Abstract
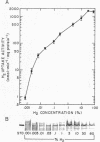
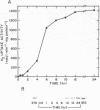
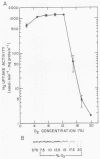
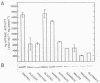
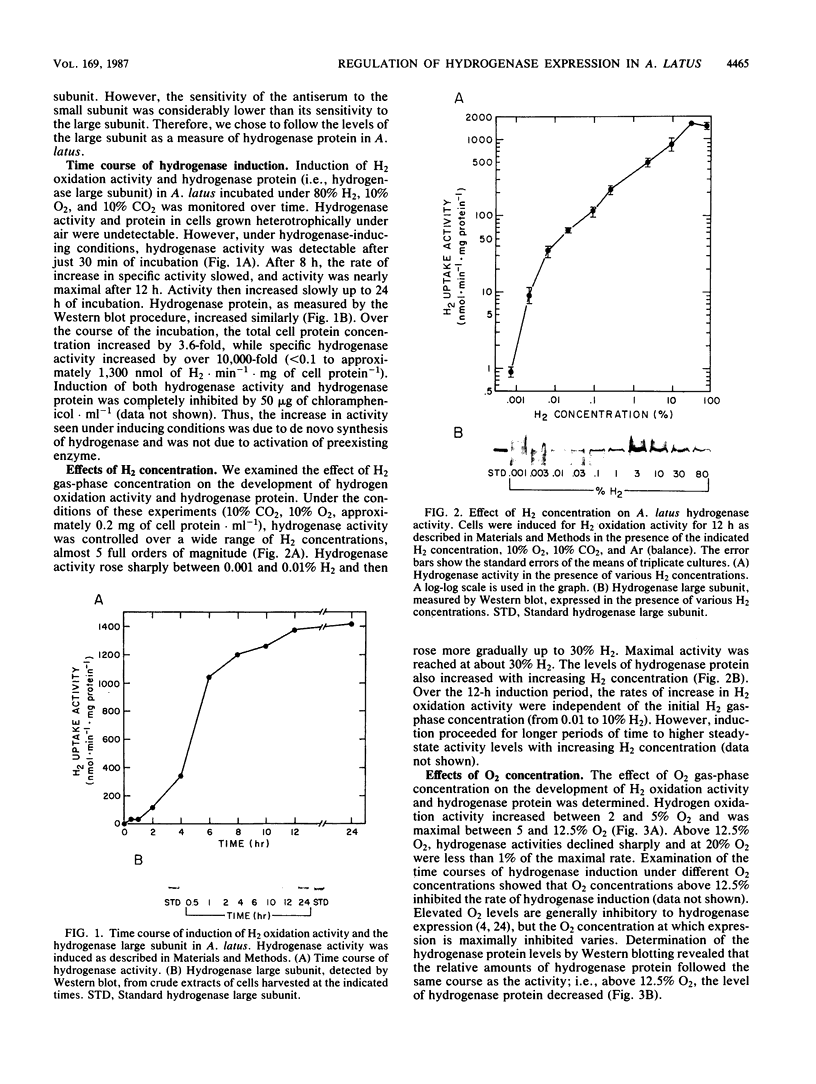
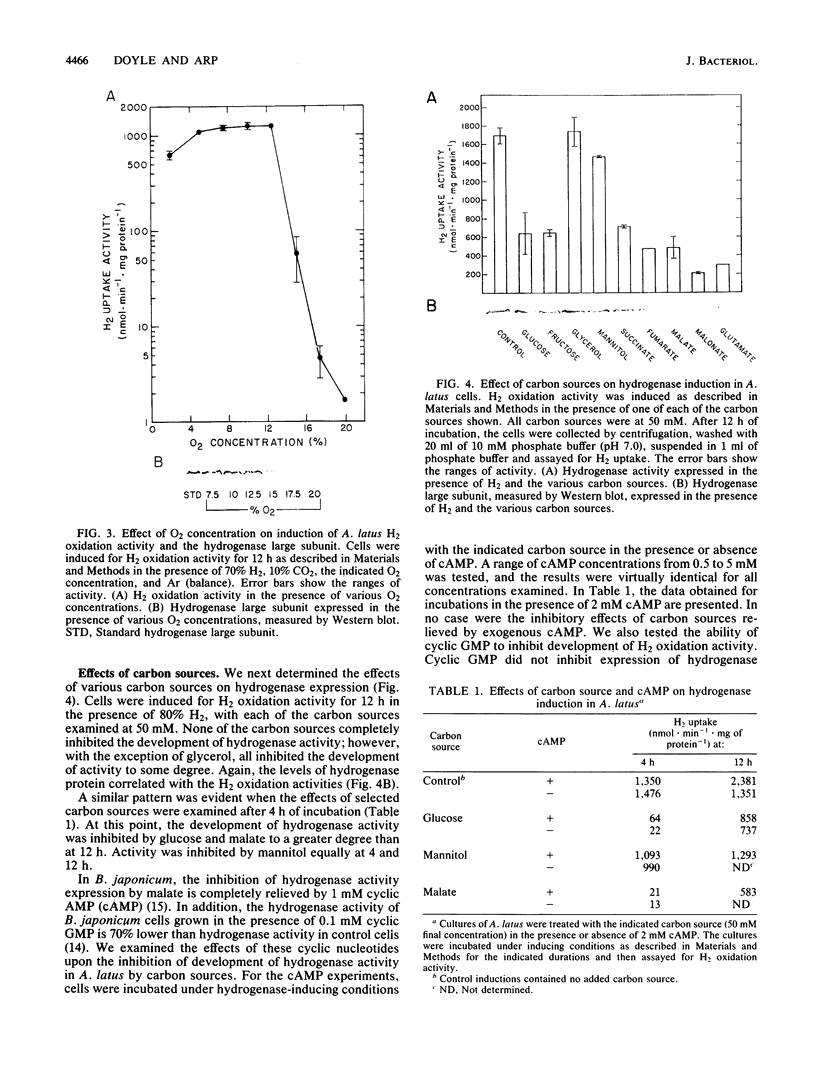
Regulation of H2 oxidation activity and hydrogenase protein levels in the free-living hydrogen bacterium Alcaligenes latus was investigated. Hydrogenase activity was induced when heterotrophically grown cells were transferred to chemolithoautotrophic conditions, i.e., in the presence of H2 and absence of carbon sources, with NH4Cl as the N source. Under these conditions, H2 oxidation activity was detectable after 30 min of incubation and reached near-maximal levels by 12 h. The levels of hydrogenase protein, as measured by a Western blot (immunoblot) assay of the hydrogenase large subunit, increased in parallel with activity. This increase suggested that the increased H2 oxidation activity was due to de novo synthesis of hydrogenase protein. H2 oxidation activity was controlled over a surprisingly wide range of H2 concentrations, between 0.001 and 30% in the gas phase. H2 oxidation activity was induced to high levels between 2 and 12.5% O2, and above 12.5% O2, H2 oxidation activity was inhibited. Almost all organic carbon sources studied inhibited the expression of hydrogenase, although none repressed hydrogenase synthesis completely. In all cases examined, hydrogenase protein, as detected by Western blot, paralleled the level of H2 oxidation activity, suggesting that control of hydrogenase activity was mediated through changes in hydrogenase protein levels.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arp D. J., McCollum L. C., Seefeldt L. C. Molecular and immunological comparison of membrane-bound, H2-oxidizing hydrogenases of Bradyrhizobium japonicum, Alcaligenes eutrophus, Alcaligenes latus, and Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):15–20. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.15-20.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkett C. R., Foster K. E., Johnson L., Gull K. Use of monoclonal antibodies to analyse the expression of a multi-tubulin family. FEBS Lett. 1985 Aug 5;187(2):211–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81244-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowien B., Schlegel H. G. Physiology and biochemistry of aerobic hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:405–452. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cangelosi G. A., Wheelis M. L. Regulation by molecular oxygen and organic substrates of hydrogenase synthesis in Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):138–144. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.138-144.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich C. G. Depression of hydrogenase during limitation of electron donors and derepression of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase during carbon limitation of Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):203–210. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.203-210.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyhse-Andersen J. Electroblotting of multiple gels: a simple apparatus without buffer tank for rapid transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide to nitrocellulose. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1984 Dec;10(3-4):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(84)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim S. T., Hennecke H., Scott D. B. Effect of cyclic guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate on nitrogen fixation in Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jul;139(1):256–263. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.1.256-263.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim S. T., Shanmugam K. T. Regulation of hydrogen utilisation in Rhizobium japonicum by cyclic AMP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 May 16;584(3):479–492. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90121-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier R. J., Hanus F. J., Evans H. J. Regulation of hydrogenase in Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):825–829. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.825-829.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merberg D., O'Hara E. B., Maier R. J. Regulation of hydrogenase in Rhizobium japonicum: analysis of mutants altered in regulation by carbon substrates and oxygen. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1236–1242. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1236-1242.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nokhal T. H., Schlegel H. G. The regulation of hydrogenase formation as a differentiating character of strains of Paracoccus denitrificans. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1980;46(2):143–155. doi: 10.1007/BF00444069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkwart M., Schneider K., Schlegel H. G. Purification and properties of the membrane-bound hydrogenase from N2-fixing Alcaligenes latus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jun 29;745(3):267–278. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seefeldt L. C., Arp D. J. Purification to homogeneity of Azotobacter vinelandii hydrogenase: a nickel and iron containing alpha beta dimer. Biochimie. 1986 Jan;68(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(86)81064-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R., Healey F. P., Myers J. Amperometric measurement of hydrogen evolution in chlamydomonas. Plant Physiol. 1971 Jul;48(1):108–110. doi: 10.1104/pp.48.1.108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]