Abstract
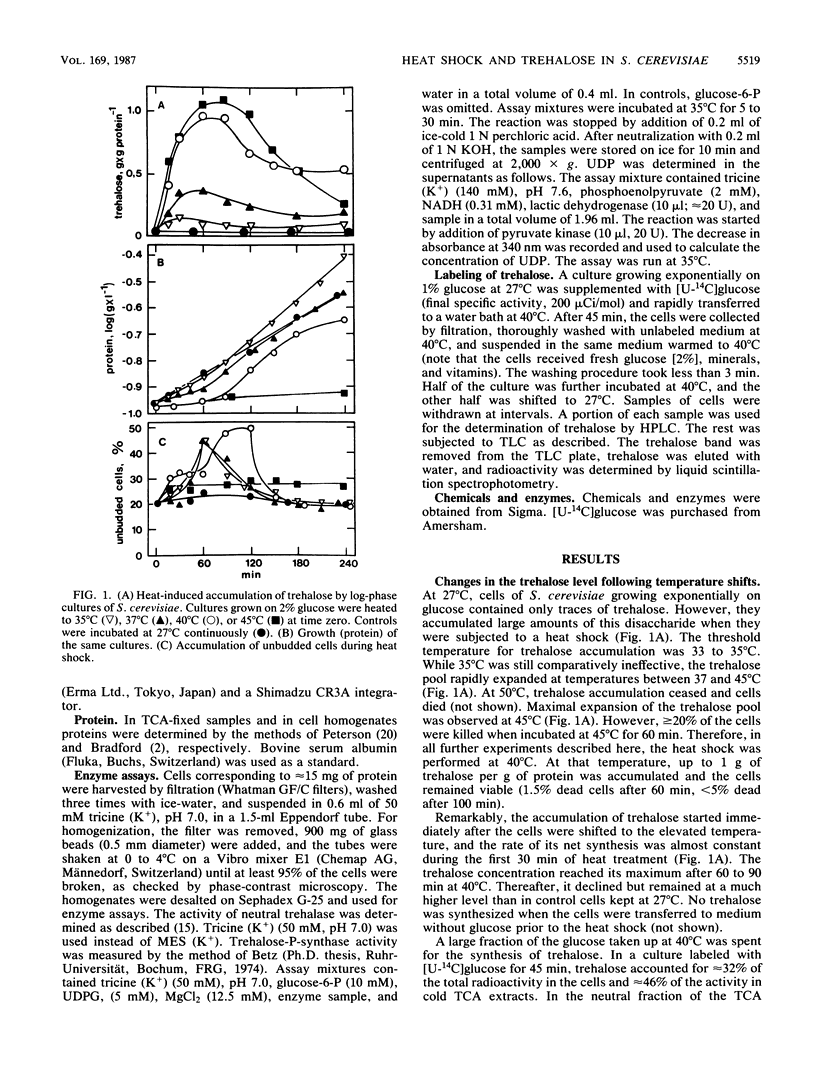
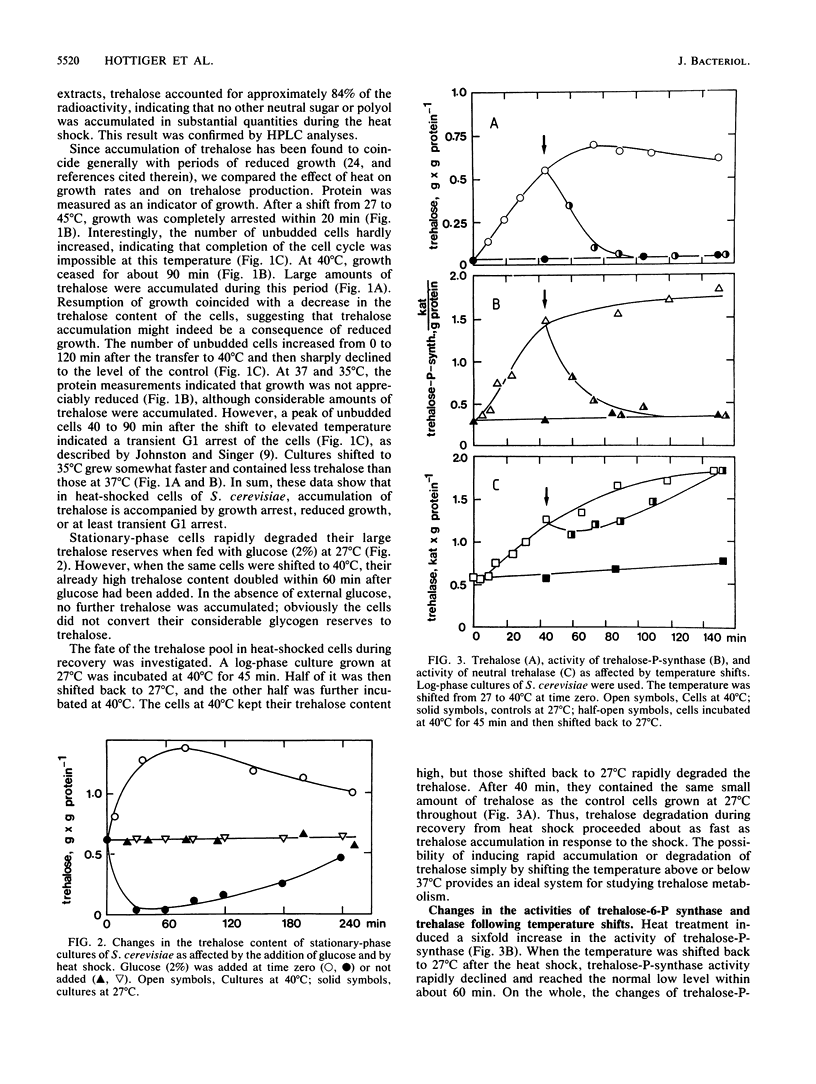
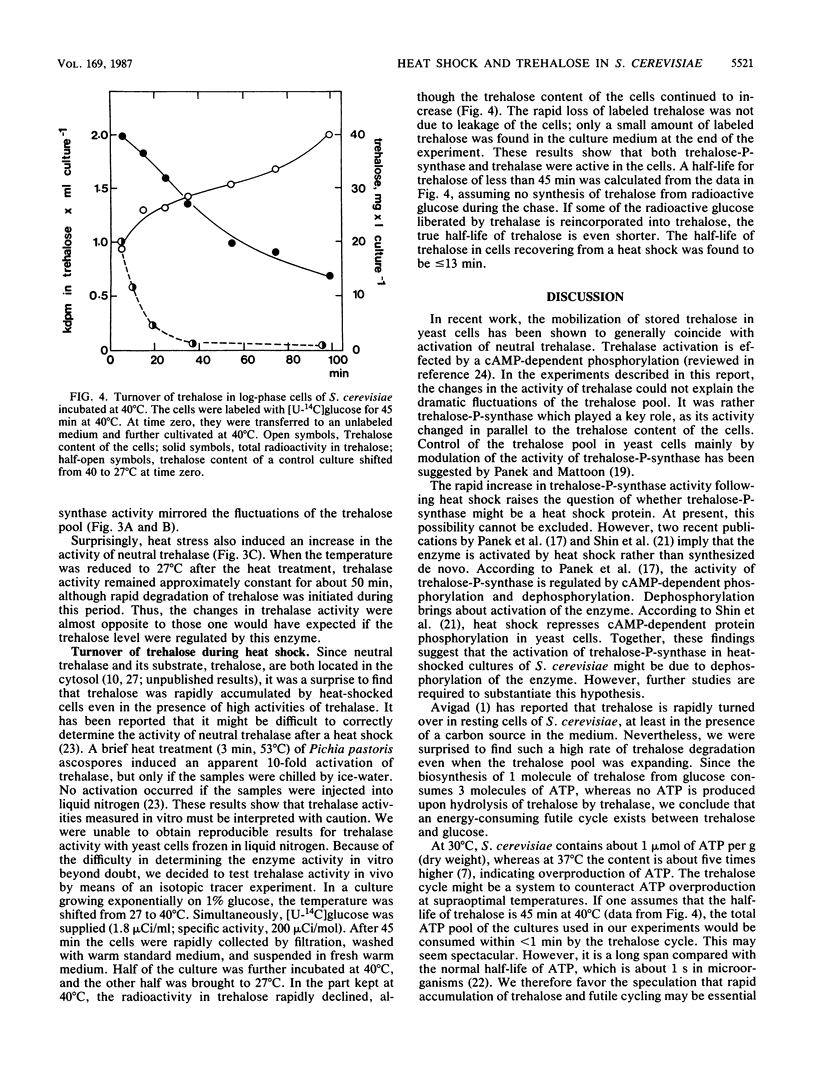
Heat shock resulted in rapid accumulation of large amounts of trehalose in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In cultures growing exponentially on glucose, the trehalose content of the cells increased from 0.01 to 1 g/g of protein within 1 h after the incubation temperature was shifted from 27 to 40 degrees C. When the temperature was readjusted to 27 degrees C, the accumulated trehalose was rapidly degraded. In parallel, the activity of the trehalose-phosphate synthase, the key enzyme of trehalose biosynthesis, increased about sixfold during the heat shock and declined to the normal level after readjustment of the temperature. Surprisingly, the activity of neutral trehalase, the key enzyme of trehalose degradation, also increased about threefold during the heat shock and remained almost constant during recovery of the cells at 27 degrees C. In pulse-labeling experiments with [14C]glucose, trehalose was found to be turned over rapidly in heat-shocked cells, indicating that both anabolic and catabolic enzymes of trehalose metabolism were active in vivo. Possible functions of the heat-induced accumulation of trehalose and its rapid turnover in an apparently futile cycle during heat shock are discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AVIGAD G. Accumulation of trehalose and sucrose in relation to the metabolism of alpha-glucosides in yeasts of defined genotype. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 May 6;40:124–134. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91322-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CABIB E., LELOIR L. F. The biosynthesis of trehalose phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1958 Mar;231(1):259–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Entian K. D. A defect in carbon catabolite repression associated with uncontrollable and excessive maltose uptake. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;179(1):169–175. doi: 10.1007/BF00268460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hottiger T., Boller T., Wiemken A. Rapid changes of heat and desiccation tolerance correlated with changes of trehalose content in Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells subjected to temperature shifts. FEBS Lett. 1987 Aug 10;220(1):113–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80886-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston G. C., Singer R. A. Ribosomal precursor RNA metabolism and cell division in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;178(2):357–360. doi: 10.1007/BF00270484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller F., Schellenberg M., Wiemken A. Localization of trehalase in vacuoles and of trehalose in the cytosol of yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae). Arch Microbiol. 1982 Jun;131(4):298–301. doi: 10.1007/BF00411175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küenzi M. T., Fiechter A. Changes in carbohydrate composition and trehalase-activity during the budding cycle of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch Mikrobiol. 1969;64(4):396–407. doi: 10.1007/BF00417021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küenzi M. T., Fiechter A. Regulation of carbohydrate composition of Saccharomyces cerevisiae under growth limitation. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;84(3):254–265. doi: 10.1007/BF00425203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie S. H., Pringle J. R. Reserve carbohydrate metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: responses to nutrient limitation. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1384–1394. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1384-1394.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londesborough J. Cyclic nucleotide-dependent inactivation of yeast fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase by ATP. FEBS Lett. 1982 Aug 2;144(2):269–272. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80652-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londesborough J., Varimo K. Characterization of two trehalases in baker's yeast. Biochem J. 1984 Apr 15;219(2):511–518. doi: 10.1042/bj2190511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PANEK A. Synthesis of trehalose by baker's yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Sep;98:349–355. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(62)90197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panek A. C., de Araujo P. S., Moura Neto V., Panek A. D. Regulation of the trehalose-6-phosphate synthase complex in Saccharomyces. I. Interconversion of forms by phosphorylation. Curr Genet. 1987;11(6-7):459–465. doi: 10.1007/BF00384607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panek A. D., Mattoon J. R. Regulation of energy metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Relationships between catabolite repression, trehalose synthesis, and mitochondrial development. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Sep;183(1):306–316. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90444-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin D. Y., Matsumoto K., Iida H., Uno I., Ishikawa T. Heat shock response of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants altered in cyclic AMP-dependent protein phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):244–250. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempest D. W., Neijssel O. M. The status of YATP and maintenance energy as biologically interpretable phenomena. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:459–486. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.002331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thevelein J. M. Regulation of trehalose mobilization in fungi. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Mar;48(1):42–59. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.1.42-59.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uno I., Matsumoto K., Adachi K., Ishikawa T. Genetic and biochemical evidence that trehalase is a substrate of cAMP-dependent protein kinase in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):10867–10872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiemken A., Schellenberg M. Does a cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation initiate the transfer of trehalase from the cytosol into the vacuoles in Saccharomyces cerevisiae? FEBS Lett. 1982 Dec 27;150(2):329–331. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80762-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Solingen P., van der Plaat J. B. Partial purification of the protein system controlling the breakdown of trehalose in baker's yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Feb 3;62(3):553–560. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90434-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



