Human DC were generated as described (35) yielding 80–90% CD1a+ cells. Murine DC were generated from C57/BL6 bone marrow as described (21).
GST Fusion Proteins
DNA fragments encoding combinations of murine CD44v exons were amplified by PCR with primers based on the murine CD44 variant sequence (49a), using cDNA synthesized from mRNA made from KLN205 cells (CRL 1453; American Type Culture Collection, Rockville, MD) as a template. These DNA fragments were cloned into pGEX vectors (43a) to create plasmids encoding GST–CD44v fusion proteins. The plasmids were introduced into DH5-α bacteria and GST–CD44v fusion protein was induced and purified as previously described (43a).
Antimurine CD44v Monoclonal Antibodies
Female DA rats were immunized with GST-CD44v4-v10 or v6–v7 fusion proteins. Hybridomas were made by using the 30% PEG spinning method (14a) to fuse SP2/0 myeloma cells to immune rat spleen cells. Hybridomas were screened for secretion of murine CD44v-specific antibodies by using the immunogen as the immobilized target in ELISA assays, in which rabbit anti–mouse antibodies coupled to horseradish peroxidase were used as the second antibody, and 2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenz-thiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt (ABTS; Sigma Chemical Co.) was used to detect antibody binding (14a). Secreted antibodies were further screened for their ability to bind to histological sections of normal murine tissue known to express CD44 variants, such as skin. The murine CD44v exon-encoded sequences recognized by positively reacting antibodies were mapped using ELISA assays. These ELISAs used fusion proteins consisting of GST fused to defined murine CD44 variant exon-encoded sequences as immobilized targets. In this way, the positively reacting antibodies 9A4 and 10D1 were shown to recognize sequences encoded by exons v6 and v4 of murine CD44, respectively. The isotypes of 9A4 and 10D1 (both IgG1, kappa) were determined using an Isostrip™ kit (Boehringer Mannheim Corp.). Purified 9A4 and 10D1 antibodies were prepared from conditioned medium as described (14a) using protein G–agarose (Dianova) as the affinity column.
Immunostaining and Flow Cytometry
Cells were stained as described (51) with one of the following mAbs: (a) human-specific pan CD44 mAbs (recognizing the NH2-terminal epitope of CD44), Leu 44 (clone L178, mouse IgG1; Becton Dickinson, Heidelberg, Germany); mAb MEM-85 (pan CD44, mouse IgG1, Monosan, Uden, The Netherlands); exon v4, 11.10 (mouse IgG1, ECACC); exon v5, VFF8 (mouse IgG1; Bender GmbH, Vienna, Austria); exon v6, VFF18 (mouse IgG1; Bender GmbH); exon v7/v8, VFF17 (mouse IgG2b; Bender GmbH); exon v9, 11.24 (mouse IgG1, ECACC); (b) murine specific: NH2terminal epitope = pan CD44, IM7 (rat IgG2b, American Type Culture Collection, Rockville, MD); exon v4, 10D1 (rat IgG1); exon v6, 9A4 (rat IgG1); isotype control, IB7 (rat IgG1; Dianova, Hamburg, Germany). Secondary antibodies: FITC-labeled goat anti–mouse (Fab)2 and goat anti–rat (Fab)2 (Dianova). Treatment with secondary antibody was followed by a 10-min incubation in 2% normal murine or rat serum, and subsequently by incubation with PE-labeled HLA-DR–specific mAb (L234, mouse IgG1; Becton Dickinson) or Iab (mouse IgG2b; PharMingen, Hamburg, Germany) or appropriate nonreactive PE-labeled control Ab (Dianova). Human DC were identified by FITC-conjugated mAb against CD1a (Okt-6, mouse IgG1, Ortho). 7-Aminoactinomycin D (2.5 μg/ml; Sigma) was added to exclude dead cells by appropriate gating. Cell Quest software (Becton Dickinson) was applied to analyze 104 HLA-DR+, CD1a+, or Iab+ viable cells each and to calculate mean fluorescence intensity.
Electron Microscopy
Skin specimen cultured for time periods mentioned were fixed for 12 h at 4°C in 3% cacodylate-buffered glutaraldehyde at pH 7.4 and then transferred to a 5% sucrose solution. Postfixation was performed with 1% osmium tetroxide and potassium ferricyanide. The specimens were washed with distilled water, dehydrated in graded alcohols, and embedded in araldit resin. Ultrathin sections of 50 nm were cut, placed on copper grids, stained with uranyl acetate and lead citrate, and examined on an electron microscope (model CM10; Philips, Eindhoven, The Netherlands) at 80 kV.
Full-Thickness Skin Organ Culture
4-mm punch biopsies containing dermis and epidermis were placed into 25mm tissue culture inserts with a 0.02-μm anopore membrane (Nunc Inc., Naperville, IL) and incubated in six-well tissue culture plates filled with supplemented DME/HAMS-F12 up to the dermal–epidermal junction. Cultures were terminated as indicated, and samples were shock-frozen in N2. Immunofluorescence double labeling was performed as described previously (32, 41). Sections (5 μm) were prepared with a Cryocut 1800 (Leica, Benzheim, Germany). First, sections were incubated with Lag mAb for 30 min (room temperature) followed by FITC-conjugated F(ab), goat anti– mouse IgG (H+L) (Dianova) overnight at 4°C. In a second step, sections were overlaid with mAb against CD44v (Leu44, MEM-85, VFF8, VFF18, VFF17, 11.24) for 30 min (room temperature), followed by a Cy3-conjugated goat F(ab)2 anti–mouse IgG (H+L) antibody for 4 h at 4°C. The following controls were performed: As control for type II interference (binding of the second step anti–mouse Ab to the mouse Ab of the first step), sections were stained with first step murine mAb, followed by unconjugated F(ab) goat anti–mouse IgG (H+L) (Dianova). Subsequently, sections were overlaid with Cy3-conjugated goat F(ab)2 anti–mouse IgG (H+L), revealing no staining at incubation times indicated above. Staining was evaluated with a microscope (model Axioskop; Carl Zeiss, Inc., Göttingen, Germany), equipped with a MC100 camera system. For quantitative analysis of total and CD44+/Lag+ double-positive LC, five highpower fields were counted and LC/mm2 was quantified as mentioned in the text.
Split Thickness Organ Culture
2 × 2-cm split thickness skin containing epidermis plus papillary dermis was prepared by dermatome (Aesculap, Tuttlingen, Germany) (34) and floated on supplemented RPMI in six-well plates (Greiner). After 48 h, cells that had migrated into the culture medium were collected. Staining with FITC-conjugated mAbs against CD1a and FACS® was performed as described above. All cells obtained from one well (5–6 × 105) were analyzed. The percentage of CD1a+ cells was calculated by Cell Quest software (Becton Dickinson). The percentage of emigrating LC from untreated samples was defined as 0% inhibition.
Lymph Node Adhesion Assay
LC or DC enriched by MACS (Miltenyi Biotec, Bergisch Gladbach, Germany) (43) with antibodies to HLA-DR or CD1a, were tested for frozensection lymph node adhesion as described (7). 10-μm fresh cryosections of human axillary lymph nodes were mounted on glass slides and blocked with RPMI containing 1% BSA (7°C, 1 h). LC or DC were suspended in HBSS/1% BSA (2 × 106/ml) and layered over the cryosections at room temperature (40 min). Slides were gently rinsed with HBSS and then fixed in acetone (4°C, 10 min). For antibody blocking, LC or DC were preincubated with mAbs MEM-85 (pan CD44, mouse IgG1), SFF-2 (pan CD44, mouse IgG1), with v exon–specific antibodies (v5, VFF-8; v6, VFF-18; v9, 11.24), ICAM-1 mAb 84H10 (anti–ICAM-1, mouse IgG1; Immunotech, Hamburg, Germany), RR1 (anti–ICAM-1, mouse IgG1, kind gift of Dr. T.A. Springer, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA) or control IgG1 (20 μg/ml, 30 min, 4°C). The slides were then stained with anti-CD1a mAb and coded and evaluated by two independent investigators. Background binding of cultured LC/DC did not exceed 1.5 cells/mm2, and positive binding was >30 cells/mm2. Data are presented as percent binding compared to samples without antibodies. SD was calculated from three slides each with nine random fields/slide using an optical grid (10× magnification).
Contact Hypersensitivity
6-wk-old female C57/BL6 mice (Harlan Winkelmann) were painted on their abdominal skin with 20 μl 0.5% 2,4-dinitro-1-fluorobenzene (DNFB; Sigma Chemical Co.) in acetone at days 0 and 1 (42). On day 6, mice were challenged by painting 10 μl 0.2% DNFB on both sides of the right ear. Ear thickness was measured with an engineer's micrometer (Mitutoyo GmbH, Neuss, Germany) before and at 24, 48, and 72 h after the challenge (42). For histology, ears were excised 24 h after challenge, fixed in formaldehyde, paraffin-embedded, sectioned, and counter-stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Photographs were taken with a camera system (model MC100; Olympus, Hamburg, Germany). Group 1 mice were either challenged only or sensitized and challenged in the absence of mAbs. Injection of mAbs (i.p.) was performed as follows: Group 2 mice received 300 μg at day −1, 100 μg each at days 0 and 1, with respect to hapten application during sensitization. Group 3 mice received 300 μg at day 5 and 100 μg each at days 6 and 7.
Results
In Vitro–activated LC and DC Upregulate pan CD44 and CD44 Variant Isoforms
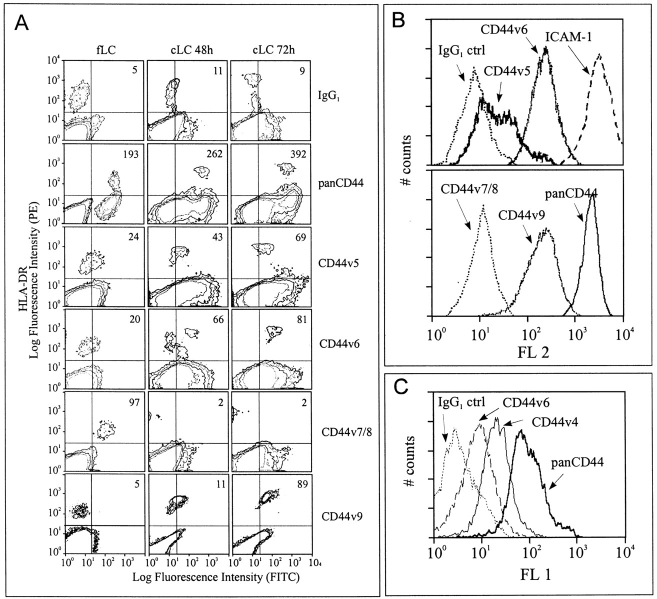
To determine whether LC express CD44 and whether this expression is altered by activation, we transferred LC freshly isolated from human epidermis into tissue culture. This procedure mimics LC activation by antigen in vivo (36). Cells were stained with mAbs against HLA-DR to identify LC and with mAbs against CD44 epitopes. HLADR+ freshly isolated LC expressed an NH2-terminal epitope of CD44 (termed pan CD44) and an epitope formed jointly by CD44 exons v7 and v8 (Fig. 1 A). Epitopes encoded by exons v5 and v6 were only weakly expressed, while epitopes encoded by exons v4, v9, and v10 were not detectable (Fig. 1 A and data not shown). LC cultured for 48 and 72 h carried enhanced levels (twofold) of the NH2-terminal epitope. The epitopes of v4, v5, v6, and v9 were also markedly upregulated (Fig. 1 A and not shown). In contrast, the CD44v7/8 epitope was lost during culture (Fig. 1 A). A CD44v10 epitope was not detectable (data not shown).
Figure 1.
Change in CD44 epitope expression during in vitro cultivation of epidermal LC and blood DC. (A) Human LC freshly isolated and after 48 and 72 h of culture and (C) mouse DC generated from C57/BL6 bone marrow were stained with mAbs against HLA-DR or Iab, 7-aminoactinomycin-D, and mAbs directed against CD44 epitopes. Mean fluorescence intensity of viable and HLA-DR+ cells was determined by FACScan® and is shown in the upper right corner of each graph. Data is representative for six independent experiments. Low expression of CD44v epitopes on freshly isolated LC was not caused by the trypsinization used during the isolation procedure, since identical trypsinization of cultured LC did not affect their CD44v expression significantly (not shown). (B) Corresponding analysis of DC generated from human peripheral blood monocytes gated for CD1a. Data is representative for four independent experiments.
LC belong to the family of dendritic cells (45). To determine whether DC from other sources express similar CD44 isoforms as LC, DC were prepared from human peripheral blood by culture in a cytokine cocktail (35). Determination of CD44 isoforms on DC revealed strong expression of panCD44 (Fig. 1 B) and epitopes of CD44v5, v6, and v9 (Fig. 1 B), whereas the v7/8 epitope was not detected (Fig. 1 B). Our data thus revealed CD44 epitope patterns identical to those on cultured LC. A very similar CD44 pattern also occurred in cultured LC and DC from C57/Bl6 murine skin or bone marrow with expression of pan CD44 epitopes and epitopes encoded by CD44v4 and v6 (Fig. 1 C and not shown).
CD44 Isoform Expression on Migrating LC
To explore at what stage LC acquire altered expression of CD44 epitopes during migration, we made use of a skin explant culture in which LC move actively from epidermis into dermis. The migration of LC was assessed by quantifying the number of Lag+ cells (mAb Lag stains Birbeck granules, specific cytoplasmic organelles of LC [24]) within epidermis and dermis after various culture intervals of skin explants. At 0 h, almost all Lag+ cells were located in the suprabasal layers of the epidermis with very few Lag+ cells detectable in the dermis. After 72 h of culture, almost half of the LC had left the epidermis, which, however, was never depleted completely of LC (Table I). This LC emigration was further investigated at the ultrastructural level by transmission EM (Fig. 2). As early as 2 h after culture, epidermal LC, identified by their characteristic intracytoplasmic Birbeck granules, had started their migration (Fig. 2, A and B) and at 12 h were found to penetrate the basement membrane of the epidermo–dermal junction. After 24 h, LC accumulated in the dermis in cordlike structures within lymphatic vessels (Fig. 2, C and D).
Table I.
CD44v Expression on Lag+ Epidermal and Dermal Langerhans Cells after Different Culture Intervals of Full-Thickness Skin Explants
| Epidermis | Dermis | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Culture period | *Number of Lag+ | ‡CD44v5+ | ‡CD44v6+ | ‡CD44v9+ | *Number of Lag+ | ‡CD44v5+ | ‡CD44v6+ | ‡CD44v9+ | ||||||||
| h | cells/mm2 | % | % | % | cells/mm2 | % | % | % | ||||||||
| 0 | 985.7 | 0 | 4.2 | 7.8 | 30.6 | 100 | 100 | 80.0 | ||||||||
| 2 | 927.4 | 0.9 | 2.8 | 6.4 | 67.3 | 95.5 | 91.6 | 83.4 | ||||||||
| 6 | 927.4 | 0 | 1.3 | 6.5 | 67.3 | 94.5 | 94.1 | 88.9 | ||||||||
| 12 | 768.4 | 2.7 | 5.1 | 7.2 | 84.6 | 88.1 | 89.0 | 83.3 | ||||||||
| 24 | 756.1 | 0 | 3.7 | 5.6 | 84.6 | 88.9 | 100 | 75.0 | ||||||||
| 48 | 675.0 | 0.7 | 5.9 | 10.7 | 76.5 | 92.3 | 96.3 | 91.0 | ||||||||
| 72 | 609.2 | 0.7 | 2.9 | 7.1 | 102.6 | 87.5 | 100 | 91.0 | ||||||||
Full-thickness skin organ culture and immunohistochemistry was performed as described in Fig. 3.
CD44v positive and negative Lag+ cells were counted in 10 high power fields and the percentage of double-positive cells was calculated. The data represent the mean of four independent experiments, the SD being below 10%.
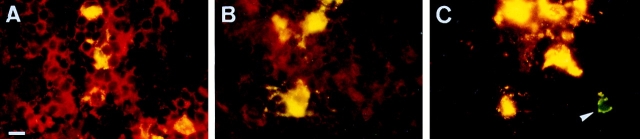
Figure 2.
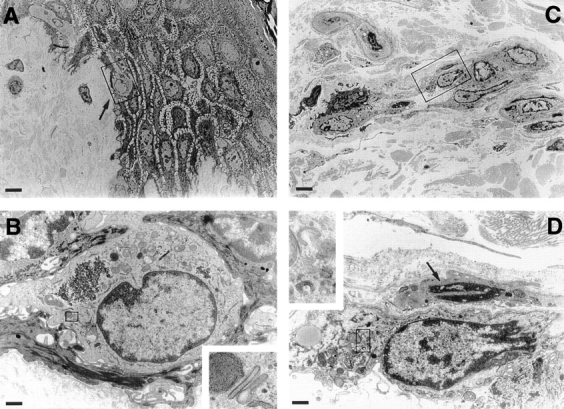
Transmission electron microscopy of LC migrating in skin organ cultures. Skin organ cultures were performed as described in Materials and Methods. 4-mm skin punch biopsies were cultured in Nunc filters for 12 h and examined by electron microscopy. (A) After 12 h of culture, an LC with a multilobulated nucleus is migrating across the dermo-epidermal junction (arrow). (B) High magnification of the same LC shown in the box in A. (Inset) Magnified from the area delineated by the box: Birbeck granules. (C) LC form cordlike structures within dermal lymphatic vessels after 24 h of culture. (D) High magnification of an LC in lymphatic vessel identified by a single layer of endothelial cells with protruding nuclei (arrow). (Inset) Magnified from the area delineated by the box: Birbeck granule remnants. Bars: (A and C) 6 μm; (B and D) 0.8 μm.
By immunohistochemical double labeling with mAb Lag (FITC, green) and CD44-specific mAbs (Cy3, red), we followed CD44 expression on LC during migration. Double staining appears as yellow. Keratinocytes stained red since they carry several CD44 epitopes (CD44v3–v10) (18, 19) but not the Lag epitope. Most intraepidermal LC expressed NH2-terminal epitopes and the epitope encoded by v7/8, whereas only few (⩽5%) of them showed staining with antibodies to epitopes encoded by exons v5, v6, or v9 (Fig. 3, A–C, E, and G). In contrast, the majority of LC that had migrated into the dermis (87.5–100%) expressed v5, v6, and v9 epitopes (Fig. 3, D, F, and H). Thus, the change in epitope presentation apparently occurs with the transition from epidermis to dermis.
Figure 3.
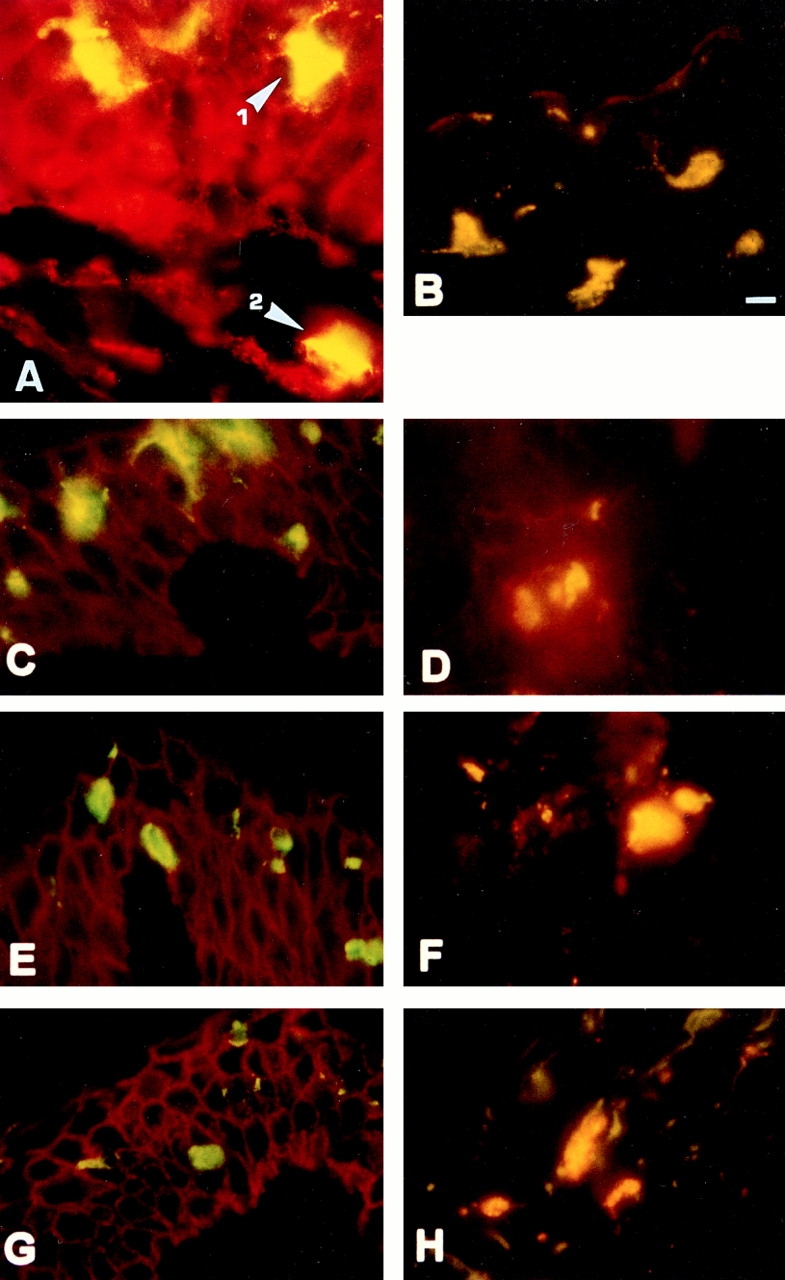
CD44 expression pattern on LC migrating from epidermis into dermis. Cryosections of skin cultured for 12 h were stained with Lag mAb followed by secondary FITC-conjugated F(ab), goat anti–mouse IgG (H+L) to detect LC (green), and CD44 mAbs followed by a Cy3-conjugated goat F(ab)2 anti–mouse IgG (H+L) antibody (red). Double-positive cells appear yellow-orange. (A) Staining with Lag and anti–pan CD44. Lag+ cells within the epidermis (1) and those that migrated into the dermis (2) stained double positive for Lag and pan CD44 (yellow). Keratinocytes express pan CD44 but not Lag (red). Lag+ intra-epidermal LC also express the epitope created by exons v7/v8 (B) but very low levels of CD44 exon v5 (C), v6 (E), and v9 (G) epitopes. Lag+ cells that migrated into dermis express CD44v5 (D), v6 (F), and v9 (H). (I and J) LC that had migrated from split thickness skin were gated for CD1a expression, stained with the mAbs indicated, and analyzed by FACS® as in Fig. 1. Bar, 10 μm.
These findings were confirmed and extended using the method described by Pope et al. (34) to examine LC that had migrated completely out of the skin. Split thickness keratome skin was floated on culture medium. After 48 h, LC were collected from the medium and their CD44 pattern was analyzed by triple color FACS® analysis. These LC carried epitopes of the CD44 NH2 terminus, v5, v6, and v9, but not v7/8 (Fig. 3, I and J). Thus the CD44 phenotype of migrating LC matched exactly that of in vitro– activated LC or DC.
To track LC migration further, we identified LC that had traveled via lymphatic vessels to the regional lymph nodes in cryosections of axillary lymph nodes. Lag+ cells were found in the paracortical T cell zones of the lymph node and the majority expressed the CD44 NH2 terminus (Fig. 4 A), epitopes of exons v4, v5, v6 (Fig. 4 B and data not shown), and v9 (Fig. 4 C), but not the v7/8 epitope (not shown). We conclude that the CD44 expression pattern acquired during emigration from the epidermis is maintained until LC have reached the lymph node.
Figure 4.
CD44 expression on LC that have homed to LN. Cryosections of axillary LN were stained as described above. (A) Pan CD44 staining of Lag+ cells (yellow) located in the paracortical T cell areas of axillary lymph nodes draining the skin. T cells also express CD44 but no Lag (red). (B) Lag-positive cells express exon v5 epitope. (C) Exon v9 epitope is expressed on the majority (yellow) but not all (arrow, green) LC. Bar, 10 μm.
CD44 Isoforms Serve a Functional Role in LC Migration Out of Skin and LC Adhesion to LN
We next used anti-CD44 mAbs to determine the functional relevance of CD44 protein expression. To check for CD44 function during LC migration, the anti-CD44 NH2terminal antibodies MEM-85 (blocks HA binding [6]) and SFF2 (does not block HA binding; Weiss, J.M., C.C. Termeer, H. Dittmar, and J.C. Simon, unpublished results), and v5-, v6-, or v9-specific mAbs were injected into the dermis of skin punch biopsies (Fig. 5 A) or added to the medium of floating split thickness keratome skin (Fig. 5, B and C). LC remaining in the epidermis (punch biopsies) or LC appearing in the medium (keratome skin) were counted by microscopy and FACS®, respectively. LC were arrested in the epidermis by two NH2-terminal–specific antibodies (60–80% inhibition) (Fig 5, A–C) but not by v exon–specific mAbs (Fig. 5 C). Other antibodies recognizing the NH2 terminus were also inhibitory (not shown), while the antibody against the v7/v8 epitope was not (Fig. 5 C).
Figure 5.
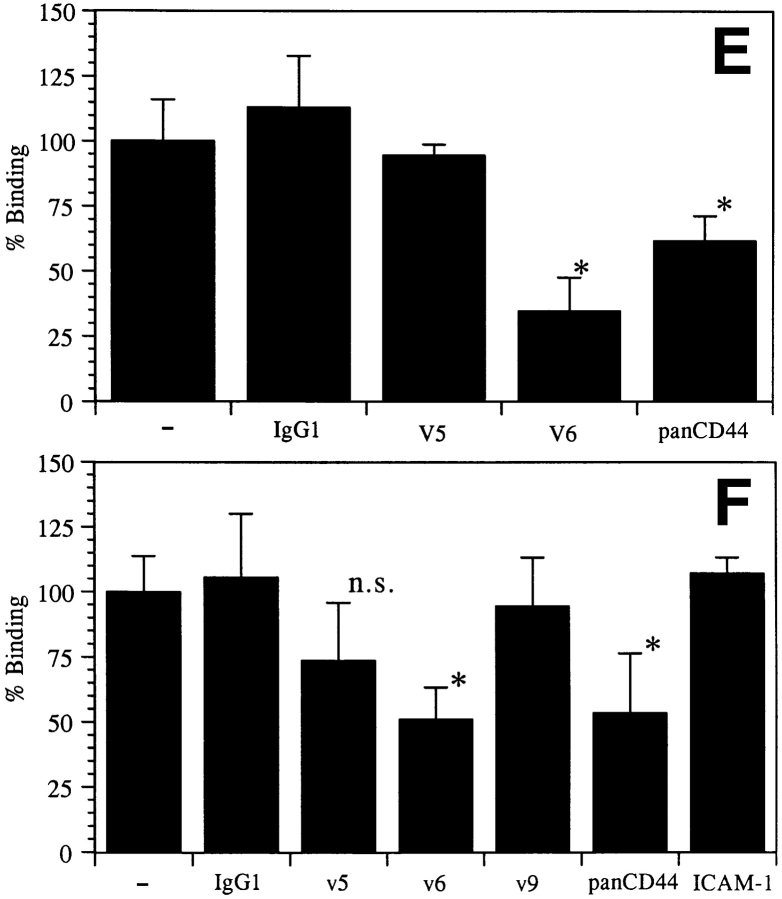
Antibodies to the CD44 NH2 terminus prevent LC activation and migration. (A) Photomicrograph of punch biopsies injected with IgG1 control or mAb MEM-85. CD1a-positive LC are labeled green. The dotted line indicates the dermo–epidermal junction. Arrow indicates a cord of emigrated LC within dermis. (B) Addition of MEM-85 or control mAb to split thickness skin cultures. The cells that had migrated out of split thickness skin into the medium were analyzed by FACS®. CD1a+, viable (PInegative) LC are circled. The fraction of these cells over total cell number is shown as percentage in the upper left corner of each graph. The CD1a− keratinocytes were forced into suspension by dermatome manipulation. (C) Inhibition of LC emigration into the medium by various anti-CD44 antibodies. Percent inhibition was calculated from five independent experiments (±SD; *statistically significant at P < 0.05, one way analysis of variance (ANOVA), Dunnett's test, SigmaStat; Jandel Scientific Software, Corte Madern, CA).
Since LC within the paracortical zones of LN were found to express high levels of pan CD44 epitopes and epitopes encoded by CD44v5, v6, and v9, we determined whether these isoforms are of functional relevance for the capacity of LC to adhere to LN. MACS-purified fresh or 48-h cultured LC were used in an LN frozen section binding assay. LC were identified by counterstaining with a CD1a mAb and specific adherence to LN was determined microscopically. Freshly isolated LC, like immature DC generated from peripheral blood, showed only weak binding to lymph node cryosections (Fig. 6 A and data not shown). By contrast, cultured LC and cytokine-activated DC adhered specifically and at enhanced efficiency to the paracortical T cell areas but not to the central follicular B cell area (Fig. 6, B and C). Preincubation with the CD44v6specific VFF18 mAb significantly inhibited the binding of cultivated LC (by 66%) and DC (by 49%) to the T cell zones (Fig. 6, D and E). The MEM-85 mAb also inhibited binding, although less efficiently. Other antibodies recognizing the NH2 terminus of CD44 or mAbs directed against other v exon epitopes or against ICAM-1, although expressed abundantly, had no effect (Fig. 6, D and E).
Figure 6.
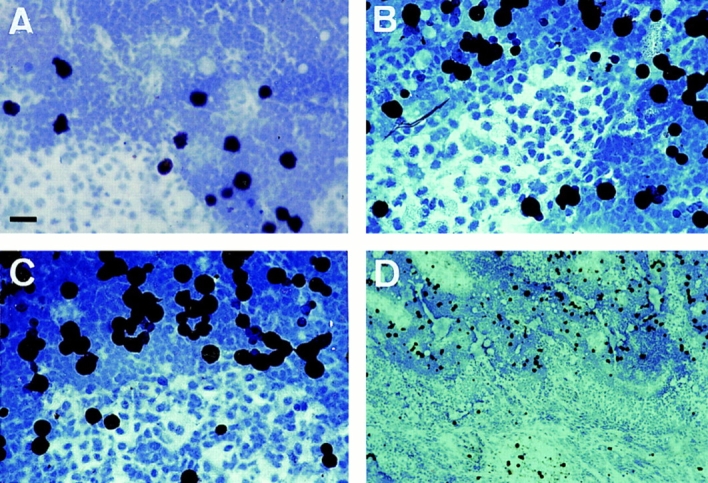
The binding of LC or DC to paracortical lymph node areas is inhibited by antibodies to CD44. Microbead-purified fresh LC (A), LC cultivated for 48 h (B and E), or cytokine-activated DC (C, D, and F) were layered on frozen sections of lymph node. LC and DC adhered preferentially to the paracortical T cell areas, with enhanced adhesion upon activation by culture, and not to the central B cell follicles. The binding was also assayed in the presence of antibodies (quantified in E and F; *statistically significant at P < 0.05, one way ANOVA, Dunnett's test). Representative for four independent experiments. Bar: (A–C) 10 μm; (D) 100 μm.
CD44 Isoforms Serve a Functional Role in Antigen Presentation by LC
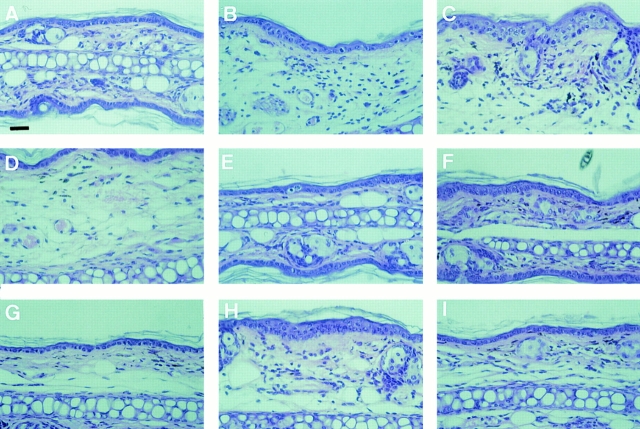
The ultimate test of LC function addresses their role in vivo in presenting an antigen encountered in skin to T cells within LN. This can be tested by the induction of delayed type hypersensitivity (DTH) against an epicutaneously applied hapten. The DTH response segregates into a sensitization and a challenge phase (12). The sensitization phase describes a set of events that occur after the first application of a hapten to skin. Within the epidermis, the hapten is picked up by LC, which then migrate into the regional LN where they present the hapten to specific T cells. During the challenge phase, the same hapten is reapplied and induces a local inflammatory response, which is dependent on leukocyte extravasation into the application site, but does not require LC (4, 13). To test the function of CD44 epitopes in DTH, mice were sensitized epicutaneously to the hapten DNFB on days 0 and 1, which upon challenge with the same hapten to ear skin at day 6 results in a massive DTH reaction measured by ear swelling, peaking at 24 h after challenge and declining during the next 72 h (Fig. 7, Group 1; Fig. 8 B). Anti-CD44 mAbs were injected i.p. at days −1, 0, and +1 with respect to hapten application (to test for interference with the sensitization phase of DTH) or at days 5, 6, and 7 (to test for an interference with the challenge phase). Antibodies to the NH2 terminus of CD44 and to the v6 epitope inhibited the challenge phase of DTH resulting in a delayed onset of DTH as reported for the pan CD44 mAb previously (8) (Fig. 7, Group 3). Most importantly, only the CD44v4 and v6, but not pan CD44 or control mAbs, inhibited markedly the sensitization phase requiring LC migration from epidermis to lymph nodes and hapten presentation (Fig. 7, Group 2). Furthermore, injection of anti-v6 and -v4 mAbs during sensitization or challenge did not delay the onset of DTH. These findings were confirmed and extended by histological examination of the challenge sites (Fig. 8). When injected during the sensitization phase, only anti-v4 and -v6 mAbs reduced tissue oedema and the influx of leukocytes into the dermis, while pan CD44 or control mAb had no effect (Fig. 8, B and D–F). When injected during the challenge, pan CD44 and anti-v6 mAb delayed the influx of leukocytes into the dermis, anti-v4 and IgG control mAb did not affect the DTH response significantly. These data suggest that CD44 splice variant expression is of key importance for the capacity of LC to induce a DTH response against epicutaneously applied haptens. During this sensitization phase, CD44 variants may play an essential role either during LC migration to LN or during their interaction with T cells. During the challenge phase, CD44 NH2terminal and v6 epitopes appear to be required for leukocyte extravasation into the site of hapten challenge.
Figure 7.
Antibodies to CD44v epitopes inhibit the sensitization phase of contact hypersensitivity in vivo. Group 2 mice were treated with mAbs i.p. as indicated both before and during sensitization, and group 3 mice were treated similarly before and during challenge. Mice in group 1 were not treated with mAbs. *Statistically significant reduction of ear swelling at P < 0.05 (one way ANOVA, Dunnett's test). Each bar represents mean ear swelling data pooled from eight animals measured 24, 48, and 72 h after challenge.
Figure 8.
Histology of DTH ear swelling response following anti-CD44 mAb injection. Mouse ears were excised 24 h after DNFB challenge, fixed in formaldehyde, embedded in paraffin, sectioned, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Mice were treated as follows: (A) unsensitized, (B) IgG control mAb injection during sensitization, (C) IgG control mAb injection during ear challenge, (D) panCD44 mAb injection during sensitization, (E) CD44v4 mAb injection during sensitization, (F) CD44v6 mAb injection during sensitization, (G) pan CD44 mAb injection during challenge, (H) anti-CD44v4 mAb injection during challenge, and (I) anti-CD44v6 mAb injection during challenge. Bar, 50 μm.
Discussion
In this study we demonstrate that LC and DC during in vitro activation and during their in vivo migration to the peripheral LN differentially upregulate pan CD44 epitopes and sequences encoded by variant exons CD44v4, v5, v6, and v9. Thus LC and DC activation or migration is accompanied by increased synthesis of CD44 and by a change of either epitope accessibility or splicing. The mechanisms underlying this change remain to be elucidated: granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF), tumor necrosis factor-α, and interleukin-1β, secreted by keratinocytes in response to antigen application to the skin, play a role in LC-maturation, emigration, and accumulation in LN (9, 11, 16). Furthermore, the generation of activated DC from peripheral blood precursors depends upon the presence of GM-CSF (35). However, at present we have no evidence that GM-CSF and tumor necrosis factorα are involved in CD44 modulation by LC or DC, since biologically active mAbs neutralizing these cytokines added during culture had no effect (not shown). Another possibility is that the change in CD44 isoform expression occurs when LC or DC encounter new ECM components during their migration to the lymph node. In fact, in skin explants we only observed upregulation of CD44 variant exon sequences after LC had penetrated the basement membrane of the epidermo–dermal junction.
We have shown that LC emigration from the epidermis is inhibited by mAbs against the NH2 terminus of CD44. In contrast, mAb directed against CD44 variant epitopes encoded by exons v5, v6, v7/8, or v9 had no effect. These results suggest that CD44 epitopes within the NH2 terminus of CD44 are involved in a very early stage of intraepidermal LC activation required for their emigration out of skin. Once LC are activated and express epitopes encoded by CD44 variant exons, antibodies recognizing pan CD44 epitopes cannot interfere with their emigration. At present, we can only speculate on the mechanisms by which pan CD44 mAb inhibits LC migration. CD44 is the major ligand for HA (2, 46), and LC emigration could be partially inhibited by mAb MEM-85, which is known to block CD44–HA interactions (6). We hypothesize that upregulation of CD44 epitopes involved in HA binding could facilitate LC movement along HA structures within the dermis. However, mAbs SFF-2 and BU52, which do not affect HA binding, also blocked, raising the possibility that these mAbs interfere with the binding of other CD44 ligands involved in cell migration such as osteopontin (50), bFGF, MIP-1β (5, 47), or the N-linked blood group Ag (27). These mAbs may also alter the clustering of CD44 on the cell surface, thereby disturbing formation and stabilization of the cell–ECM attachments essential for migration (28).
Expression of distinct CD44 isoforms is also of functional relevance for the homing of lymphocytes or tumor cells to lymphatic tissues (15). Monoclonal Abs against pan CD44 epitopes interfere with the homing of nontransformed lymphocytes or lymphoma cells to peripheral lymph nodes (22, 33, 52). CD44 isoforms containing v6 epitopes are required for the initial phase of lymphogenic spread of rat pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell lines (14, 38). In humans, a high potential for lymphogenic metastasis of non-Hodgkin lymphomas has been linked to expression of CD44v6 exon sequences (25, 44). Here we demonstrate that the ability of LC and DC to home to peripheral LN is related to the expression of CD44 variant exon v6 encoded isoforms. Specifically, LC freshly isolated from skin and immature DC from peripheral blood, which do not express CD44v exon–encoded sequences, showed low specific binding to LN. In contrast, after upregulation of CD44v exon–containing isoforms, cultured LC or DC strongly adhered to the marginal sinus and the paracortical T cell areas but not to the central B cell follicle or the LN medulla. Preincubation with CD44v6-specific mAb significantly inhibited this binding to the T cell zones. The pan CD44 mAb MEM-85 also inhibited binding, although less efficiently, while other antibodies recognizing the NH2 terminus of CD44, or directed against other v exon epitopes or ICAM-1, had no effect. The data with the anti-v6 mAbs suggest that CD44 mediates the binding of LC and DC to an unidentified partner in the T cell zone of lymph nodes. The effect of MEM-85 may indicate a role of binding to HA (which is presumably not confined to T cell zones) or more likely to the same partner affected by the anti-v6 mAb.
We have shown that LC use a differential modulation of CD44 isoforms for adhesion to T cell zones in LN, suggesting that such modulation is of central importance for their ability to induce primary T cell responses within that LN. We also show that CD44 isoform expression by LC is of relevance for their capacity to induce a DTH response to epicutaneously applied hapten. We found that v4- and v6specific antibodies strongly inhibited sensitization, which is dependent upon LC migration and LN homing. The interference of anti-CD44v6 antibodies with LC function may partly explain their effect on primary immune responses (1, 31). We conclude that CD44 variants play an essential role in LC function, either during migration to the lymph nodes or in the interaction with T cells during sensitization. In contrast, antibodies to the NH2 terminus of CD44 and to the v6 epitope delayed the extravasation phase of DTH. Inhibition by NH2-terminal CD44 antibodies of the extravasation phase of DTH has been reported earlier (8). The inability of NH2-terminal–specific antiCD44 antibodies to inhibit LC activation in the epidermis during the sensitization phase as they can in vitro is probably either due to basement membrane barriers that prevent efficient entry of antibody into the epidermis after systemic application (8) or due to functional differences of the CD44 mAbs used in the in vitro and in vivo assays.
In conclusion, we have demonstrated that during in vitro activation as well as during their migration to peripheral lymph nodes, LC and DC upregulate pan CD44 epitopes and sequences encoded by CD44 variant exons. These CD44 proteins play an essential role in LC and DC function since mAbs against different CD44 epitopes inhibit the migration of LC out of skin, the adhesion of LC and DC to LN T cell areas and the capacity of LC to initiate a DTH response to epicutaneously applied hapten. The interesting parallel of LC and DC behavior with the lymphatic spread of metastasizing tumor cells and the inhibition of both by anti-CD44v6 antibodies strongly suggests a similar role for CD44 in both processes. We propose that selection for and mimicry of the molecular function of CD44 on LC and DC occurs during tumor progression.
Acknowledgments
We thank Brigit Mai and Anke Stingl for expert technical assistance and Dr. Imamura (Kyoto University, Japan), Dr. Jalkanen (University of Turku, Finland), and Dr. Adolf (Bender GmbH, Vienna, Austria) for the gift of mAbs. IL-4 and GM-CSF were kind gifts of Schering-Plough Corp. (Kenilworth, NJ). We are grateful to Prof. Margot Zöller for her assistance at the beginning of the project to make the antimurine CD44v antibodies and to Anja Steffan for technical assistance.
This work was supported by grants from the Bundesministerium für Bildung, Wissenschaft, und Forschung (BMBF 01 GB 9405), the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG Si 397/2-3), and the European Community (EVSV-CT 940563).
Abbreviations used in this paper
- ANOVA
analysis of variance
- CD44v
CD44 variant
- DC
dendritic cells
- DTH
delayed type hypersensitivity
- ECM
extracellular matrix
- GM-CSF
granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor
- HA
hyaluronate
- LC
Langerhans cells
- LN
lymph nodes
- MFI
mean fluorescence intensity
Footnotes
Address all correspondence to Johannes M. Weiss, Department of Dermatology, University of Freiburg, Hauptstrasse 7, D-79104 Freiburg, Germany. Tel.: 49 761-270-6831. Fax: 49 761-270-6829.
References
- 1.Arch R, Wirth K, Hofmann M, Ponta H, Matzku S, Herrlich P, Zoller M. Participation in normal immune responses of a metastasis- inducing splice variant of CD44. Science (Wash DC) 1992;257:682–685. doi: 10.1126/science.1496383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Aruffo A, Stamenkovic I, Melnick M, Underhill CB, Seed B. CD44 is the principal cell surface receptor for hyaluronate. Cell. 1990;61:1303–1313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90694-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Austyn JM. New insights into the mobilization and phagocytic activity of dendritic cells. J Exp Med. 1996;183:1287–1292. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.4.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Becker D, Knop J. Mechanism in allergic contact dermatitis. Exp Dermatol. 1993;2:63–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.1993.tb00010.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bennett KL, Jackson DG, Simon JC, Tanczos E, Peach R, Modrell B, Stamenkovic I, Plowman G, Aruffo A. CD44 isoforms containing exon V3 are responsible for the presentation of heparin-binding growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1995;128:687–698. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.4.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bennett KL, Modrell B, Greenfield B, Bartolazzi A, Stamenkovic I, Peach R, Jackson DG, Spring F, Aruffo A. Regulation of CD44 binding to hyaluronan by glycosylation of variably spliced exons. J Cell Biol. 1995;131:1623–1633. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.6.1623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Butcher EC, Scollay RG, Weissman IL. Lymphocyte adherence to high endothelial venules: characterization of a modified in vitro assay, and examination of the binding of syngeneic and allogeneic lymphocyte populations. J Immunol. 1979;123:1996–2003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Camp RL, Scheynius A, Johansson C, Pure E. CD44 is necessary for optimal contact allergic responses but is not required for normal leukocyte extravasation. J Exp Med. 1993;178:497–507. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.2.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cumberbatch M, Fielding I, Kimber I. Modulation of epidermal Langerhans' cell frequency by tumour necrosis factor-α. Immunology. 1994;81:395–401. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Denning SM, Le PT, Singer KH, Haynes BF. Antibodies against the CD44 p80, lymphocyte homing receptor molecule augment human peripheral blood T cell activation. J Immunol. 1990;144:7–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Enk AH, Katz SI. Early molecular events in the induction phase of contact sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992;89:1398–1402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Enk AH, Katz SI. Contact sensitivity as a model for T-cell activation in skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1995;105:80S–83S. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12316112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Grabbe S, Steinbrink K, Steinert M, Luger TA, Schwarz T. Removal of the majority of epidermal Langerhans cells by topical or systemic steroid application enhances the effector phase of murine contact hypersensitivity. J Immunol. 1995;155:4207–4217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gunthert U, Hofmann M, Rudy W, Reber S, Zoller M, Haussmann I, Matzku S, Wenzel A, Ponta H, Herrlich P. A new variant of glycoprotein CD44 confers metastatic potential to rat carcinoma cells. Cell. 1991;65:13–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90403-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14a.Harlow, E., and D. Lane. 1988. Antibodies: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
- 15.Herrlich P, Zoller M, Pals ST, Ponta H. CD44 splice variants: metastases meet lymphocytes. Immunol Today. 1993;14:395–399. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90141-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Heufler C, Koch F, Schuler G. Granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interleukin 1 mediate the maturation of murine epidermal Langerhans cells into potent immunostimulatory dendritic cells. J Exp Med. 1988;167:700–705. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hirano H, Screaton GR, Bell MV, Jackson DG, Bell JI, Hodes RJ. CD44 isoform expression mediated by alternative splicing: tissue-specific regulation in mice. Int Immunol. 1994;6:49–59. doi: 10.1093/intimm/6.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hofmann M, Rudy W, Gunthert U, Zimmer SG, Zawadzki V, Zoller M, Lichtner RB, Herrlich P, Ponta H. A link between ras and metastatic behavior of tumor cells: ras induces CD44 promoter activity and leads to low-level expression of metastasis-specific variants of CD44 in CREF cells. Cancer Res. 1993;53:1516–1521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hudson DL, Sleeman J, Watt FM. CD44 is the major peanut lectin-binding glycoprotein of human epidermal keratinocytes and plays a role in intercellular adhesion. J Cell Sci. 1995;108:1959–1970. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.5.1959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Huet S, Groux H, Caillou B, Valentin H, Prieur AM, Bernard A. CD44 contributes to T cell activation. J Immunol. 1989;143:798–801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Inaba K, Inaba M, Romani N, Aya H, Deguchi M, Ikehara S, Muramatsu S, Steinman RM. Generation of large numbers of dendritic cells from mouse bone marrow cultures supplemented with granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Exp Med. 1992;176:1693–1702. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.6.1693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Jalkanen, S., R.F. Bargatze, J. de los Toyos, and E.C. Butcher. 1987. Lymphocyte recognition of high endothelium: antibodies to distinct epitopes of an 85–95-kD glycoprotein antigen differentially inhibit lymphocyte binding to lymph node, mucosal, or synovial endothelial cells. J. Cell Biol. 105:983–990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 23.Jalkanen S, Saari S, Kalimo H, Lammintausta K, Vainio E, Leino R, Duijvestijn AM, Kalimo K. Lymphocyte migration into the skin: the role of lymphocyte homing receptor (CD44) and endothelial cell antigen (HECA-452) J Invest Dermatol. 1990;94:786–792. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12874646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kashihara M, Ueda M, Horiguchi Y, Furukawa F, Hanaoka M, Imamura S. A monoclonal antibody specifically reactive to human Langerhans cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1986;87:602–607. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12455849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Koopman G, Heider KH, Horst E, Adolf GR, van den Berg F, Ponta H, Herrlich P, Pals ST. Activated human lymphocytes and aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphomas express a homologue of the rat metastasis-associated variant of CD44. J Exp Med. 1993;177:897–904. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.4.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kripke ML, Munn CG, Jeevan A, Tang JM, Bucana C. Evidence that cutaneous antigen-presenting cells migrate to regional lymph nodes during contact sensitization. J Immunol. 1990;145:2833–2838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Labarriere N, Piau JP, Otry C, Denis M, Lustenberger P, Meflah K, Le Pendu J. H blood group antigen carried by CD44V modulates tumorigenicity of rat colon carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1994;54:6275–6281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lauffenburger DA, Horwitz AF. Cell migration: a physically integrated molecular process. Cell. 1996;84:359–369. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81280-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Miyake K, Medina KL, Hayashi S, Ono S, Hamaoka T, Kincade PW. Monoclonal antibodies to Pgp-1/CD44 block lympho-hemopoiesis in long-term bone marrow cultures. J Exp Med. 1990;171:477–488. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Moll, H. 1995. The Immune Functions of Epidermal Langerhans Cells. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, Germany. 133 pp.
- 31.Moll J, Schmidt A, van der Putten H, Plug R, Ponta H, Herrlich P, Zoller M. Accelerated immune response in transgenic mice expressing rat CD44v4-v7 on T cells. J Immunol. 1996;156:2085–2094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Negoescu A, Labat-Moleur F, Lorimier P, Lamarcq L, Guillermet C, Chambaz E, Brambilla E. F(ab) secondary antibodies: a general method for double immunolabeling with primary antisera from the same species. Efficiency control by chemiluminescence. J Histochem Cytochem. 1994;42:433–437. doi: 10.1177/42.3.7508473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Picker, L.J., J. de los Toyos, M.J. Telen, B.F. Haynes, and E.C. Butcher. 1989. Monoclonal antibodies against the CD44 [In(Lu)-related p80], and Pgp-1 antigens in man recognize the Hermes class of lymphocyte homing receptors. J. Immunol. 142:2046–2051. [PubMed]
- 34.Pope M, Betjes MG, Hirmand H, Hoffman L, Steinman RM. Both dendritic cells and memory T lymphocytes emigrate from organ cultures of human skin and form distinctive dendritic-T-cell conjugates. J Invest Dermatol. 1995;104:11–17. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12613452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sallusto F, Lanzavecchia A. Efficient presentation of soluble antigen by cultured human dendritic cells is maintained by granulocyte/ macrophage colony-stimulating factor plus interleukin 4 and downregulated by tumor necrosis factor alpha. J Exp Med. 1994;179:1109–1118. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.4.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Schuler G, Koch F, Heufler C, Kampgen E, Topar G, Romani N. Murine epidermal Langerhans cells as a model to study tissue dendritic cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1993;329:243–249. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-2930-9_41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Screaton GR, Bell MV, Jackson DG, Cornelis FB, Gerth U, Bell JI. Genomic structure of DNA encoding the lymphocyte homing receptor CD44 reveals at least 12 alternatively spliced exons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992;89:12160–12164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.12160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Seiter S, Arch R, Reber S, Komitowski D, Hofmann M, Ponta H, Herrlich P, Matzku S, Zoller M. Prevention of tumor metastasis formation by anti-variant CD44. J Exp Med. 1993;177:443–455. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Shimizu Y, Van Seventer GA, Siraganian R, Wahl L, Shaw S. Dual role of the CD44 molecule in T cell adhesion and activation. J Immunol. 1989;143:2457–2463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Simon JC, Tigelaar RE, Bergstresser PR, Edelbaum D, Cruz PD., Jr Ultraviolet B radiation converts Langerhans cells from immunogenic to tolerogenic antigen–presenting cells. Induction of specific clonal anergy in CD4+ T helper 1 cells. J Immunol. 1991;146:485–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Simon JC, Dietrich A, Mielke V, Wuttig C, Vanscheidt W, Linsley PS, Schopf E, Sterry W. Expression of the B7/BB1 activation antigen and its ligand CD28 in T-cell-mediated skin diseases. J Invest Dermatol. 1994;103:539–543. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12395743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Simon JC, Mosmann T, Edelbaum D, Schopf E, Bergstresser PR, Cruz PD., Jr In vivo evidence that ultraviolet B-induced suppression of allergic contact sensitivity is associated with functional inactivation of Th1 cells. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 1994;10:206–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Simon JC, Dittmar HC, de Roche R, Wilting J, Christ B, Schöpf E. Rapid purification of human Langerhans cells using paramagnetic microbeads. Exp Dermatol. 1995;4:155–161. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.1995.tb00239.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43a.Smith DB, Johnson KS. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia colias fusions with glutathione S–transferase. Gene. 1988;67:31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Stauder R, Eisterer W, Thaler J, Gunthert U. CD44 variant isoforms in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: a new independent prognostic factor. Blood. 1995;85:2885–2899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Steinman RM, Witmer-Pack M, Inaba K. Dendritic cells: antigen presentation, accessory function and clinical relevance. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1993;329:1–9. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-2930-9_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Tammi, R., U.M. Agren, A.-L. Tuhkanen, and M. Tammi. 1994. Hyaluronan metabolism in skin. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart, Germany. 78 pp. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 47.Tanaka Y, Adams DH, Hubscher S, Hirano H, Siebenlist U, Shaw S. T-cell adhesion induced by proteoglycan-immobilized cytokine MIP-1β. Nature (Lond) 1993;361:79–82. doi: 10.1038/361079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Thomas L, Byers HR, Vink J, Stamenkovic I. CD44H regulates tumor cell migration on hyaluronate-coated substrate. J Cell Biol. 1992;118:971–977. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.4.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Thomas L, Etoh T, Stamenkovic I, Mihm MC, Jr, Byers HR. Migration of human melanoma cells on hyaluronate is related to CD44 expression. J Invest Dermatol. 1993;100:115–120. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12462776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49a.Tölg C, Hofmann M, Herrlich P, Ponta H. Splicing choice from ten variant exons establishes CD44 variability. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993;21:1225–1229. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.5.1225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Weber GF, Ashkar S, Glimcher MJ, Cantor H. Receptorligand interaction between CD44 and Osteopontin (Eta-1) Science (Wash DC) 1996;271:509–512. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5248.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Weiss JM, Renkl AC, Denfeld RW, de Roche R, Spitzlei M, Schöpf E, Simon JC. Low-dose UVB radiation perturbs the functional expression of B7.1 and B7.2 co-stimulatory molecules on human Langerhans cells. Eur J Immunol. 1995;25:2858–2862. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830251022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Zahalka MA, Okon E, Gosslar U, Holzmann B, Naor D. Lymph node (but not spleen) invasion by murine lymphoma is both CD44- and hyaluronate-dependent. J Immunol. 1995;154:5345–5355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]