Abstract
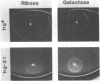
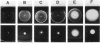
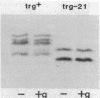
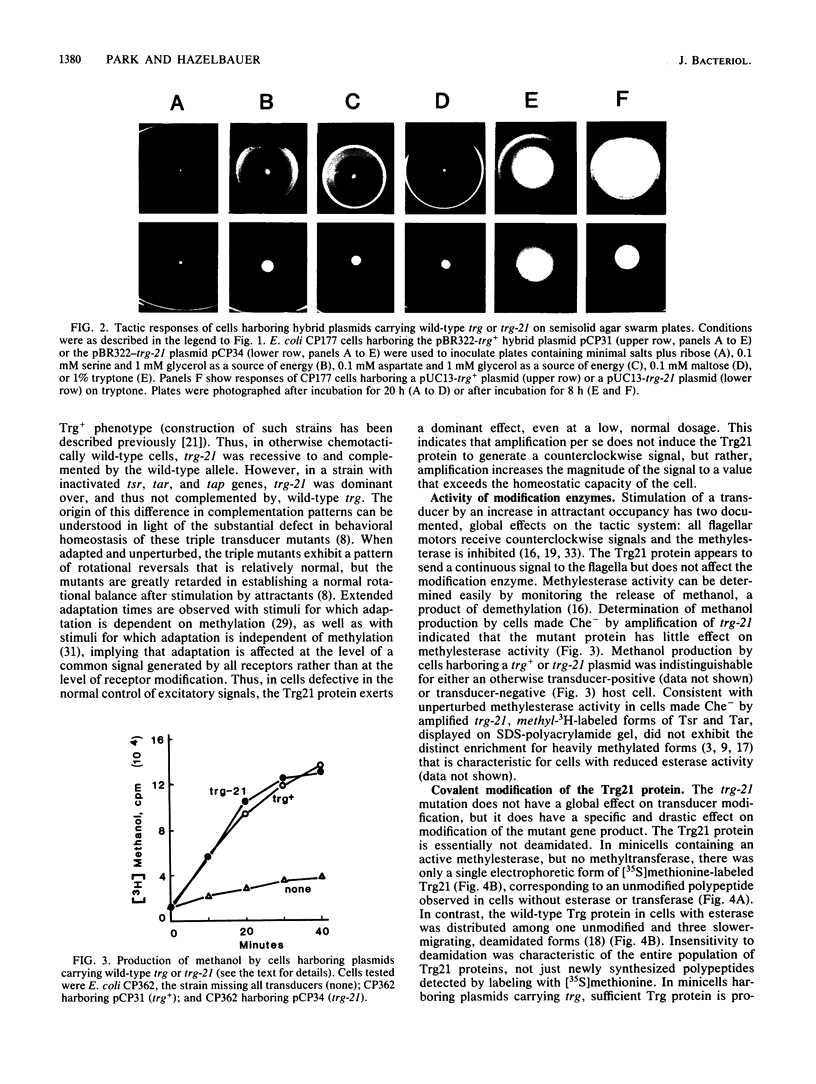
Transducers are transmembrane receptor proteins that generate intracellular signals on stimulation and participate in adaptation by appropriate changes in the level of methylation. The transducer mutation trg-21 conferred a Trg- phenotype and defective taxis to galactose and ribose but a normal response to other attractants when present in a single chromosomal copy. Amplification of trg-21 by a multicopy plasmid made host cells generally nonchemotactic. The dominant phenotype resulted from a strong counterclockwise rotational bias of flagellar motors in Che- cells. Apparently, the Trg21 transducer sends a continuous counterclockwise signal to flagella independent of tactic stimulation. It appears that the cell has a homeostatic capacity that is sufficient to compensate for the effect of mutant transducers produced from a single chromosomal copy of trg-21, but the capacity is exceeded in cells that have multiple copies of the gene. The Trg21 protein did not have a significant effect on methylesterase activity, indicating that the two global effects of a stimulated transducer, that is, on flagellar rotation and on modification enzymes, can occur independently. The mutant protein exhibited essentially normal turnover of methyl groups but had a drastic defect in deamidation which thus reduced the number of methyl-accepting sites. The trg-21 mutation substitutes a threonine for Ala-419. This alanine is a conserved residue in all sequenced transducers and is in a region of the carboxy-terminal domain in which homology among the transducers is very high. The Trg21 phenotype implicates this conserved region in the generation of the excitatory signal which is directed at the flagella.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bollinger J., Park C., Harayama S., Hazelbauer G. L. Structure of the Trg protein: Homologies with and differences from other sensory transducers of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3287–3291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan A. M., Parkinson J. S. Genetics of methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins in Escherichia coli: cheD mutations affect the structure and function of the Tsr transducer. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):96–104. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.96-104.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S., Koshland D. E., Jr Membrane receptors for aspartate and serine in bacterial chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9695–9702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engström P., Nowlin D., Bollinger J., Magnuson N., Hazelbauer G. L. Limited homology between trg and the other transducer proteins of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1268–1274. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1268-1274.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harayama S., Engström P., Wolf-Watz H., Iino T., Hazelbauer G. L. Cloning of trg, a gene for a sensory transducer in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):372–383. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.372-383.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harayama S., Palva E. T., Hazelbauer G. L. Transposon-insertion mutants of Escherichia coli K12 defective in a component common to galactose and ribose chemotaxis. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Mar 20;171(2):193–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00270005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Engström P. Multiple forms of methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins distinguished by a factor in addition to multiple methylation. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):35–42. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.35-42.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Engström P. Parallel pathways for transduction of chemotactic signals in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):98–100. doi: 10.1038/283098a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Harayama S. Mutants in transmission of chemotactic signals from two independent receptors of E. coli. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):617–625. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Harayama S. Sensory transduction in bacterial chemotaxis. Int Rev Cytol. 1983;81:33–70. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62334-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedblom M. L., Adler J. Genetic and biochemical properties of Escherichia coli mutants with defects in serine chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):1048–1060. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.1048-1060.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehry M. R., Bond M. W., Hunkapiller M. W., Dahlquist F. W. Enzymatic deamidation of methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins in Escherichia coli catalyzed by the cheB gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3599–3603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehry M. R., Dahlquist F. W. The methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins of Escherichia coli. Identification of the multiple methylation sites on methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein I. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10378–10386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehry M. R., Doak T. G., Dahlquist F. W. Aberrant regulation of methylesterase activity in cheD chemotaxis mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):105–112. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.105-112.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehry M. R., Doak T. G., Dahlquist F. W. Stimulus-induced changes in methylesterase activity during chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11828–11835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehry M. R., Engström P., Dahlquist F. W., Hazelbauer G. L. Multiple covalent modifications of Trg, a sensory transducer of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5050–5055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleene S. J., Hobson A. C., Adler J. Attractants and repellents influence methylation and demethylation of methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins in an extract of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6309–6313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koiwai O., Hayashi H. Studies on bacterial chemotaxis. IV. Interaction of maltose receptor with a membrane-bound chemosensing component. J Biochem. 1979 Jul;86(1):27–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krikos A., Mutoh N., Boyd A., Simon M. I. Sensory transducers of E. coli are composed of discrete structural and functional domains. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):615–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manson M. D., Blank V., Brade G., Higgins C. F. Peptide chemotaxis in E. coli involves the Tap signal transducer and the dipeptide permease. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):253–256. doi: 10.1038/321253a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosawa K., Imae Y. Demethylation of methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins in Escherichia coli induced by the repellents glycerol and ethylene glycol. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):576–581. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.576-581.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park C., Hazelbauer G. L. Mutations specifically affecting ligand interaction of the Trg chemosensory transducer. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):101–109. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.101-109.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park C., Hazelbauer G. L. Transfer of chromosomal mutations to plasmids via Hfr-mediated conduction. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jan;165(1):312–314. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.1.312-314.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S. Novel mutations affecting a signaling component for chemotaxis of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jun;142(3):953–961. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.3.953-961.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Revello P. T. Sensory adaptation mutants of E. coli. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1221–1230. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90048-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Protein methylation in behavioural control mechanisms and in signal transduction. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):279–284. doi: 10.1038/280279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Maderis A. M., Koshland D. E., Jr Bacterial chemotaxis in the absence of receptor carboxylmethylation. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90358-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger T. C., Koshland D. E., Jr Sites of methyl esterification and deamination on the aspartate receptor involved in chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7719–7725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toews M. L., Goy M. F., Springer M. S., Adler J. Attractants and repellents control demethylation of methylated chemotaxis proteins in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5544–5548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]