Abstract
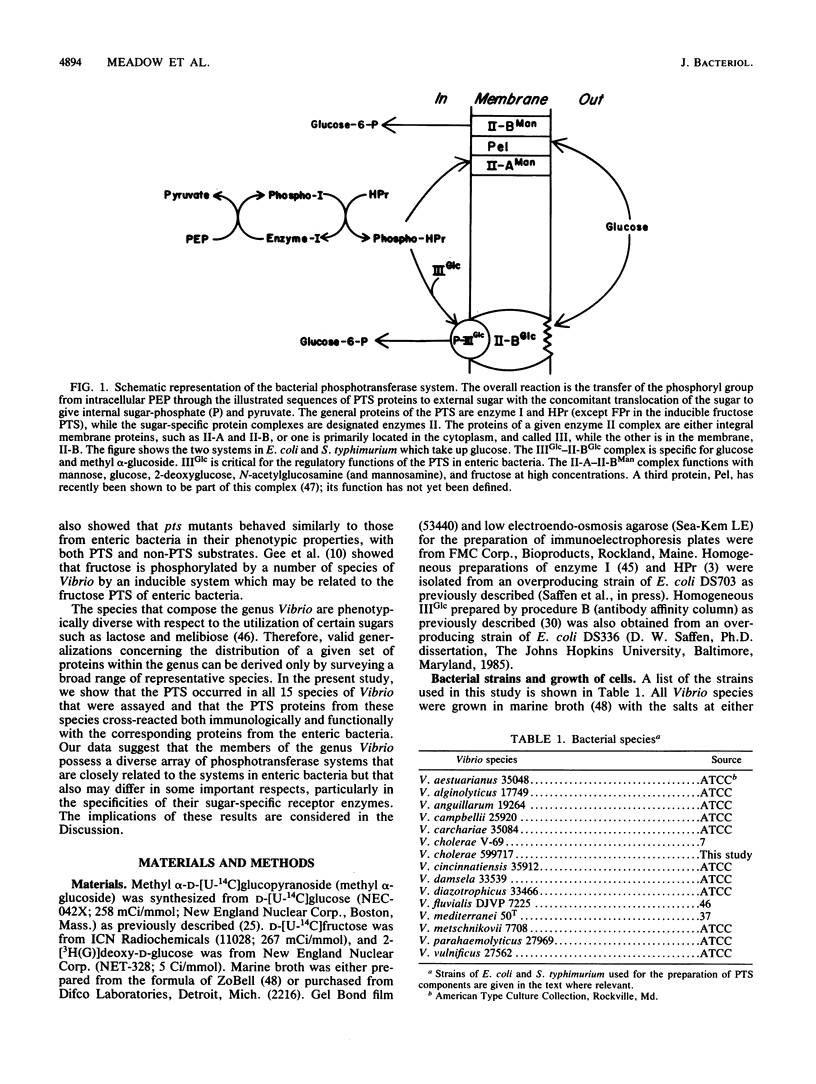
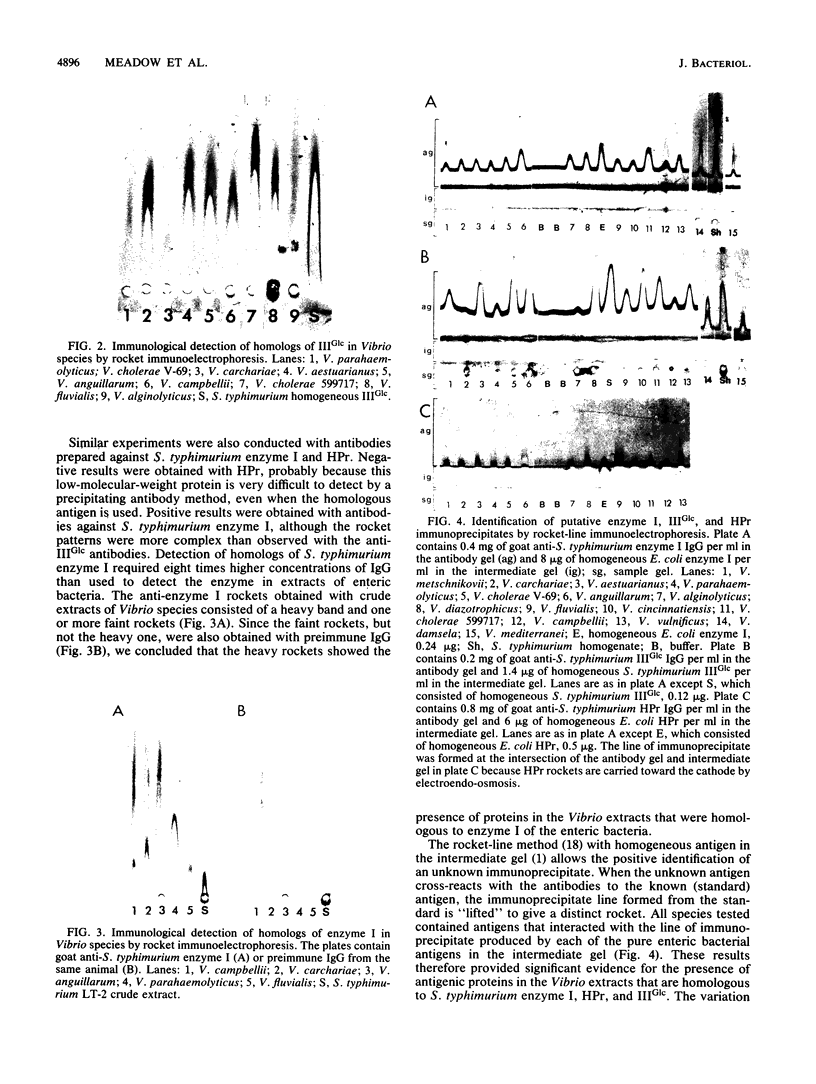
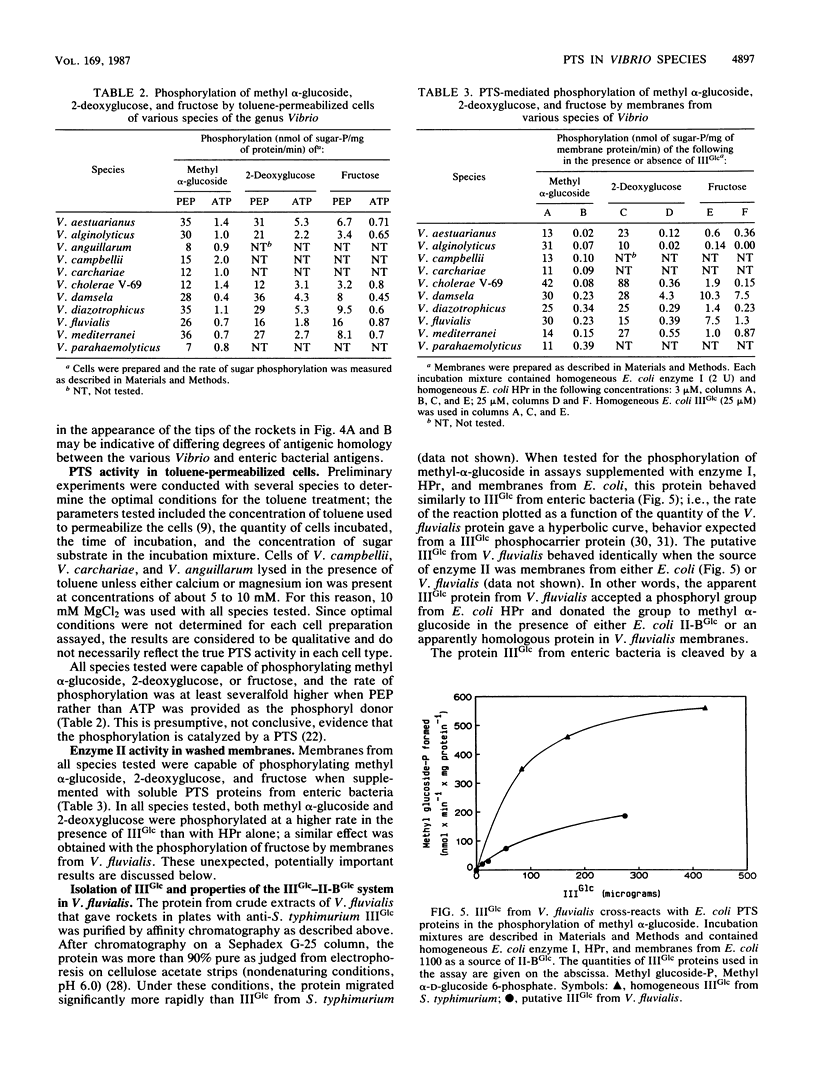
The genus Vibrio is one of the most common and widely distributed groups of marine bacteria. Studies on the physiology of marine Vibrio species were initiated by examining 15 species for the bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate:glycose phosphotransferase system (PTS). All species tested contained a PTS analogous to the glucose-specific (IIGlc) system in enteric bacteria. Crude extracts of the cells showed immunological cross-reactivity with antibodies to enzyme I, HPr, and IIIGlc from Salmonella typhimurium when assayed by the rocket-line method. Toluene-permeabilized cells of 11 species were tested and were active in phosphorylating methyl alpha-D-glucoside with phosphoenolpyruvate but not ATP as the phosphoryl donor. Membranes from 10 species were assayed, and they phosphorylated methyl alpha-D-glucoside when supplemented with a phospho-IIIGlc-generating system composed of homogeneous proteins from enteric bacteria. Toluene-permeabilized cells and membranes of seven species were assayed, as were phosphorylated fructose and 2-deoxyglucose. IIIGlc was isolated from Vibrio fluvialis and was active in phosphorylating methyl alpha-D-glucoside when supplemented with a phospho-HPr-generating system composed of homogeneous proteins from Escherichia coli and membranes from either E. coli or V. fluvialis. These results show that the bacterial PTS is widely distributed in the marine environment and that it is likely to have a significant role in marine bacterial physiology and in the marine ecosystem.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelsen N. H. Intermediate gel in crossed and in fused rocket immunoelectrophoresis. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:71–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03782.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beneski D. A., Nakazawa A., Weigel N., Hartman P. E., Roseman S. Sugar transport by the bacterial phosphotransferase system. Isolation and characterization of a phosphocarrier protein HPr from wild type and mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14492–14498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvet O. M., Grimont P. A. Diversity of the phosphoenolpyruvate/glucose phosphotransferase system in the Enterobacteriaceae. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1987 Jan-Feb;138(1):3–13. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(87)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colwell R. R., Seidler R. J., Kaper J., Joseph S. W., Garges S., Lockman H., Maneval D., Bradford H., Roberts N., Remmers E. Occurrence of Vibrio cholerae serotype O1 in Maryland and Louisiana estuaries. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Feb;41(2):555–558. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.2.555-558.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Stackebrandt E., Hespell R. B., Gibson J., Maniloff J., Dyer T. A., Wolfe R. S., Balch W. E., Tanner R. S., Magrum L. J. The phylogeny of prokaryotes. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):457–463. doi: 10.1126/science.6771870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gachelin G. A new assay of the phosphotransferase system in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Feb 21;34(4):382–387. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90392-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee D. L., Baumann P., Baumann L. Enzymes of D-fructose catabolism in species of Beneckea and Photobacterium. Arch Microbiol. 1975 Apr 7;103(2):205–207. doi: 10.1007/BF00436351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geerse R. H., Ruig C. R., Schuitema A. R., Postma P. W. Relationship between pseudo-HPr and the PEP: fructose phosphotransferase system in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Jun;203(3):435–444. doi: 10.1007/BF00422068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll J. Rocket-line immunoelectrophoresis (76). Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:83–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubota Y., Iuchi S., Fujisawa A., Tanaka S. Separation of four components of the phosphoenolpyruvate: glucose phosphotransferase system in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Microbiol Immunol. 1979;23(3):131–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1979.tb00450.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kukuruzinska M. A., Harrington W. F., Roseman S. Sugar transport by the bacterial phosphotransferase system. Studies on the molecular weight and association of enzyme I. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14470–14476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kundig W., Roseman S. Sugar transport. I. Isolation of a phosphotransferase system from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1393–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Electroimmuno assay. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1972;124:21–37. doi: 10.3109/00365517209102748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu K. D., Roseman S. Kinetic characterization and regulation of phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent methyl alpha-D-glucopyranoside transport by Salmonella typhimurium membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7142–7145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meadow N. D., Coyle P., Komoryia A., Anfinsen C. B., Roseman S. Limited proteolysis of IIIGlc, a regulatory protein of the phosphoenolpyruvate:glycose phosphotransferase system, by membrane-associated enzymes from Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13504–13509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meadow N. D., Roseman S. Sugar transport by the bacterial phosphotransferase system. Isolation and characterization of a glucose-specific phosphocarrier protein (IIIGlc) from Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14526–14537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meadow N. D., Rosenberg J. M., Pinkert H. M., Roseman S. Sugar transport by the bacterial phosphotransferase system. Evidence that crr is the structural gene for the Salmonella typhimurium glucose-specific phosphocarrier protein IIIGlc. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14538–14542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meadow N. D., Saffen D. W., Dottin R. P., Roseman S. Molecular cloning of the crr gene and evidence that it is the structural gene for IIIGlc, a phosphocarrier protein of the bacterial phosphotransferase system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2528–2532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monthony J. F., Wallace E. G., Allen D. M. A non-barbital buffer for immunoelectrophoresis and zone electrophoresis in agarose gels. Clin Chem. 1978 Oct;24(10):1825–1827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postma P. W., Cordaro J. C., Roseman S. Sugar transport. A pleiotropic membrane mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7862–7876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postma P. W., Lengeler J. W. Phosphoenolpyruvate:carbohydrate phosphotransferase system of bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):232–269. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.232-269.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano A. H., Eberhard S. J., Dingle S. L., McDowell T. D. Distribution of the phosphoenolpyruvate: glucose phosphotransferase system in bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):808–813. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.808-813.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Simoni R. D., Roseman S. The physiological behavior of enzyme I and heat-stable protein mutants of a bacterial phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5870–5873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simidu U., Tsukamoto K. Habitat segregation and biochemical activities of marine members of the family vibrionaceae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Oct;50(4):781–790. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.4.781-790.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoni R. D., Roseman S., Saier M. H., Jr Sugar transport. Properties of mutant bacteria defective in proteins of the phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6584–6597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waygood E. B., Mattoo R. L., Peri K. G. Phosphoproteins and the phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli: evidence for IIImannose, IIIfructose, IIIglucitol, and the phosphorylation of enzyme IImannitol and enzyme IIN-acetylglucosamine. J Cell Biochem. 1984;25(3):139–159. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240250304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waygood E. B., Meadow N. D., Roseman S. Modified assay procedures for the phosphotransferase system in enteric bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1979 May;95(1):293–304. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90219-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel N., Waygood E. B., Kukuruzinska M. A., Nakazawa A., Roseman S. Sugar transport by the bacterial phosphotransferase system. Isolation and characterization of enzyme I from Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14461–14469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams N., Fox D. K., Shea C., Roseman S. Pel, the protein that permits lambda DNA penetration of Escherichia coli, is encoded by a gene in ptsM and is required for mannose utilization by the phosphotransferase system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8934–8938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]