Abstract
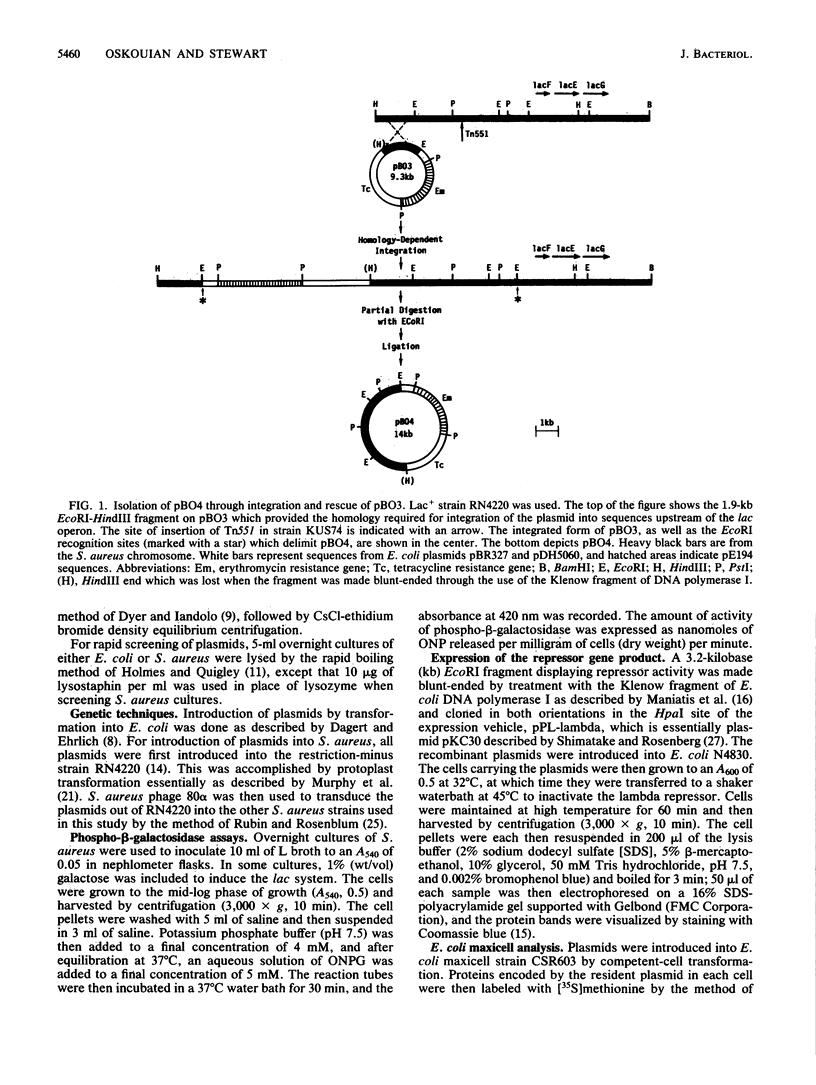
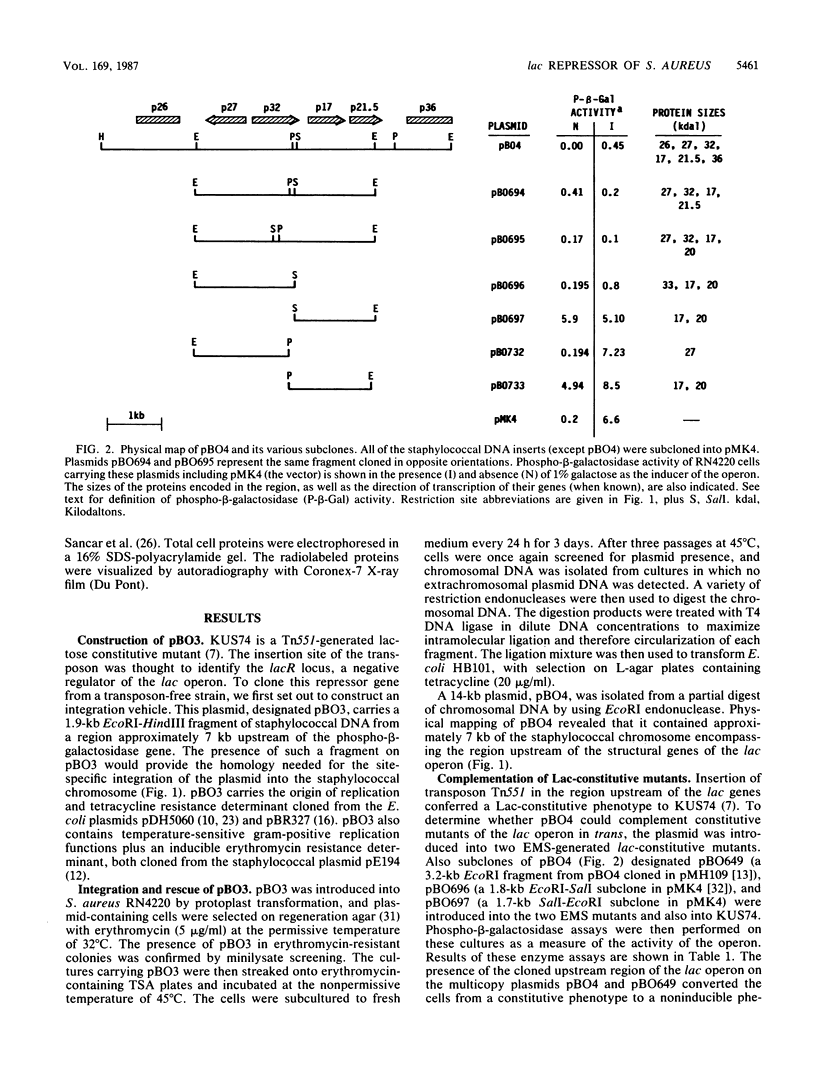
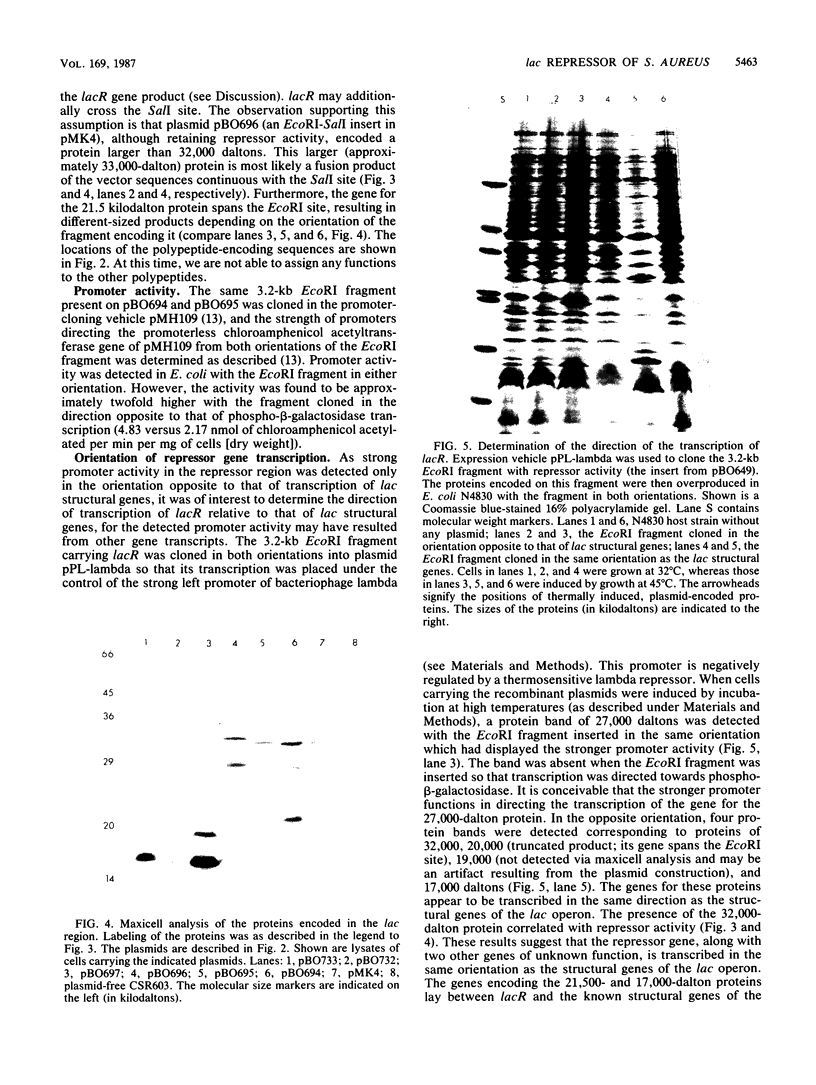
The genes responsible for utilization of lactose in Staphylococcus aureus are organized as an inducible operon, with galactose 6-phosphate being the intracellular inducer. To clone the repressor gene of this operon, we constructed an integration vehicle carrying 1.9 kilobases (kb) of DNA sequences from a region upstream of the structural genes of the operon. Through integration and subsequent rescue of this plasmid, we were able to clone approximately 7 kb of staphylococcal chromosomal DNA. We have shown that the plasmid insert complemented lac constitutive mutants. This repressor activity was localized to a 1.8-kb DNA fragment and, through maxicell analysis, was shown to correlate with the presence of a polypeptide with an apparent molecular weight of 32,000. Furthermore, a region between the repressor gene and the other genes of the operon was identified which, when carried on multicopy plasmids, resulted in expression of the operon in the absence of any exogenous induction. This region may represent an operator-type element capable of titrating repressor molecules away from chromosomal operator, allowing transcription of the operon in the absence of induction.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissett D. L., Anderson R. L. Lactose and D-galactose metabolism in Staphylococcus aureus. III. Purification and properties of D-tagatose-6-phosphate kinase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8745–8749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissett D. L., Anderson R. L. Lactose and D-galactose metabolism in Staphylococcus aureus. IV. Isolation and properties of a class I D-ketohexose-1,6-diphosphate aldolase that catalyzes the cleavage of D-tagatose 1,6-diphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8750–8755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissett D. L., Anderson R. L. Lactose and D0galactose metabolism in Staphylococcus aureus: pathway of D-galactose 6-phosphate degradation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 15;52(2):641–647. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90761-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissett D. L., Wenger W. C., Anderson R. L. Lactose and D-galactose metabolism in Staphylococcus aureus. II. Isomerization of D-galactose 6-phosphate to D-tagatose 6-phosphate by a specific D-galactose-6-phosphate isomerase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8740–8744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breidt F., Jr, Stewart G. C. Cloning and expression of the phospho-beta-galactosidase gene of Staphylococcus aureus in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):1061–1066. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.1061-1066.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer D. W., Iandolo J. J. Rapid isolation of DNA from Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):283–285. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.283-285.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray O., Chang S. Molecular cloning and expression of Bacillus licheniformis beta-lactamase gene in Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):422–428. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.422-428.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horinouchi S., Weisblum B. Nucleotide sequence and functional map of pE194, a plasmid that specifies inducible resistance to macrolide, lincosamide, and streptogramin type B antibodies. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):804–814. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.804-814.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson M. C., Stewart G. C. Differential utilization of Staphylococcus aureus promoter sequences by Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. Gene. 1986;48(1):93–100. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90355-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreiswirth B. N., Löfdahl S., Betley M. J., O'Reilly M., Schlievert P. M., Bergdoll M. S., Novick R. P. The toxic shock syndrome exotoxin structural gene is not detectably transmitted by a prophage. Nature. 1983 Oct 20;305(5936):709–712. doi: 10.1038/305709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCLATCHY J. K., ROSENBLUM E. D. INDUCTION OF LACTOSE UTILIZATION IN STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Dec;86:1211–1215. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.6.1211-1215.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse M. L., Hill K. L., Egan J. B., Hengstenberg W. Metabolism of lactose by Staphylococcus aureus and its genetic basis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2270–2274. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2270-2274.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E., Phillips S., Edelman I., Novick R. P. Tn554: isolation and characterization of plasmid insertions. Plasmid. 1981 May;5(3):292–305. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVICK R. P., RICHMOND M. H. NATURE AND INTERACTIONS OF THE GENETIC ELEMENTS GOVERNING PENICILLINASE SYNTHESIS IN STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;90:467–480. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.2.467-480.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostroff G. R., Pène J. J. Molecular cloning with bifunctional plasmid vectors in Bacillus subtilis. I. Construction and analysis of B. subtilis clone banks in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(2):299–305. doi: 10.1007/BF00330684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin S. J., Rosenblum E. D. Effects of the recipient strain and ultraviolet irradiation on transduction kinetics of the penicillinase plasmid of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1192–1199. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1192-1199.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Hack A. M., Rupp W. D. Simple method for identification of plasmid-coded proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):692–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.692-693.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simatake H., Rosenberg M. Purified lambda regulatory protein cII positively activates promoters for lysogenic development. Nature. 1981 Jul 9;292(5819):128–132. doi: 10.1038/292128a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoni R. D., Nakazawa T., Hays J. B., Roseman S. Sugar transport. IV. Isolation and characterization of the lactose phosphotransferase system in Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 10;248(3):932–940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoni R. D., Roseman S. Sugar transport. VII. Lactose transport in Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 10;248(3):966–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl M. L., Pattee P. A. Computer-assisted chromosome mapping by protoplast fusion in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):395–405. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.395-405.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan M. A., Yasbin R. E., Young F. E. New shuttle vectors for Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli which allow rapid detection of inserted fragments. Gene. 1984 Jul-Aug;29(1-2):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90161-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]