Abstract
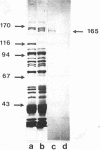
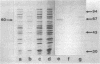
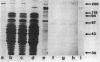
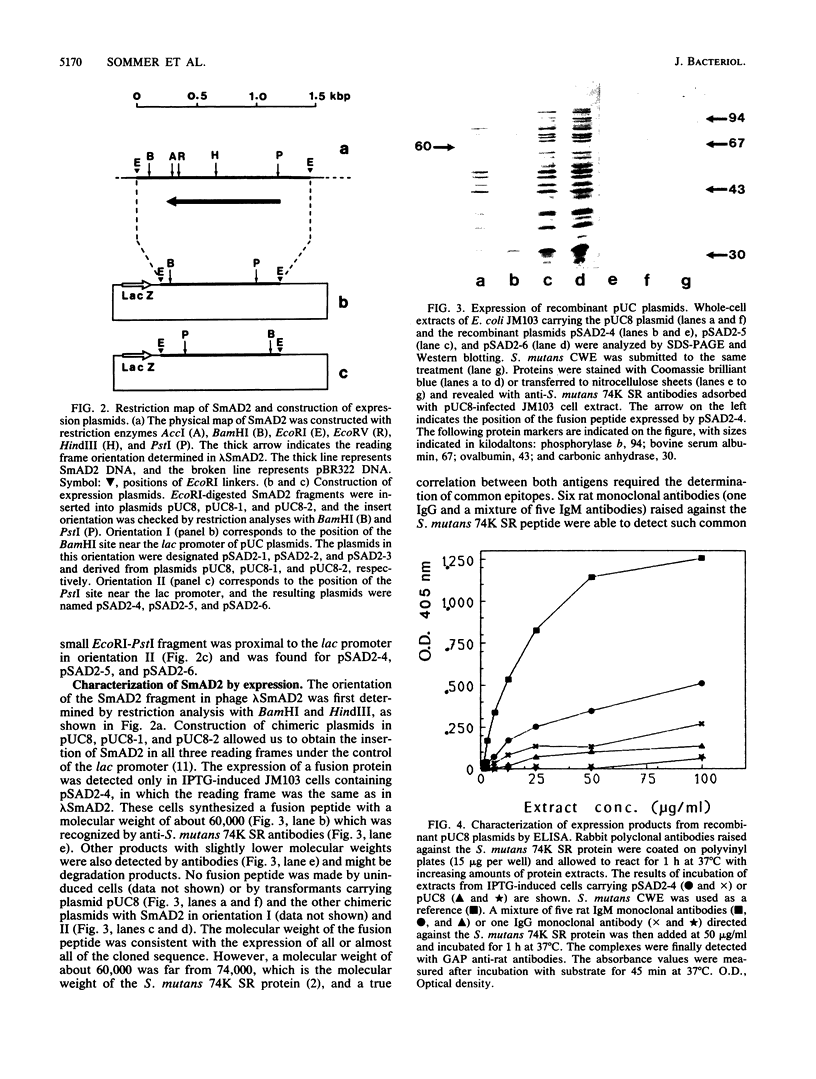
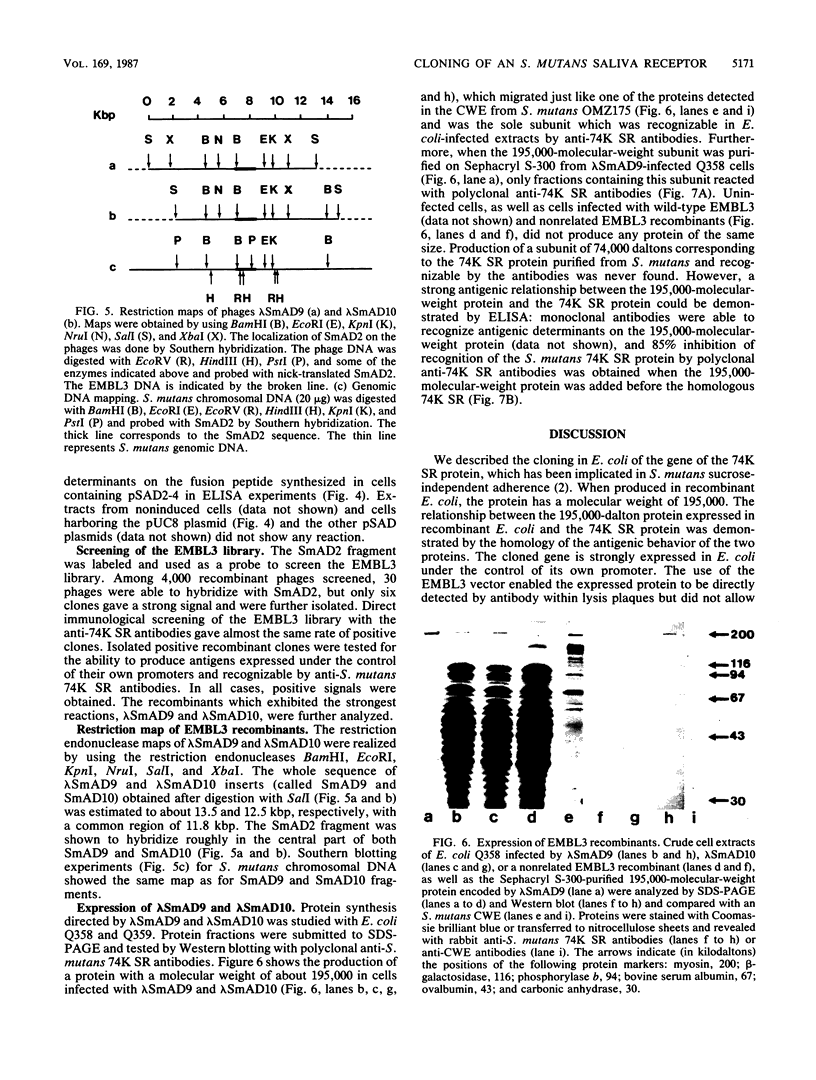
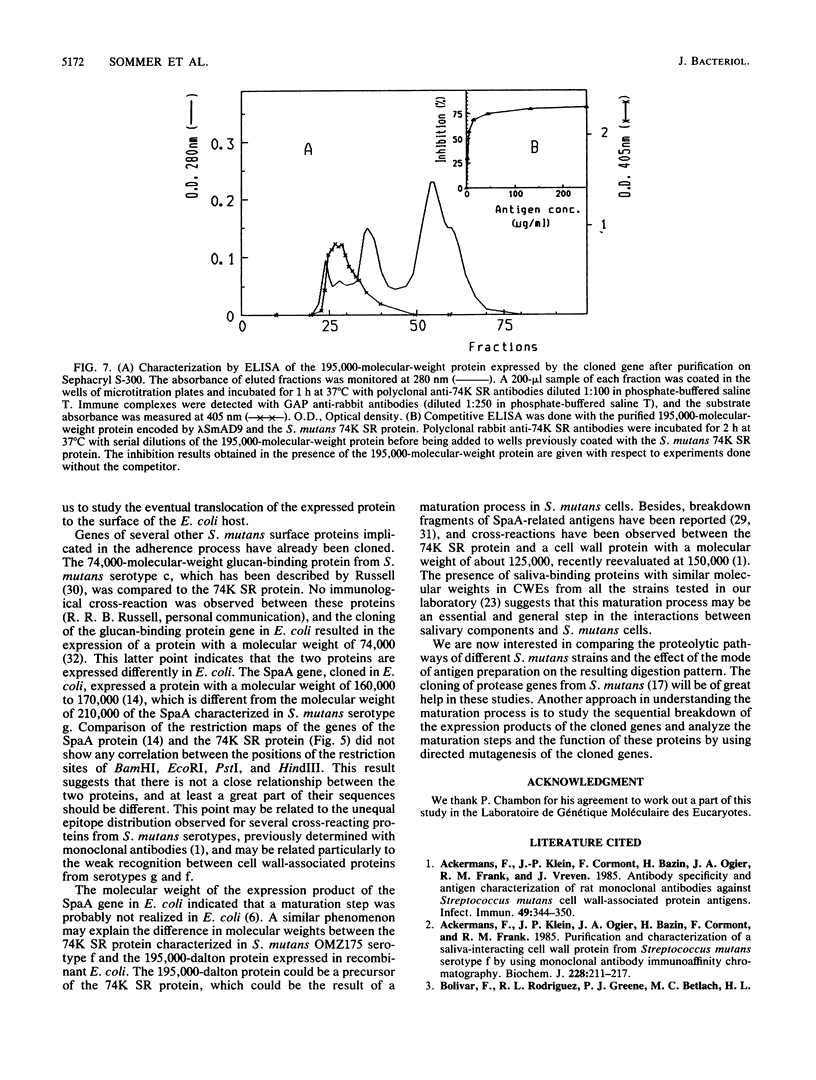
Genomic libraries from Streptococcus mutans OMZ175 were constructed in bacteriophage vectors. DNA fragments 1 to 2 kilobases in length were cloned in expression vector lambda gt11. S. mutans DNA fragments 15 to 20 kilobases in length were inserted in the BamHI site of phage EMBL3. Rabbit antiserum raised against an S. mutans saliva-interacting protein with a molecular weight of 74,000, designated 74K SR, was used to screen the lambda gt11 library. A recombinant phage carrying an S. mutans DNA sequence of 1.45 kilobases, lambda SmAD2, was detected and isolated. This fragment, named SmAD2, was used to construct the recombinant expression plasmid pSAD2-4 which encoded for the expression of a 60,000-molecular-weight protein controlled by the beta-galactosidase promoter from plasmid pUC8. The SmAD2 fragment and polyclonal anti-74K SR antibodies were used to screen the EMBL3 library. A total coincidence between the screening with antibodies and the DNA probe was observed, and two phages, lambda SmAD9 and lambda SmAD10, were isolated. They contained a common S. mutans DNA sequence of about 11.8 kilobases and coded for a protein with a molecular weight of about 195,000, which comigrated with a protein of an S. mutans cell wall extract. The expressed protein was purified, and a very strong relationship with the S. mutans 74K SR protein was found by competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Thus, cloning of the 74K SR gene allowed us to demonstrate that the saliva receptor appears to be a part of an S. mutans precursor molecule with a molecular mass of 195,000 daltons.
Full text
PDF

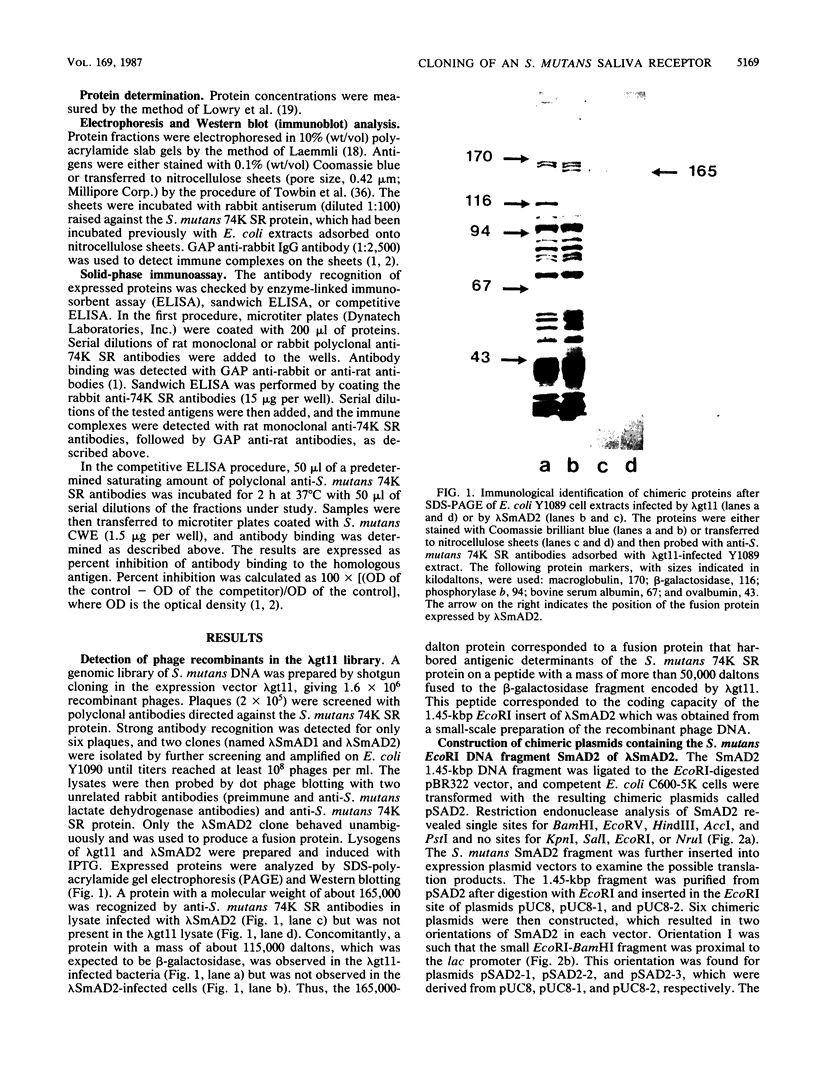

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermans F., Klein J. P., Cormont F., Bazin H., Ogier J. A., Frank R. M., Vreven J. Antibody specificity and antigen characterization of rat monoclonal antibodies against Streptococcus mutans cell wall-associated protein antigens. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):344–350. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.344-350.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackermans F., Klein J. P., Ogier J., Bazin H., Cormont F., Frank R. M. Purification and characterization of a saliva-interacting cell-wall protein from Streptococcus mutans serotype f by using monoclonal-antibody immunoaffinity chromatography. Biochem J. 1985 May 15;228(1):211–217. doi: 10.1042/bj2280211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark W. B., Gibbons R. J. Influence of salivary components and extracellular polysaccharide synthesis from sucrose on the attachment of Streptococcus mutans 6715 to hydroxyapatite surfaces. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):514–523. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.514-523.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss R., 3rd 1984 Kreshover lecture. Genetic analysis of Streptococcus mutans virulence and prospects for an anticaries vaccine. J Dent Res. 1986 Aug;65(8):1034–1045. doi: 10.1177/00220345860650080101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Etherden I. Comparative hydrophobicities of oral bacteria and their adherence to salivary pellicles. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1190–1196. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1190-1196.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna Z., Fregeau C., Préfontaine G., Brousseau R. Construction of a family of universal expression plasmid vectors. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):247–250. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. In vitro packaging of lambda and cosmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:299–309. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt R. G., Abiko Y., Saito S., Smorawinska M., Hansen J. B., Curtiss R., 3rd Streptococcus mutans genes that code for extracellular proteins in Escherichia coli K-12. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):147–156. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.147-156.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubacek J., Glover S. W. Complementation analysis of temperature-sensitive host specificity mutations in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1970 May 28;50(1):111–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90108-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs W. R., Barrett J. F., Clark-Curtiss J. E., Curtiss R., 3rd In vivo repackaging of recombinant cosmid molecules for analyses of Salmonella typhimurium, Streptococcus mutans, and mycobacterial genomic libraries. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):101–109. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.101-109.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogier J. A., Klein J. P., Sommer P., Frank R. M. Identification and preliminary characterization of saliva-interacting surface antigens of Streptococcus mutans by immunoblotting, ligand blotting, and immunoprecipitation. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):107–112. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.107-112.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell R., Neilan J., Gannon F. Plaque dot assay. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1541–1541. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robeson J. P., Barletta R. G., Curtiss R., 3rd Expression of a Streptococcus mutans glucosyltransferase gene in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):211–221. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.211-221.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. W., Bergmeier L. A., Zanders E. D., Lehner T. Protein antigens of Streptococcus mutans: purification and properties of a double antigen and its protease-resistant component. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):486–493. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.486-493.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R., Coleman D., Dougan G. Expression of a gene for glucan-binding protein from Streptococcus mutans in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Feb;131(2):295–299. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-2-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R. Glucan-binding proteins of Streptococcus mutans serotype c. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 May;112(1):197–201. doi: 10.1099/00221287-112-1-197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R. Wall-associated protein antigens of Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Sep;114(1):109–115. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-1-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöller M., Klein J. P., Frank R. M. Common antigens of streptococcal and non-streptococcal oral bacteria: immunochemical studies of extracellular and cell-wall-associated antigens from Streptococcus sanguis, Streptococcus mutans, Lactobacillus salivarius, and Actinomyces viscosus. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):52–60. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.52-60.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer P., Klein J. P., Schöller M., Frank R. M. Lactate dehydrogenase from Streptococcus mutans: purification, characterization, and crossed antigenicity with lactate dehydrogenases from Lactobacillus casei, Actinomyces viscosus, and Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):489–495. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.489-495.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., Jacobs T. Cell wall-associated protein antigens of Streptococcus salivarius: purification, properties, and function in adherence. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):233–242. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.233-242.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]