Abstract
The glycophosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchors of proteins expressed on human erythrocytes and nucleated cells differ with respect to acylation of an inositol hydroxyl group, a structural feature that modulates their cleavability by PI-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC). To determine how this GPI anchor modification is regulated, the precursor and protein-associated GPIs in two K562 cell transfectants (ATCC and .48) exhibiting alternatively PI-PLC-sensitive and resistant surface proteins were analyzed and the temporal relationship between GPI protein transfer and acquisition of PI-PLC sensitivity was determined. Nondenaturing PAGE analyses demonstrated that, whereas in .48 transfectants the GPI anchors in decay accelerating factor (DAF) and placental alkaline phosphatase (PLAP) were >95% acylated, in ATCC transfectants, they were 60 and 33% unsubstituted, respectively. In contrast, TLC analyses revealed that putative GPI donors in the two lines were identical and were ≥95% acylated. Studies of de novo DAF biosynthesis in HeLa cells bearing proteins with >90% unacylated anchors showed that within 5 min at 37°C (or at 18°C, which does not permit endoplasmic reticilum exit), >50% of the anchor in nascent 44-kDa proDAF protein exhibited PI-PLC sensitivity. In vitro analyses of the microsomal processing of miniPLAP, a truncated PLAP reporter protein, demonstrated that the anchor donor initially transferred to prominiPLAP was acylated and then progressively was deacylated. These findings indicate that (i) the anchor moiety that initially transfers to nascent proteins is acylated, (ii) inositol acylation in mature surface proteins is regulated via posttransfer deacylation, which in general is cell-specific but also can be protein-dependent, and (iii) deacylation occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum immediately after GPI transfer.
A characteristic of surface proteins that are membrane-anchored by glycophosphatidylinositol (GPI) structures is that they can be cleaved from cells by PI-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC)(reviewed in refs. 1 and 2). Only 5–15% of acetylcholinesterase (3), decay accelerating factor (DAF) (4–7), LFA-3, and CD59 (8–10) expressed on human erythrocytes, however, are PI-PLC cleavable either in situ (4, 6, 7) or after purification (4–6). In contrast, ≈90% of these and other GPI-anchored proteins on most nucleated cells are cleaved by the enzyme (5, 6). Structural analyses of the human erythrocyte protein anchors have shown that their PI-PLC resistance is due to acylation (C14:0) of an inositol hydroxyl group (5, 11, 12). Analyses of DAF and CD59 on several leukocyte types similarly have shown that the residual 5–10% of molecules that resist PI-PLC cleavage possess GPI anchors containing acylated inositol (5, 10). These findings have raised the question of how GPI anchor acylation is regulated and at what site in cells this control is effected.
Unlike mammalian GPI-anchored proteins, variant surface glycoproteins, the major coat protein of Trypanosoma brucei (Tryp) (when purified) exhibit >99% PI-PLC sensitivity. Accordingly, intracellular GPI precursors in these organisms are predominantly unacylated (13, 14) and an unacylated GPI donor, termed A′, transfers to nascent variant surface glycoprotein polypeptides (15). In contrast, in mammalian cells intracellular GPIs contain predominantly acylated inositol (16–21) and it remains unclear whether an acylated GPI precursor serves as the donor moiety and whether this donor differs in cells with PI-PLC-sensitive and resistant surface proteins. In previous studies (22), fusions of murine lymphoma cells bearing surface Thy-1 protein with an unacylated GPI anchor to L929 cells bearing Ly-6 protein with an acylated anchor yielded cells bearing both surface proteins with unacylated GPI anchors, arguing that a deacylation reaction occurs sometime during biosynthesis. Three possibilities therefore exist: (i) deacylation occurs before protein addition, (ii) deacylation occurs in association with or immediately after protein addition, or (iii) deacylation occurs later in protein processing after transit out of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
In the present study, the nature of the reaction that regulates inositol acylation of mammalian GPI-anchored surface proteins was investigated. Placental alkaline phosphatase (PLAP) transfectants of two sublines of human leukemic K562 cells (K562ATCC and .48 subline) (ref. 23, see Discussion) found to alternatively express DAF proteins with unsubstituted and acylated GPI structures were compared with respect to (i) the GPI anchors of their surface proteins and (ii) their intercellular GPI precursors. The HeLa cell line that expresses large amounts of (>90%) PI-PLC-sensitive proteins then was used (i) in protein biosynthetic studies in vivo, and (ii) as a source of microsomes for in vitro microsomal processing analyses of miniPLAP, an engineered PLAP reporter protein, to assess the roles of GPI donors and of subsequent posttranslational processing steps in conferring the differences in GPI anchor acylation of the expressed mammalian surface proteins.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cells and Reagents.
K562.ATCC cells were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA) and the .48 subline from T. Rosenberry (Mayo Research Foundation, Jacksonville, FL). Murine anti-DAF mAb IA10 (24), anti-PLAP mAbs H7 and D10 (25), rat anti-CD59 mAb YTH53.1 (26), and PLAP (27)/miniPLAP (28) cDNAs were obtained as described. PI-PLC (B. thuringiensis) was a gift of M. Low (Columbia University, New York), and REP3 provided by M. Tykocinski (Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH).
PI-PLC digestion analyses.
Assays were performed (4, 24) using 106 cells in 25 μl of PBS containing sequentially diluted PI-PLC (400 units/ml) and 37°C incubations for 1 hr. Washed cells were stained with anti-DAF, anti-PLAP, anti-CD59, or corresponding nonrelevant mAbs (5 μg/ml each) followed by fluorescein isothiocyanate-anti-murine or rat IgG.
Transfections, Labeling, and Affinity Purifications.
PLAP cDNA (27) [excised from pBT (Stratagene) with XbaI and XhoI] was inserted into the NheI and XhoI sites of REP3. Transfections were carried out as described (29).
Transfectants (108) were surface-labeled with 2 mCi 125I (1 Ci = 37 GBq) and extracted at 37°C as described (10). Labeled proteins precipitated with 50 μl of IA10-, D10-, and BSA-Sepharose were eluted with 500 μl of 0.05 M diethylamine (pH 11.5), 0.14 M of NaCl containing 0.2% Triton X-100, dialyzed, and concentrated to 50 μl. In some experiments, affinity purified DAF and PLAP from unlabeled cells were radiomethylated with [14C]CHO (40 Ci/mol) and NaCNBH3 (30).
Deacylation of Inositol and Nondenaturing (ND)-PAGE Analyses.
Labeled proteins were incubated overnight on ice either with 1 M of hydroxylamine hydrochloride, 0.1 M of triethylamine (pH 10.7), or with 0.1 M of Tris⋅HCl (pH 7.4), and after dialysis and reconcentration to 50 μl, further incubated at 37°C for 60 min with 25 μl of 1:50 PI-PLC in PBS or PBS alone (5). Reaction products (10 μl) were electrophoresed (5) on 7.5% ND-PAGE gels containing 8 M urea and 0.5% Triton X-100 detergent in an LKB Multiphor II unit.
Analyses of Intracellular GPIs.
Cells (2 × 107) were labeled with D-[2-3H]mannose (250 μCi) for 2 hr at 37°C and Tryp lysates with GDP-[3H]mannose for 90 min at 37°C as described (31). Labeled cells or lysates were extracted with chloroform:methanol:water (10:10:3), and lipid species that partitioned into butanol were resolved on Silica Gel 60 TLC plates with chloroform:methanol:water (10:10:3) and scanned as described (31).
Analyses of de Novo Synthesized DAF Protein.
Semiconfluent (60–70%) HeLa cell monolayers were preincubated for 1 hr with cysteine- and methionine-free RPMI 1640 medium containing 10% dialyzed fetal bovine serum, [35S]C (100 μCi; Amersham) added, and the plates were either labeled continuously at 37°C (4) or pulsed for 5 min at 37°C and chased at 18°C. At the specified times, medium was aspirated and the cells extracted with boiling 2% SDS. DAF proteins purified as described (4) were concentrated to 50 μl and incubated at 37°C for 4 hr with 1:50 PI-PLC on buffer control. Treated proteins were partitioned in 100 μl of 2% TX-114 detergent, immunoprecipitated from the aqueous and detergent phases, and analyzed on 7.5% non-reduced gels treated with Enhance (DuPont).
Cotranslational Processing Studies of MiniPLAP.
Rough microsomal membranes (RM) were prepared, cotranslational processing with rabbit reticulocyte lysate carried out at 30°C, and products analyzed on 15% SDS/PAGE gels as described (28). For PI-PLC digestions, 100 μl of incubated cotranslation mix was centrifuged through a 100 μl cushion of 500 mM sucrose in 50 mM triethanolamine buffer (pH 7.5), in a TLA-100 rotor. The pellet, dissolved in 5 μl of 0.5% Triton X-100 and resuspended to 50 μl in 50 mM of Tris (pH 7.4), was incubated for 4 hr at 37°C with 1:50 PI-PLC. In some experiments, the pellet dissolved in 5 μl of 0.5% Triton X-100 was alternatively incubated overnight on ice in 50 μl of 50 mM of Tris (pH 7.4) or 50 mM of Tris, 1 M of hydroxylamine, pH 10.7. After dialysis against 50 mM Tris (pH 7.5) containing 0.1% Triton X-100, products then were subjected to PI-PLC digestions.
For TX-114 fractionations, the pellet of 100 μl of incubated reaction mix was resuspended in 50 μl of 50 mM Tris (pH 7.5) containing 2% TX-114 detergent at 0°C. After warming to 37°C for 5 min, the mixture was centrifuged at 14,000 rpm in a microfuge and the phases separated. After repeat partitioning of each phase twice, immunoprecipitated miniPLAP proteins from the aqueous and detergent phases were analyzed by SDS/PAGE/autoradiography.
RESULTS
GPI Anchors of DAF and Transfected PLAP Proteins Expressed on K562 ATCC and .48 Lines.
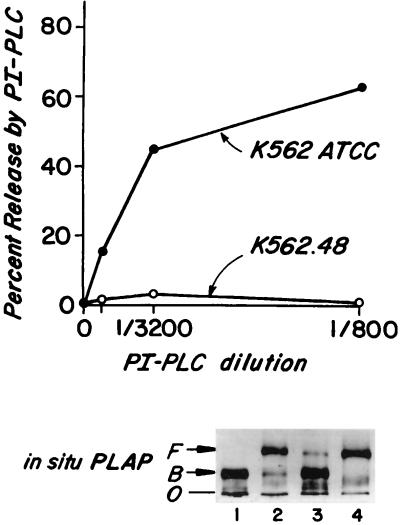
In initial studies, ATCC and .48 cells were compared with respect to their endogenous DAF proteins. As seen in Fig. 1A, upon incubation of the ATCC subline with increasing concentrations of PI-PLC, increasing proportions of DAF were released reaching 63% at a 1:800 dilution (0.5 units/ml) of the enzyme. In four repeat experiments, almost identical release was observed (see Discussion). In contrast, after similar treatment of the .48 subline, <5% of DAF was released even when the PI-PLC concentration was further augmented to 8 units/ml (not shown).
Figure 1.
(A) In situ cleavage by PI-PLC of endogenous DAF in K562 ATCC and K562.48 cells. Cells were treated with PI-PLC and then stained with anti-DAF or nonrelevant mAbs and analyzed by flow cytometry. Percent DAF released equals the difference between the fluorescence of buffer- and PI-PLC-treated cells. (B) ND-PAGE analyses of in situ PLAP protein. Samples in lanes 1 and 2 were treated with buffer at 0°C overnight, and in lanes 3 and 4 treated with hydroxylamine, pH 10.7 at 0°C overnight. Samples in lanes 1 and 3 then were incubated with buffer and samples in lanes 2 and 4 with PI-PLC (1:50) at 37°C for 2 hr. F, protein freed from detergent micelles; B, protein bound to detergent micelles; O, origin.
Alkaline hydroxylamine treatment deacylates inositol and renders acylated-GPI anchors susceptible to PI-PLC cleavage (32). To verify that the differences in DAF release from the ATCC and .48 sublines reflected differences in inositol acylation, the cells were 125I-surface-labeled. Aliquots of affinity-purified labeled DAF protein then were treated with buffer or with alkaline/hydroxylamine, the treated samples incubated with PI-PLC, and the products of each reaction analyzed by ND-PAGE and densitometry. With this technique, molecules bearing unacylated anchors are cleaved and migrate rapidly. In contrast, detergent-associated molecules bearing acylated anchors migrate slowly but if inositol first is deacylated, these molecules behave similarly to unacylated molecules. In the case of both sublines, the proportions of [125I]DAF exhibiting rapid migration after treatment by PI-PLC alone corresponded to the proportions of DAF proteins released from the cell surface by the enzyme [not shown (see Table 1 below)]. The residual slowly migrating DAF proteins that remained detergent-associated were rendered PI-PLC-sensitive by alkaline hydroxylamine pretreatment, indicative of inositol acylation.
Table 1.
ND-PAGE analyses of the GPI anchors in DAF, PLAP, and CD59 from KAPLAP and K48PLAP transfectants
| Cell type | Unmodified inositol | Acylated inositol |
|---|---|---|
| Placenta | ||
| PLAP protein | 91.0 | 9.0 |
| K48PLAP | ||
| DAF protein | <5 | >95 |
| PLAP protein | <5 | >95 |
| PLAP activity | <5 | >95 |
| KAPLAPa | ||
| DAF protein | 60.3 ± 4.1* | 39.7 ± 4.1 |
| PLAP protein | 30.1 ± 1.6 | 69.9 ± 1.6 |
| PLAP activity† | 29.7 ± 3.8 | 70.3 ± 3.8 |
| CD59 protein | 59.8 ± 16 | 40.2 ± 16 |
| KAPLAPb | ||
| DAF protein | 49.2 | 50.8 |
| PLAP protein | 36.7 | 63.3 |
The proportions of hydrophilic and detergent-bound DAF and PLAP in each lane were determined by densitometry of autoradiographs or stained gels. Values represent the mean and SD of two separate analyses.
Gels were stained for alkaline phosphatase activity with an alkaline phosphatase assay kit (Sigma). Bands were visualized using an indigogenic dye substrate. Values represent the mean and SD of three analyses.
Preliminary to studies with transfected PLAP proteins, the GPI anchor of PLAP as it is expressed in situ was analyzed. Accordingly, purified (postsurgical) placental PLAP (33) was [14C]-radiomethylated and the labeled protein assayed as above by ND-PAGE. Because under nondenaturing conditions, PLAP is able to multimerize (34, 35), experiments were conducted on gels prepared in 8 M urea. Densitometric analyses of autoradiographs (Fig. 1B and Table 1) showed that 91% of the sample treated with PI-PLC alone (Fig. 1B, lane 2) and the remaining 9% treated first with hydroxylamine and then with PI-PLC (Fig. 1B, lane 4) migrated as hydrophilic proteins. The analyses thus indicated that, in situ in placental tissue, >90% of PLAP molecules contain GPI anchors with unacylated inositol.
PLAP proteins on PLAP/ATCC and .48 cell transfectants next were analyzed. By fluorescence activated cell sorting, the transfectants (designated KAPLAPa and K48PLAP) exhibited equivalent surface PLAP levels. As shown in Table 1, similarly to DAF in the .48 line, >95% of PI-PLC-treated PLAP purified from K48PLAP cells remained detergent-associated but when pretreated with hydroxylamine, all of the protein migrated as a hydrophilic protein indicative of inositol acylation. In contrast, as observed with DAF in the KAPLAPa transfectant (Table 1, 60.3% release), a portion of PLAP, in this case 30.1%, was released after treatment with PI-PLC alone. When pretreated with hydroxylamine and then PI-PLC, the remaining 69.9% was released.
In view of the differences in unsubstituted inositol of PLAP and DAF (≈30 vs. ≈60%) in KAPLAPa cells, additional control experiments with ATCC cells were conducted: The results are given in Table 1. (i) Analyses of a second K562/ATCC transfectant, KAPLAPb, showed PI-PLC cleavage of 37% of PLAP as compared with 49% of DAF. (ii) Experiments in which 8 M urea or 2-mercaptoethanol was included in the PI-PLC digestion reactions as well as in the ND-PAGE analyses (to exclude inaccessibility of PLAP anchors to the enzyme) gave similar results (not shown). (iii) When PLAP bands were quantitated by enzymatic activity, the measured cleavage of PLAP was the same. (iv) To exclude heterogeneity of PLAP molecules among individual cells, transfectants were sorted for high PLAP expression and the extent of acylation of PLAP’s anchor in the sorted cells was analyzed. Similar results again were observed (not shown). (v) Analyses of another endogenous protein, CD59, showed that whereas <5% could be released from .48 cells even at 1:50 PI-PLC, 60% was released from ATCC cells. Accordingly, in ND-PAGE analyses of [125I]-CD59 protein purified from KAPLAPa cells, 59.8% exhibited a migration pattern characteristic of unacylated inositol. Taken together the data indicated that whereas GPI-anchored proteins in .48 cells uniformly exhibited anchors with >95% acylated inositol, the same proteins in ATCC cells exhibited anchors with unsubstituted inositol, although the proportions of unsubstituted inositol in different proteins did not strictly conform (30–60%).
Intracellular GPI Species and de Novo Synthesized GPI Anchored Proteins.
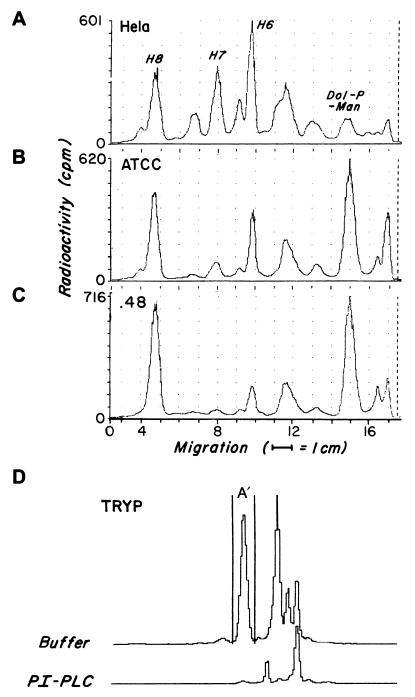
To determine if the differences in GPI anchor acylation of ATCC and .48 cell surface proteins related to differences in their GPI precursors, [3H]mannose-labeled GPI intermediates in the two lines were compared. As shown in Fig. 2B and C, products corresponding in TLC mobilities to dolichol-phosphoryl-mannose and previously characterized H2-H8 (Fig. 2A) were identifiable in both cell lines. The amounts of each intermediate in the two lines were similar, no products were unique to either line, and the fully assembled putative donor(s) H7 and H8, were roughly comparable.
Figure 2.
TLC analyses of GPI products deriving from [3H]mannose labeling of K562 ATCC and .48 lines. [3H]mannose-labeled GPI intermediates from tunicamycin-pretreated HeLa cells (A), K562 ATCC cells (B), or K562.48 cells (C) were separated on TLC plates developed in chloroform:methanol:water (10:10:3). The positions of previously characterized HeLa cell bands H6, H7, and H8 and of dolichol-phosphoryl-mannose are indicated. As control (D) [3H]mannose-labeled Tryp GPIs were prepared from Tryp lysate (1 × 107 cell equivalent) incubated with 10 μCi GDP-[3H]mannose. Aliquots of GPI products deriving from each source alternatively were incubated with buffer or PI-PLC. The radioactivity (cpm) falling within the peak (H8 and H7 for the K562 cell lines and A′ for Tryp) was electronically measured.
To assess the extent of inositol acylation of H7 and H8 in the two lines, labeled GPIs synthesized by each line and generated with Tryp control lysates were incubated alternatively with buffer or PI-PLC and the products examined by TLC. Under conditions in which 97% of the fully-assembled Tryp donor A′ was cleaved, 5.1 ± 2.7 of H8 in ATCC cells vs. 3.6% of H8 in .48 cells was cleaved. Similar results (≤5.3% cleavage) were obtained for H7.
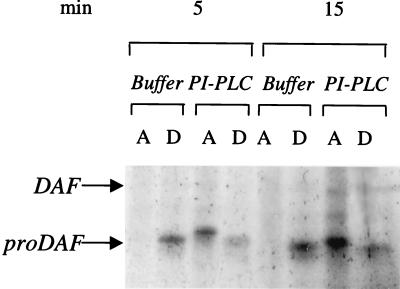
Based on the essential equivalency of the putative donors in the two lines, the anchor structures in de novo synthesized GPI-anchored protein next were analyzed. For this analysis, DAF was studied because proDAF (44 kDa) is easily distinguishable from a 70-kDa mature (O-glycosylated) surface DAF. HeLa cells were used because they express >105 DAF molecules/cell with >90% unacylated GPI anchors (5). Cells were labeled with [35S]C for 5 or 15 min, [35S]C-labeled DAF polypeptides isolated by affinity chromatography, and the purified proteins treated alternatively with buffer or PI-PLC. The treated samples then were partitioned in TX-114, and the organic and aqueous phases of each sample analyzed by SDS/PAGE autoradiography. As shown in Fig. 3, at 5 and 15 min of labeling 56.3% and 81.3%, respectively, of the 44 kDa proDAF protein exhibited sensitivity to PI-PLC indicative of deacylation occurring before arrival in the Golgi. To verify that the reaction was localized in the ER, a pulse chase analysis was done in which cells were pulsed for 5 min at 37°C and then chased with unlabeled C at 18°C, a temperature that does not permit exit from the ER. As observed with the continuous labeling, >60% of the 44-kDa proDAF exhibited PI-PLC sensitivity at 20 min of 18°C chase.
Figure 3.
GPI anchor acylation in newly synthesized DAF polypeptides. HeLa cells were labeled with [35S]C for 5 or 15 min at 37°C, [35S]-labeled surface proteins affinity purified, and products eluted from the anti-DAF beads were incubated with PI-PLC or corresponding buffer and partitioned in TX-114 detergent. [35S]-labeled proteins in the aqueous and organic phases were then repurified with IA10-Sepharose.
Transfer of GPI Donors to Nascent Polypeptides.
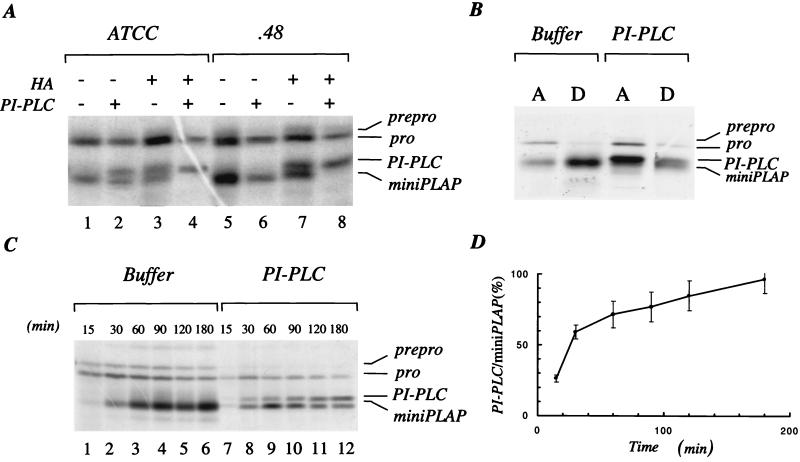
In view of the finding of unacylated 44-kDa proDAF in HeLa cells, studies next were done to determine if inositol deacylation occurs before, during, or after anchor transfer to protein. For this analysis, the miniPLAP in vitro translation system, which allows direct analysis of the C-terminal GPI substitution reaction, was employed. In this system, N-terminal processing of the 28.0-kDa preprominiPLAP—the miniPLAP mRNA translation product—yields 27.0-kDa prominiPLAP, and C-terminal processing of this N-terminally processed intermediate yields 24.7-kDa “mature miniPLAP.”
Initial studies examined 24.7-kDa mature miniPLAP generated after 90 min in the presence of ATCC or .48 cell microsomes. As seen in Fig. 4A, although PI-PLC alone cleaved ≈60% of the ATCC microsome-generated product (resulting in an upward shift in mobility), no PI-PLC cleavage of the .48 microsome-generated product occurred without hydroxylamine-pretreatment. To verify that the upward-shifted band at ≈25 kDa represented PI-PLC-cleaved miniPLAP, TX-114 partitioning was performed. Anti-PLAP immunoprecipitates of the aqueous and detergent phases of (i) buffer and (ii) hydroxylamine and PI-PLC-treated samples of a 90 min reaction mixture are shown in Fig. 4B. Whereas the 24.7-kDa miniPLAP in the buffer-treated sample partitioned with the detergent phase, the 25-kDa miniPLAP in the hydroxylamine and PI-PLC-treated sample partitioned in the aqueous phase.
Figure 4.
Microsomal processing of preprominiPLAP. miniPLAP RNA was added in cotranslational assays with [35S]M and RM. (A) Products deriving from processing of preprominiPLAP by K562.ATCC (lanes 1–4) and .48 RM (lanes 5–8), treated with buffer alone (lanes 1 and 5), buffer and PI-PLC (lanes 2 and 6), alkaline/hydroxylamine alone (lanes 3 and 7), or alkaline/hydroxylamine and PI-PLC (lanes 4 and 8). (B) Products deriving from HeLa cell RM were treated with buffer or hydroxylamine and PI-PLC and then partitioned in TX-114 detergent. A, aqueous phase; D, detergent phase. (C and D) Cotranslational processing of preprominiPLAP in the presence of HeLa RM was stopped after the indicated times, the mixture treated with buffer (lanes 1–6) or PI-PLC (lanes 7–12) and the products analyzed. (D) Densitometric data.
To examine the inositol phospholipid in 24.7-kDa mature miniPLAP as a function of the time of its production, microsomes from HeLa cells that produce high levels of unacylated GPI-anchored surface proteins (5) were used. As seen from the data in Fig. 4C and from densitometry measurements in Fig. 4D, the inositol phospholipid in the initial protein-associated product was resistant to PI-PLC and then progressively was rendered sensitive to PI-PLC. The results thus indicated that the GPI donor that initially transfers to nascent polypeptides is a “three lipid structure” bearing acylated inositol. This unit subsequently is deacylated.
DISCUSSION
In this study the GPI anchors of PLAP proteins expressed by two K562 lines differing in acylation of the GPI anchors in their endogenous surface proteins were examined. Findings that deacylation of inositol in the PLAP GPI anchor paralleled but did not precisely correspond to that of other proteins argue that this structural feature is in general regulated in a global fashion but also can be protein dependent. Observations that the putative GPI donors synthesized intracellularly in the two cell lines were ≥95% acylated but that the GPI anchors in newly synthesized proproteins were unsubstituted indicate that this regulation involves deacylation that is effected in the course of anchor transfer to protein. In vitro analyses of the kinetics of anchor attachment and of acquisition of PI-PLC sensitivity using microsomes from cells exhibiting PI-PLC-sensitive proteins showed that the anchor donor initially transfers with acylated inositol and subsequently is deacylated. Correlation of the in vitro processing data with in vivo biosynthetic findings that deacylation of proDAF is 50% complete within 5 min and proceeds at 18°C established that the enzymatic activity responsible for inositol deacylation is localized in the ER.
K562 cells (36) correspond phenotypically to an erythroleukemic blast. They can be induced by butyrate (37) to differentiate further toward red cells. The K562.48 subline (23) expresses more hemoglobin and glycophorin than the original ATCC subline, suggesting that it is further differentiated along the erythroid pathway. Because acylation of anchor inositol similar to that in endogenous human erythrocyte DAF is seen in K562.48 DAF and not in K562 ATCC DAF (Fig. 1A), this anchor modification may result from a decrease in enzyme expression accompanying transition of erythroid progenitors to mature human erythrocytes.
Our analyses of purified 14C-labeled endogenous PLAP protein demonstrated that 91% was cleavable by PI-PLC (Fig. 1B, lane 2 and Table 1). This in situ value is similar to the >90% release found when PLAP labeled with [3H]stearic acid in JEG-3 cells (38) or PLAP transfected in HeLa cells (39) was treated with PI-PLC. Our finding that PLAP expressed in the K48PLAP transfectant differed from placental, JEG-3 or HeLa cell PLAP in that its GPI anchor was >95% acylated establishes that cell-specific processing primarily regulates GPI anchor inositol acylation. The accompanying result that in KAPLAPa/b transfectants up to 37% of the PLAP molecules exhibited PI-PLC sensitivity further substantiates this interpretation. The finding that different proportions (30–60%) of PLAP, DAF, and CD59 molecules exhibited behavior indicative of unacylated inositol supports the proposition that protein-specific factors can also play a role. In previous studies, it was found that 65% of acetylcholinesterase molecules (40) and that 71% of transfected CD8⋅DAF molecules on K562 ATCC cells are releasable by PI-PLC (29). Although it cannot be excluded that the apparent lesser proportion of PLAP molecules with unacylated inositol observed with KAPLAP transfectants could be artificially low, the previous results with JEG-3 and HeLa cell PLAP (38, 39) and the demonstration in this study that >90% of PLAP isolated from placental cells exhibited PI-PLC release under identical conditions strongly argue that the difference is cell dependent and not due to any unusual property; e.g., enzyme inaccessibility of this protein. In view of our findings that deacylation occurs after anchor addition to protein (see below), it is plausible that protein structure could influence reaction efficiency of the deacylation enzyme.
Our characterization of intracellular precursors in the ATCC and .48 lines revealed that they were identical and were ≥ 95% acylated. No distinctive PI-PLC-sensitive species was identifiable in the PI-PLC-sensitive ATCC line. In mammalian cells, two acyl inositol-containing terminal precursors H7 and H8 (that differ with respect to the absence or presence of an ethanolamine-phosphate on mannose 2) (17, 20, 21) are synthesized and it is not yet established whether one or both can serve as donors. The results of our kinetic studies with the miniPLAP in vitro translation system, showing that the initially transferred anchor donor contained acylated inositol, as in free H7 and H8, do not exclude the possibility that small amounts of GPI precursors containing unacylated inositol, if present, might also be able to transfer to nascent polypeptides. The findings from our in vivo studies of de novo DAF biosynthesis that the deacylase enzyme was located in the ER and that 44 kDa proDAF was 56% deacylated within as little as 5 min establish that inositol deacylation reaction occurs immediately after anchor transfer.
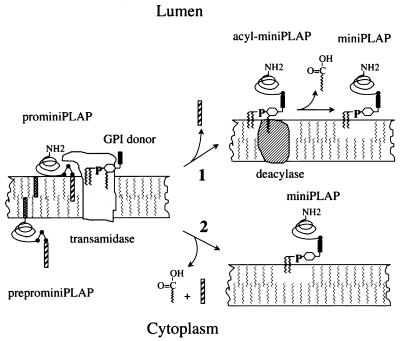
The cellular machinery that provides for transfer of fully-assembled GPIs to nascent polypeptides is a subject of current investigation. The transfer reaction has been shown to consist of a transamidation (41) and there is evidence that the GPI donor is an essential component in the reaction (42). At least two factors termed Gaa1p (43) and Gpi8p (44) are known to be involved, and studies in a human K562 cell mutant (45) have shown that defective transamidation (46) results from mutation of GPI8 (47). Our finding that in human cells deacylation occurs after anchor transfer favors the proposal that these reactions are mediated by separate factors (see Fig. 5). It alternatively is possible that deacylation may occur as part of a concerted stepwise reaction mediated by a multiprotein enzyme complex.
Figure 5.
Proposed relationship between GPI anchor transfer and deacylation. The anchor initially transfers in an acylated form. Inositol deacylation then occurs either(i) as a subsequent reaction physically unassociated with transamidation mediated by separate factor (deacylase) or (ii) as a concerted reaction carried out by a multiprotein transamidase deacylation complex. Hatched bar, C-terminal signal peptide; solid bar, EthN-P-containing glycan of GPI donor; striped bar, N-terminal signal peptide.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank M. Tykocinski for providing REP3; J. Knez for technical assistance; and B. McCarty, R. Mocny, and S. Cechner for manuscript preparation. This investigation was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (AI23598, HL55773, and PO1DK38181).
ABBREVIATIONS
- DAF
decay-accelerating factor
- GPI
glycophosphatidylinositol
- PI-PLC
PI-specific phospholipase C
- Tryp
Trypanosoma brucei
- PLAP
placental alkaline phosphatase
- miniPLAP
PLAP minigene
- ND
nondenaturing
- RM
rough microsomal membrane
- ER
endoplasmic reticulum
References
- 1.Ferguson M A J, Williams A F. Ann Rev Biochem. 1988;57:285–320. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Low M G. FASEB J. 1989;3:1600–1608. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.5.2522071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Low M G, Finean J B. FEBS Lett. 1977;82:143–146. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80905-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Medof M E, Walter E I, Roberts W L, Haas R, Rosenberry T L. Biochemistry. 1986;25:6740–6747. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Walter E I, Roberts W L, Rosenberry T L, Ratnoff W D, Medof M E. J Immunol. 1990;144:1030–1036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Davitz M A, Low M G, Nussenzweig V. J Exp Med. 1986;163:1150–1161. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lublin D M, Atkinson J P. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:5–58. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.000343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Medof M E, Selvaraj P, Dustin M L, Ayers D G, Walter E I, Stafford H A, Green R, Tykocinski M L, Springer T A. Complement. 1987;4:192. (abstr.). [Google Scholar]
- 9.Selvaraj P, Dustin M L, Silber R, Low M G, Springer T A. J Exp Med. 1987;166:1011–1025. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ratnoff W D, Knez J J, Prince G M, Okada H, Lachmann P J, Medof M E. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992;87:415–421. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb03012.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Roberts W L, Myher J J, Kukis A, Low M G, Rosenberry T L. J Biol Chem. 1988;203:18766–18775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Roberts W L, Santikern S, Reinhold U N, Rosenberry T L. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:18776–18784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Masterson W J, Doering T C, Hart G W, Englund P T. Cell. 1989;56:793–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90684-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Menon A K, Mayor S, Ferguson M A, Duszenko M, Cross G A M. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:1970–1977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mayor S, Menon A K, Cross G A M. J Cell Biol. 1991;114:61–71. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lemansky P, Gupta D K, Meyale S, Tucker G, Tartakoff A M. Mol Cell Biol. 1991;11:3879–3885. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.3879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kamitani T, Menon A K, Hallaq Y, Warren C D, Yeh E T H. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:24611–24619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Puoti A, Desponds C, Fankhauser C, Conzelmann A. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:21051–21059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hirose S, Ravi L, Prince G M, Rosenfeld M G, Silber R, Andresen S W, Hazra S V, Medof M E. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992;89:6025–6029. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hirose S, Prince G M, Sevlever D, Ravi L, Rosenberry T L, Ueda E, Medof M E. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:16968–16974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ueda E, Sevlever D, Prince G M, Rosenberry T L, Hirose S, Medof M E. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:9998–10002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Singh N, Singleton D, Tartakoff A. Mol Cell Biol. 1991;11:2362–2374. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Testa U, Vainchenker W, Beucard Y, Rouyer-Fessard P, Guerrasio A, Titeux M, Laporte P, Bouguet J, Breton-Gorius J, Rosa J. Eur J Biochem. 1982;121:649–655. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05835.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kinoshita T, Medof M E, Silber R, Nussenzweig V. J Exp Med. 1985;162:75–92. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Millan J L, Stigbrand T. Eur J Biochem. 1983;136:1–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07697.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Davies A, Simmons D L, Hale G, Harrison R A, Tighe H, Lachmann P J, Waldmann H. J Exp Med. 1989;170:637–654. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Millan J L. J Biol Chem. 1986;261:3112–3115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kodakula K, Micanovic R, Gerber L, Tamburrini M, Brink L, Udenfriend S. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:4464–4470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Tykocinski M L, Shu H K, Ayers D J, Walter E I, Getty R R, Groger R K, Hauer C A, Medof M E. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1988;85:3555–3559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Haas R, Rosenberry T L. Anal Biochem. 1985;148:154–162. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90640-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hirose S, Mohney R P, Mutka S C, Ravi L, Singleton D R, Perry G, Tartakoff A M, Medof M E. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:5272–5278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Toutant J-P, Roberts W L, Murray N R, Rosenberry T L. Eur J Biochem. 1989;180:503–508. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ogata S, Hayashi Y, Takami N, Ikehara Y. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:10489–10494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hawrylak K, Stinson R S. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:14368–14373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Holingren P A, Stigbrand T. Biochem Genet. 1976;14:777–789. doi: 10.1007/BF00485341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lozzio L B, Lozzio B B. Blood. 1975;45:321–324. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Villeval J L, Pelicci P G, Tabilio A, Titeux M, Henri A, Houesche F, Thomopoulos P, Vainchenker W, Garbaz M, Rochant H, et al. Exp Cell Res. 1983;146:428–435. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Takami N, Ogata S, Oda K, Misumi Y, Ikehara Y. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:3016–3021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Singh N, Zoeller R A, Tykocinski M L, Lazarow P B, Tartakoff A M. Mol Cell Biol. 1994;14:21–31. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Toutant J-P, Richards M K, Krall J A, Rosenberry T L. Eur J Biochem. 1990;187:31–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Maxwell S E, Ramalingam S, Gerber L D, Brink L, Udenfriend S. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:19576–19582. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.33.19576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kodukula K, Amthauer R, Cines D, Yeh E, Brink L, Thomas L, Udenfriend S. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992;89:4982–4985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Hamburger D, Egerton M, Riezman H. J Cell Biol. 1995;129:629–639. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Benghezal M, Lipke P N, Conzelmann A. J Cell Biol. 1995;130:1333–1344. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.6.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Mohney R P, Knez J J, Ravi L, Sevlever D, Rosenberry T L, Hirose S, Medof M E. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:6536–6542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Chen R, Udenfriend S, Prince G M, Maxwell S E, Ramalingam S, Gerber L D, Knez J, Medof M E. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:2280–2284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.6.2280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Yu J, Nagarajan S, Knez J J, Udenfriend S, Chen R, Medof M E. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:12580–12585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.23.12580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]