Abstract
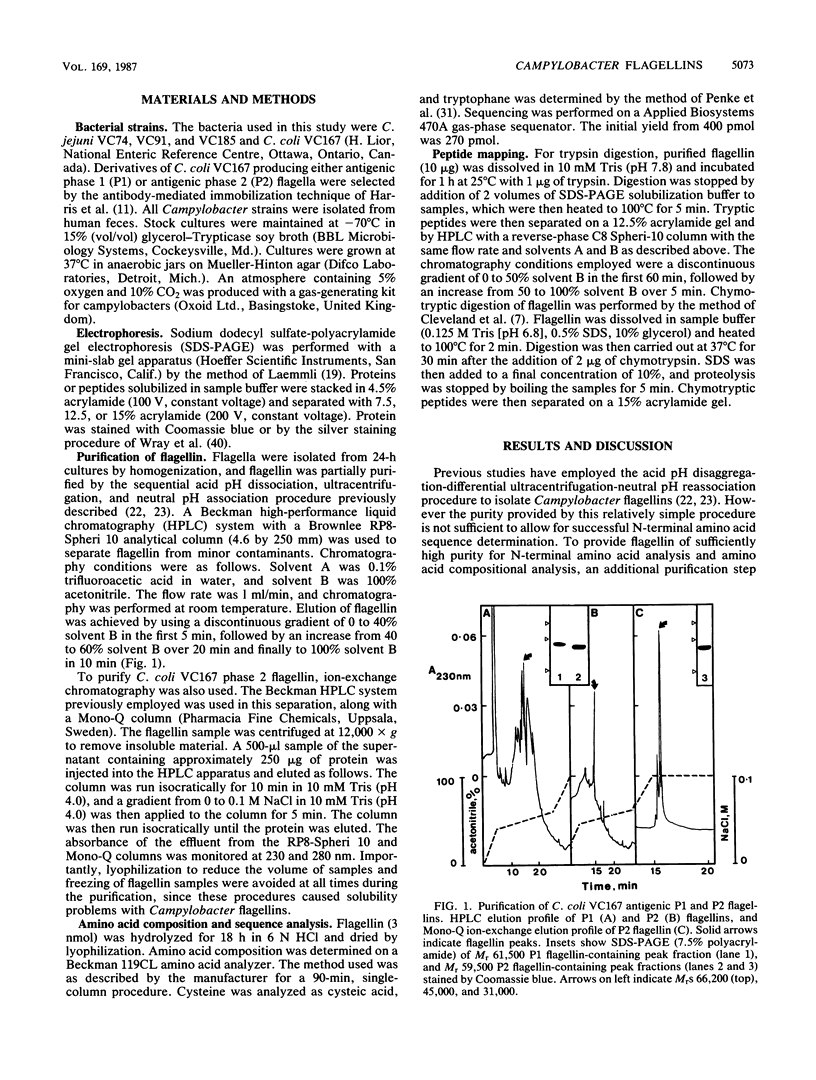
Sequential acid pH dissociation, differential ultracentrifugation, and neutral pH reassociation were used to partially purify serotypically distinct flagella from three strains of Campylobacter jejuni and the two antigenic phases of flagella of Campylobacter coli VC167. Each C. jejuni flagellin and C. coli VC167 antigenic phase 1 flagellin were purified to homogeneity by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography with a C8 Spheri-10 column. C. coli VC167 antigenic phase 2 was purified to homogeneity by ion-exchange chromatography with a Mono-Q column. Amino acid compositional analysis put the C. jejuni flagellin molecular weight in the range 63,200 to 63,800 and the C. coli antigenic phase 1 and 2 flagellins at 61,500 and 59,500, respectively. The amino acid compositions of the C. jejuni were similar to each other and to the C. coli VC167 antigenic phase 1 and phase 2 flagellins. One-dimensional peptide mapping of the C. jejuni flagellins by partial digestion with trypsin or chymotrypsin confirmed the structural similarities of the C. jejuni flagellins and the C. coli VC167 antigenic phase 1 flagellin and showed that C. coli VC167 antigenic phase 2 flagellin was structurally distinct from the phase 1 flagellin. The antigenic phase 2 flagellin was especially sensitive to digestion by chymotrypsin. Amino-terminal sequence analysis showed that the 20 N-terminal amino acids of the Campylobacter flagellins were highly conserved. The Campylobacter flagellins also shared limited sequence homology with the N-terminal sequences reported for Salmonella and Bacillus flagellins.
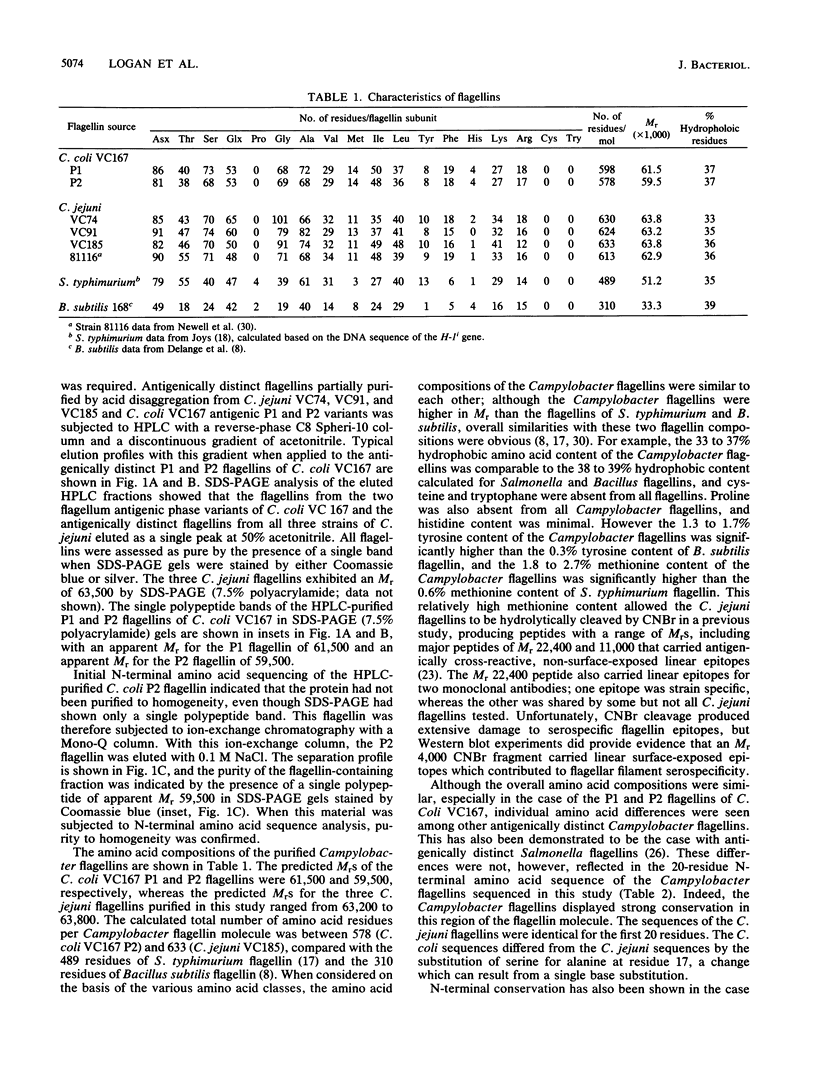
Full text
PDF
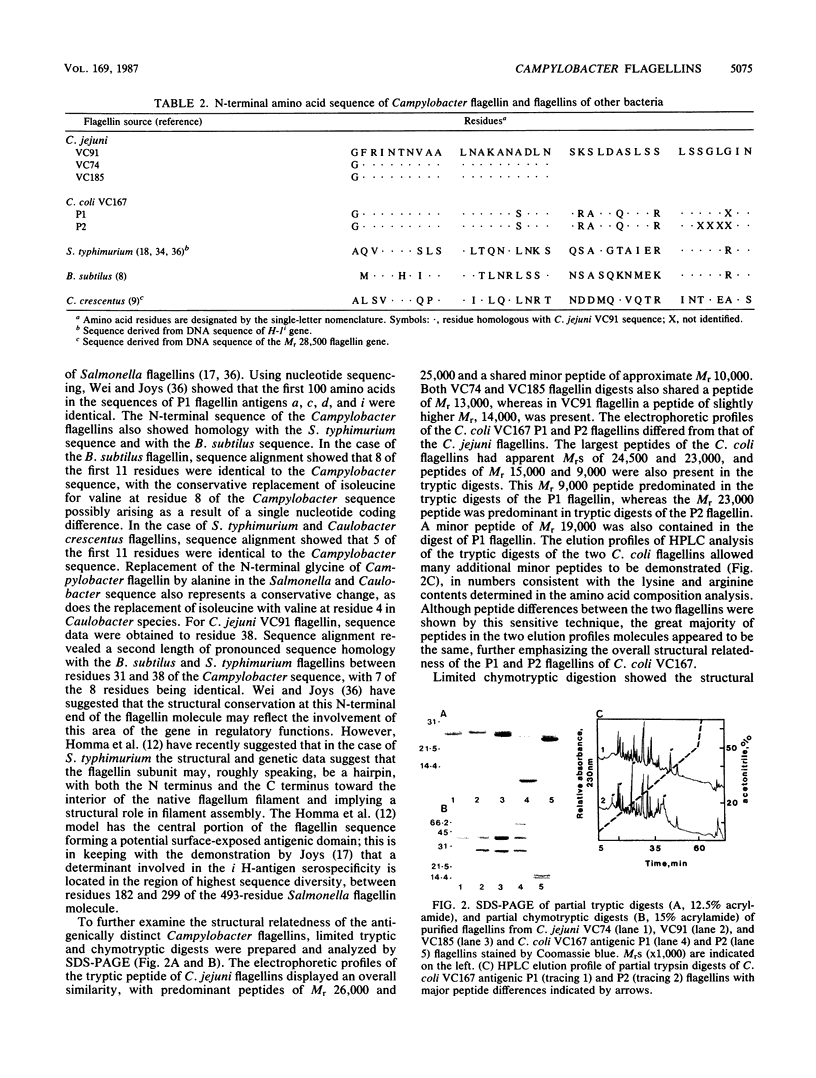


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attridge S. R., Rowley D. The role of the flagellum in the adherence of Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):864–872. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Hopkins J. A., Perez-Perez G. I., Cody H. J., Newell D. G. Antigenicity of Campylobacter jejuni flagella. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):47–52. doi: 10.21236/ada265460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butzler J. P., Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis. Clin Gastroenterol. 1979 Sep;8(3):737–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell M. B., Guerry P., Lee E. C., Burans J. P., Walker R. I. Reversible expression of flagella in Campylobacter jejuni. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):941–943. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.941-943.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carsiotis M., Weinstein D. L., Karch H., Holder I. A., O'Brien A. D. Flagella of Salmonella typhimurium are a virulence factor in infected C57BL/6J mice. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):814–818. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.814-818.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury M. N. Campylobacter jejuni enteritis; a review. Trop Geogr Med. 1984 Sep;36(3):215–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delange R. J., Chang J. Y., Shaper J. H., Martinez R. J., Komatsu S. K., Glazer A. N. On the amino-acid sequence of flagellin from Bacillus subtilis 168: comparison with other bacterial flagellins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3428–3431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill P. R., Agabian N. The nucleotide sequence of the Mr = 28,500 flagellin gene of Caulobacter crescentus. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7395–7401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guentzel M. N., Berry L. J. Motility as a virulence factor for Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):890–897. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.890-897.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris L. A., Logan S. M., Guerry P., Trust T. J. Antigenic variation of Campylobacter flagella. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5066–5071. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5066-5071.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Fujita H., Yamaguchi S., Iino T. Regions of Salmonella typhimurium flagellin essential for its polymerization and excretion. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):291–296. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.291-296.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim G. F., Fleet G. H., Lyons M. J., Walker R. A. Immunological relationships between Salmonella flagella and their potential application for salmonellae detection by immunoassay. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1985;174(2):87–99. doi: 10.1007/BF02123230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim G. F., Fleet G. H., Lyons M. J., Walker R. A. Immunological relationships between Salmonella flagellins and between these and flagellins from other species of Enterobacteriaceae. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1985;174(2):101–113. doi: 10.1007/BF02123231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino T. Genetics of structure and function of bacterial flagella. Annu Rev Genet. 1977;11:161–182. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.11.120177.001113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Isaacson R. E. Proteinaceous bacterial adhesins and their receptors. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1983;10(3):229–260. doi: 10.3109/10408418209113564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joys T. M. Identification of an antibody binding site in the phase-1 flagellar protein of Salmonella typhimurium. Microbios. 1976;15(61-62):221–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joys T. M. The covalent structure of the phase-1 flagellar filament protein of Salmonella typhimurium and its comparison with other flagellins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15758–15761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A., O'Rourke J. L., Barrington P. J., Trust T. J. Mucus colonization as a determinant of pathogenicity in intestinal infection by Campylobacter jejuni: a mouse cecal model. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):536–546. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.536-546.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lior H., Woodward D. L., Edgar J. A., Laroche L. J., Gill P. Serotyping of Campylobacter jejuni by slide agglutination based on heat-labile antigenic factors. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):761–768. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.761-768.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan S. M., Trust T. J. Location of epitopes on Campylobacter jejuni flagella. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):739–745. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.739-745.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan S. M., Trust T. J. Molecular identification of surface protein antigens of Campylobacter jejuni. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):675–682. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.675-682.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCDONOUGH M. W. AMINO ACID COMPOSITION OF ANTIGENICALLY DISTINCT SALMONELLA FLAGELLAR PROTEINS. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jun;12:342–355. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80258-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills S. D., Bradbury W. C., Penner J. L. Isolation and characterization of a common antigen in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jul;24(1):69–75. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.1.69-75.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montie T. C., Doyle-Huntzinger D., Craven R. C., Holder I. A. Loss of virulence associated with absence of flagellum in an isogenic mutant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the burned-mouse model. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):1296–1298. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.1296-1298.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morooka T., Umeda A., Amako K. Motility as an intestinal colonization factor for Campylobacter jejuni. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Aug;131(8):1973–1980. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-8-1973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell D. G., McBride H., Dolby J. M. Investigations on the role of flagella in the colonization of infant mice with Campylobacter jejuni and attachment of Campylobacter jejuni to human epithelial cell lines. J Hyg (Lond) 1985 Oct;95(2):217–227. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400062653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penke B., Ferenczi R., Kovács K. A new acid hydrolysis method for determining tryptophan in peptides and proteins. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk P. J., Zoltowska B., Trust T. J., Lane D. J., Olsen G. J., Pace N. R., Stahl D. A. Campylobacter pylori, the spiral bacterium associated with human gastritis, is not a true Campylobacter sp. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2137–2141. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2137-2141.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis: a "new" disease. Br Med J. 1977 Jul 2;2(6078):9–11. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6078.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szekely E., Simon M. DNA sequence adjacent to flagellar genes and evolution of flagellar-phase variation. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):74–81. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.74-81.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. I., Caldwell M. B., Lee E. C., Guerry P., Trust T. J., Ruiz-Palacios G. M. Pathophysiology of Campylobacter enteritis. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Mar;50(1):81–94. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.1.81-94.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei L. N., Joys T. M. Covalent structure of three phase-1 flagellar filament proteins of Salmonella. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 20;186(4):791–803. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90397-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein D. L., Carsiotis M., Lissner C. R., O'Brien A. D. Flagella help Salmonella typhimurium survive within murine macrophages. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):819–825. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.819-825.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenman W. M., Chai J., Louie T. J., Goudreau C., Lior H., Newell D. G., Pearson A. D., Taylor D. E. Antigenic analysis of Campylobacter flagellar protein and other proteins. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):108–112. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.108-112.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




