Abstract
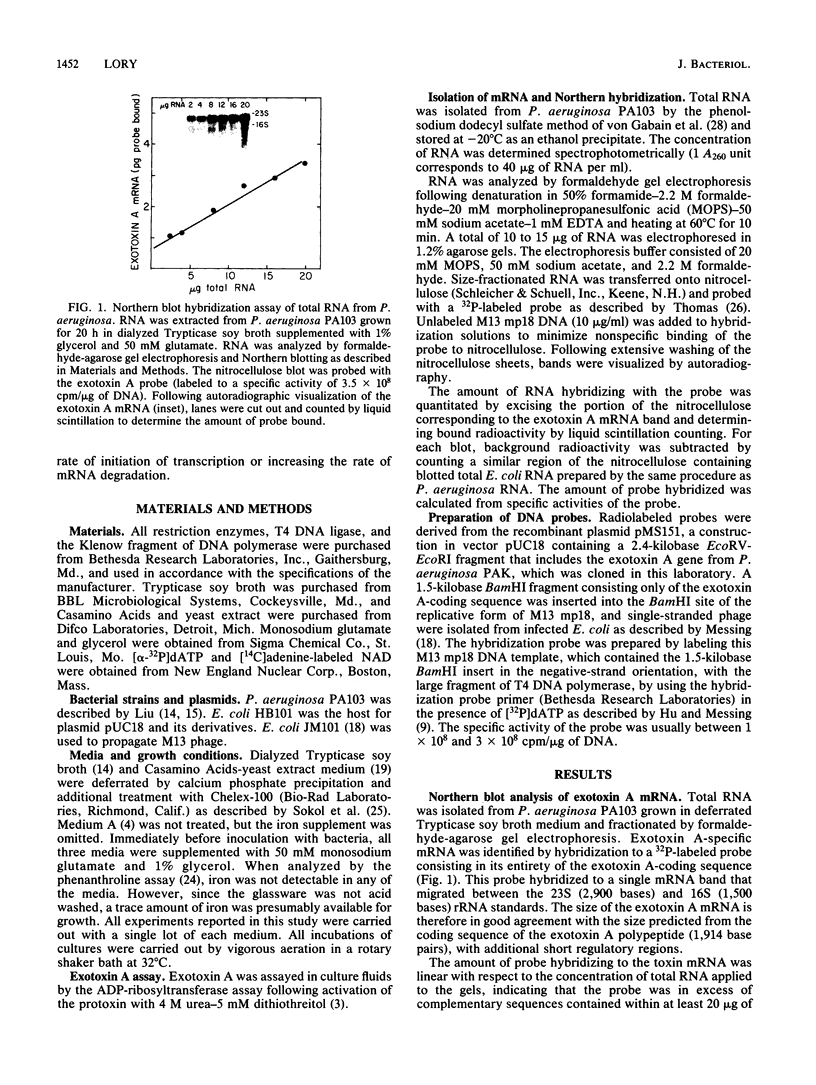
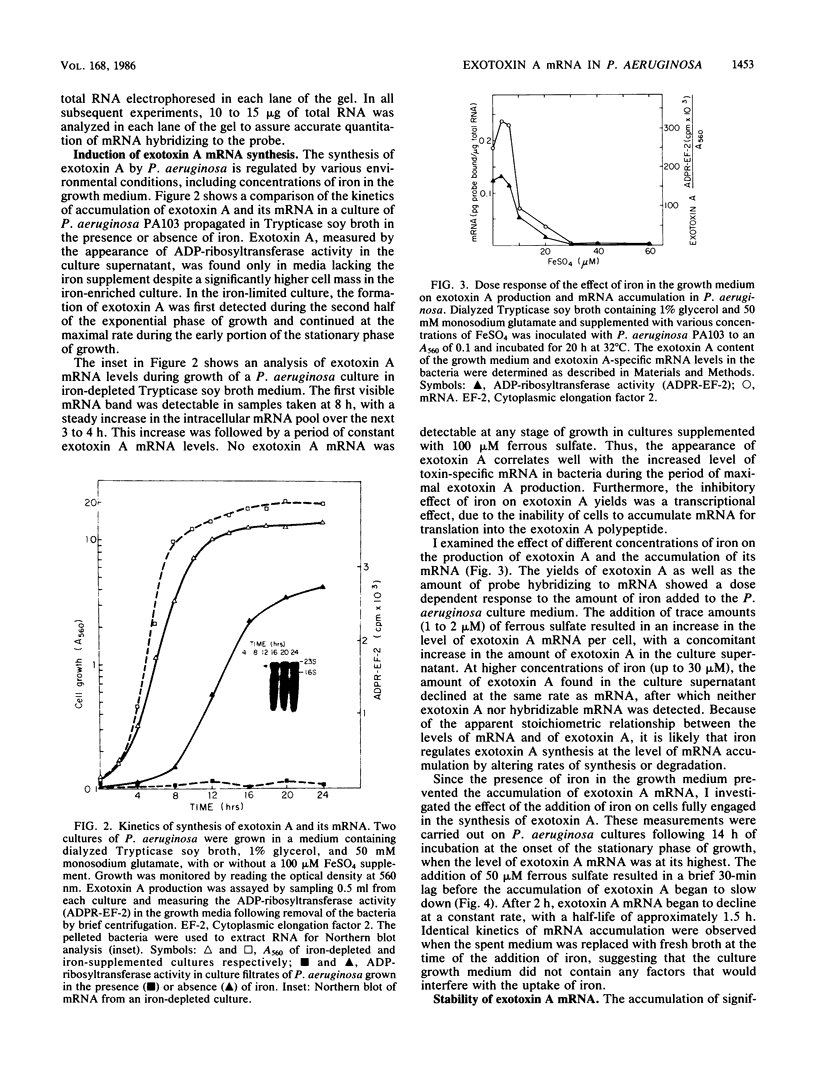
A DNA probe from an internal fragment of the exotoxin A structural gene was used to study the effects of selected culture conditions on steady-state levels of exotoxin-specific mRNA in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Cells grown under conditions of iron deprivation began to synthesize and excrete the exotoxin A polypeptide during the late exponential phase of growth and throughout the stationary phase of growth, concomitant with a sharp increase in exotoxin A mRNA pools in P. aeruginosa cells. The addition of iron to the medium resulted in the failure of these cells to synthesize exotoxin A mRNA, despite significantly enhanced growth. The inhibition of the production of exotoxin A and the accumulation of its mRNA by iron was dose dependent, with a half-maximal inhibitory concentration of FeSO4 of 5 to 10 microM. A blockade of the initiation of transcription by rifampin resulted in the decay of exotoxin A mRNA, with a half-life of approximately 8 to 10 min, depending on the media used for growth. The addition of iron to cells actively engaged in exotoxin A synthesis also resulted in a gradual decrease in the amount of this mRNA in bacteria. However, the rate of decline of mRNA induced by iron was relatively slow (half-life, 90 min), with a considerable lag time between the iron addition and the first detectable effect on mRNA. While iron clearly appears to influence the production of exotoxin A at the transcriptional level, the molecular basis of this effect may involve several interacting factors affecting the initiation of transcription and perhaps mRNA turnover.
Full text
PDF
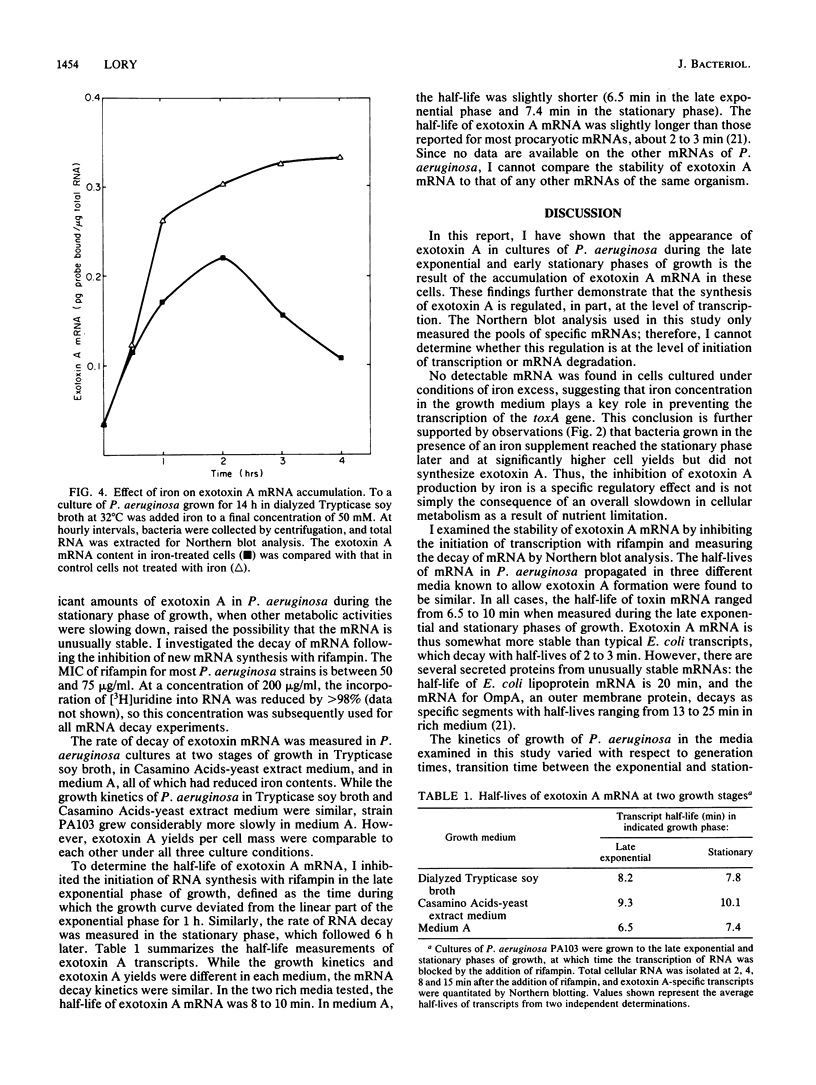


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bjorn M. J., Iglewski B. H., Ives S. K., Sadoff J. C., Vasil M. L. Effect of iron on yields of exotoxin A in cultures of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA-103. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):785–791. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.785-791.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorn M. J., Sokol P. A., Iglewski B. H. Influence of iron on yields of extracellular products in Pseudomonas aeruginosa cultures. J Bacteriol. 1979 Apr;138(1):193–200. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.1.193-200.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung D. W., Collier R. J. Enzymatically active peptide from the adenosine diphosphate-ribosylating toxin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):832–841. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.832-841.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. L., Smith D. H., Baldridge J. S., Harkins R. N., Vasil M. L., Chen E. Y., Heyneker H. L. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression in Escherichia coli of the exotoxin A structural gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2645–2649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. L., Vasil M. L. Isolation and genetic characterization of toxin-deficient mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. J Bacteriol. 1981 Aug;147(2):275–281. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.2.275-281.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanne L. F., Howe T. R., Iglewski B. H. Locus of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin A gene. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):383–386. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.383-386.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedstrom R. C., Funk C. R., Kaper J. B., Pavlovskis O. R., Galloway D. R. Cloning of a gene involved in regulation of exotoxin A expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):37–42. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.37-42.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu N., Messing J. The making of strand-specific M13 probes. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Kabat D. NAD-dependent inhibition of protein synthesis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin,. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2284–2288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczorek M., Zettlmeissl G., Delpeyroux F., Streeck R. E. Diphtheria toxin promoter function in Corynebacterium diphtheriae and Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3147–3159. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong D., Murphy J. R. Characterization of the diphtheria tox transcript in Corynebacterium diphtheriae and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1114–1119. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1114-1119.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. Exotoxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. I. Factors that influence the production of exotoxin A. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(4):506–513. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.4.506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lory S., Collier R. J. Expression of enzymic activity by exotoxin A from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):494–501. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.494-501.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson G., Belasco J. G., Cohen S. N., von Gabain A. Growth-rate dependent regulation of mRNA stability in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1984 Nov 1;312(5989):75–77. doi: 10.1038/312075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman D. E., Sadoff J. C., Iglewski B. H. Toxin A-deficient mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA103: isolation and characterization. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):899–908. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.899-908.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Diphtheria toxin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:69–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokol P. A., Cox C. D., Iglewski B. H. Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants altered in their sensitivity to the effect of iron on toxin A or elastase yields. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):783–787. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.783-787.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA transferred or dotted nitrocellulose paper. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:255–266. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasil M. L., Kabat D., Iglewski B. H. Structure-activity relationships of an exotoxin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):353–361. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.353-361.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Gabain A., Belasco J. G., Schottel J. L., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Decay of mRNA in Escherichia coli: investigation of the fate of specific segments of transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):653–657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]