Abstract
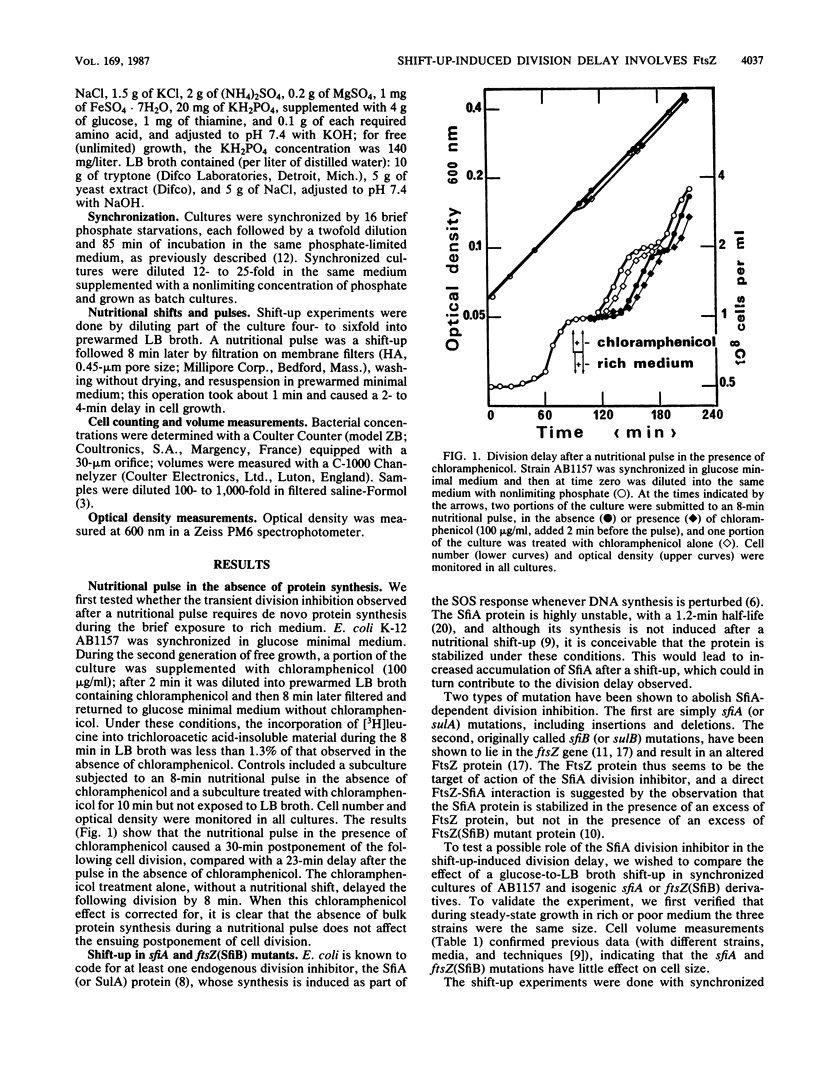
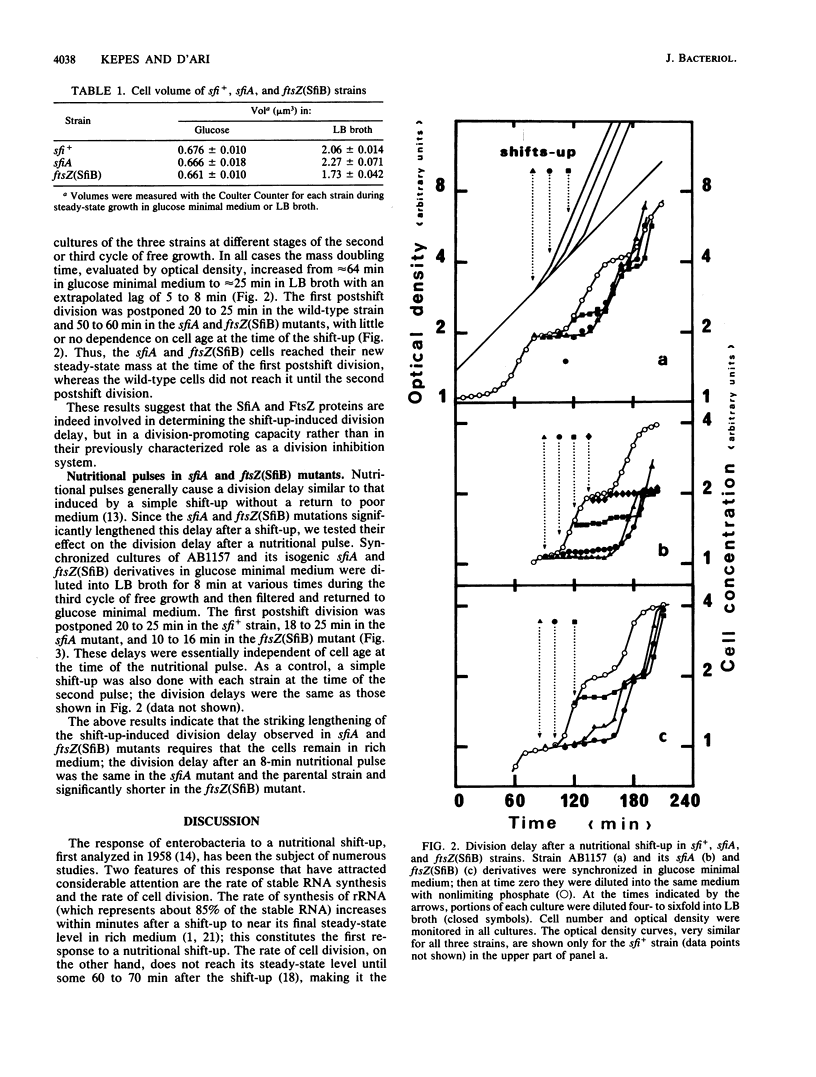
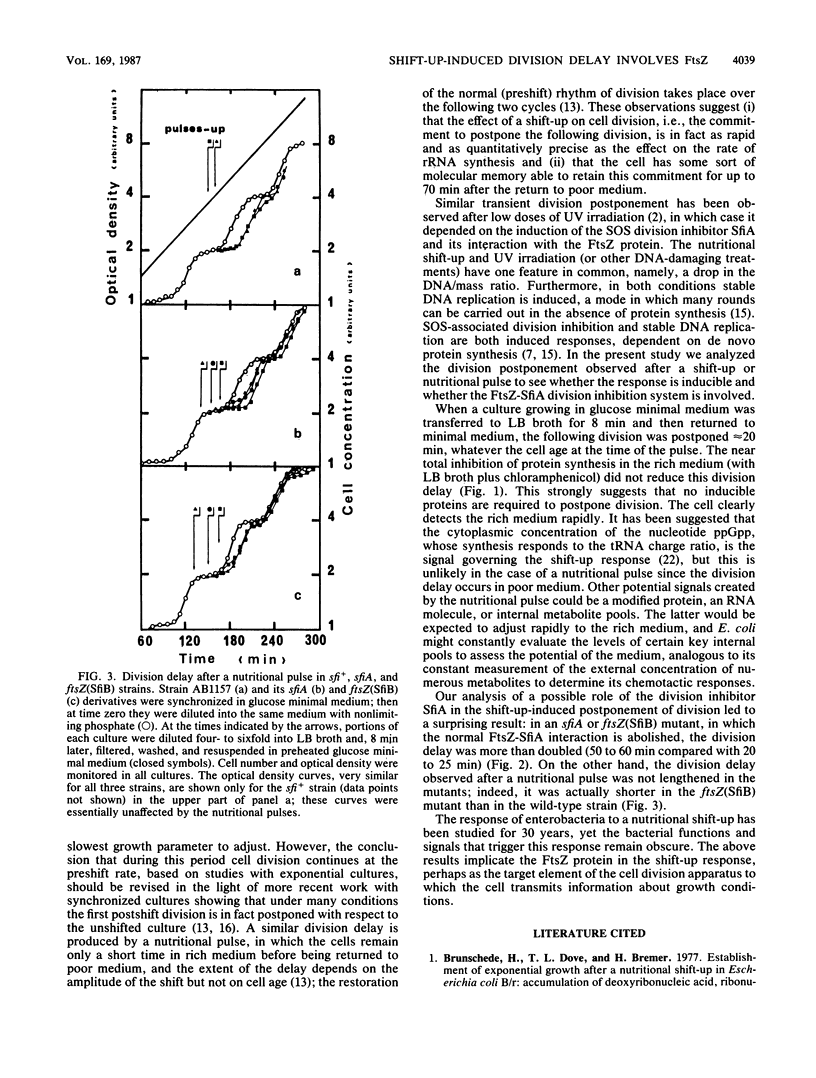
A nutritional shift-up from glucose minimal medium to LB broth was previously shown to cause a division delay of about 20 min in synchronized cultures of Escherichia coli, and a similar delay was observed after a nutritional pulse (a shift-up followed rapidly by a return to glucose minimal medium). Using synchronized cultures, we show here that the pulse-induced division delay does not require protein synthesis during the period in LB broth, suggesting that a nonprotein signal is generated by the shift-up and transmitted to the cell division machinery. The cell division protein FtsZ, target of the SOS-associated division inhibitor SfiA (or SulA), seems to be involved in the postshift division delay. Mutants in which the FtsZ-SfiA interaction is reduced, either sfiA (loss of SfiA) or ftsZ(SfiB) (modification of FtsZ), have a 50- to 60-min division delay after a shift-up. Furthermore, after a nutritional pulse, the ftsZ(SfiB) mutant had only a 10- to 16-min delay. These results suggest that the FtsZ protein is the target element of the cell division machinery to which the shift-up signal is transmitted.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burton P., Holland I. B. Two pathways of division inhibition in UV-irradiated E. coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;190(2):309–314. doi: 10.1007/BF00330656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ari R., Huisman O. Novel mechanism of cell division inhibition associated with the SOS response in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;156(1):243–250. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.1.243-250.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmstetter C., Cooper S., Pierucci O., Revelas E. On the bacterial life sequence. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:809–822. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland I. B., Jones C. The role of the FtsZ protein (SfiB) in UV-induced division inhibition and in the normal Escherichia coli cell division cycle. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1985 Jan-Feb;136A(1):165–171. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(85)80037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman O., D'Ari R. An inducible DNA replication-cell division coupling mechanism in E. coli. Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):797–799. doi: 10.1038/290797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman O., D'Ari R., George J. Inducible sfi dependent division inhibition in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;177(4):629–636. doi: 10.1007/BF00272673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman O., D'Ari R., Gottesman S. Cell-division control in Escherichia coli: specific induction of the SOS function SfiA protein is sufficient to block septation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4490–4494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman O., Jacques M., D'ari R., Caro L. Role of the sfiA-dependent cell division regulation system in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):1072–1074. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.1072-1074.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. A., Holland I. B. Inactivation of essential division genes, ftsA, ftsZ, suppresses mutations at sfiB, a locus mediating division inhibition during the SOS response in E. coli. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1181–1186. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01948.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C., Holland I. B. Role of the SulB (FtsZ) protein in division inhibition during the SOS response in Escherichia coli: FtsZ stabilizes the inhibitor SulA in maxicells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6045–6049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KJELDGAARD N. O., MAALOE O., SCHAECHTER M. The transition between different physiological states during balanced growth of Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Dec;19(3):607–616. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-3-607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kepes F., Kepes A. Synchronisation automatique de la croissance de Escherichia coli. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1980 Jan-Feb;131(1):3–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogoma T., Lark K. G. Characterization of the replication of Escherichia coli DNA in the absence of protein synthesis: stable DNA replication. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 15;94(2):243–256. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90081-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb A., McGrath B. E., Navre J. M., Pierucci O. Cell division during nutritional upshifts of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):631–637. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.631-637.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutkenhaus J. F. Coupling of DNA replication and cell division: sulB is an allele of ftsZ. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1339–1346. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1339-1346.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguin E., Brody H., Hill C. W., D'Ari R. SOS-associated division inhibition gene sfiC is part of excisable element e14 in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):464–466. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.464-466.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizusawa S., Gottesman S. Protein degradation in Escherichia coli: the lon gene controls the stability of sulA protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):358–362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierlich D. P. Regulation of ribonucleic acid synthesis in growing bacterial cells. I. Control over the total rate of RNA synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 30;72(3):751–764. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90189-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryals J., Little R., Bremer H. Control of rRNA and tRNA syntheses in Escherichia coli by guanosine tetraphosphate. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1261–1268. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1261-1268.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloan J. B., Urban J. E. Growth response of Escherichia coli to nutritional shift-up: immediate division stimulation in slow-growing cells. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):302–308. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.302-308.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



