Abstract
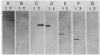
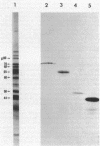
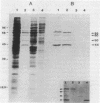
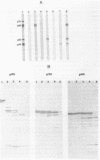
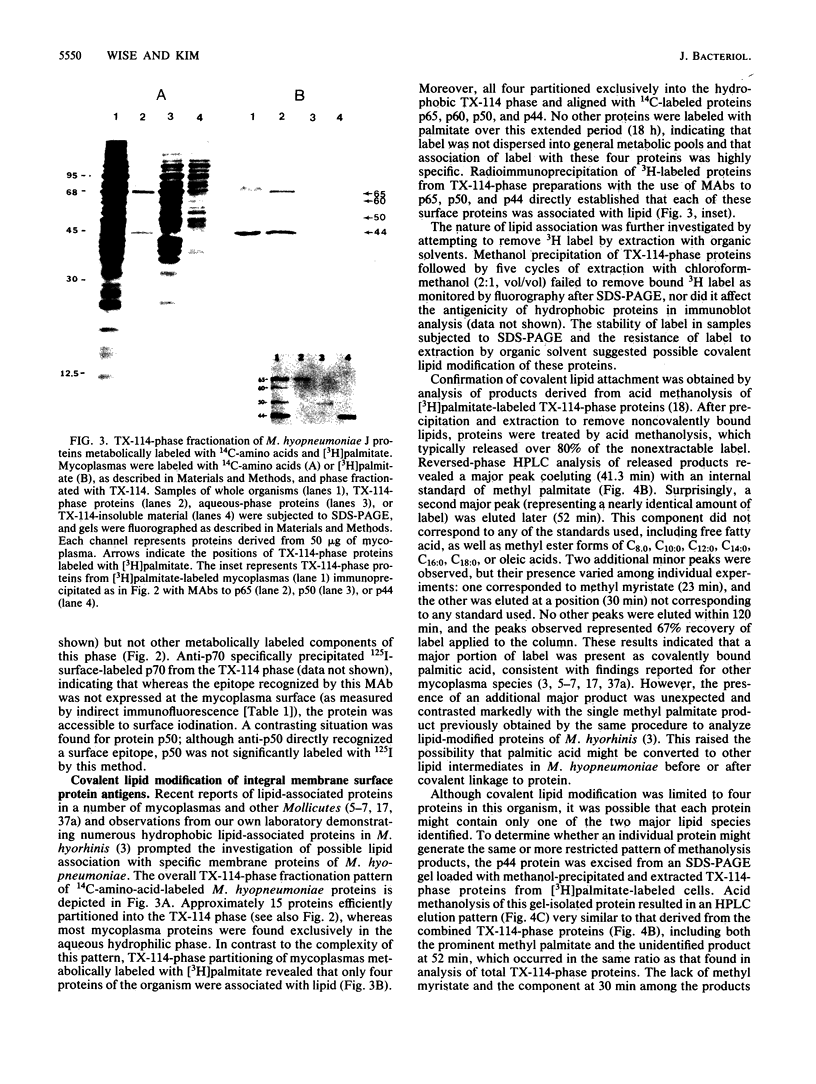
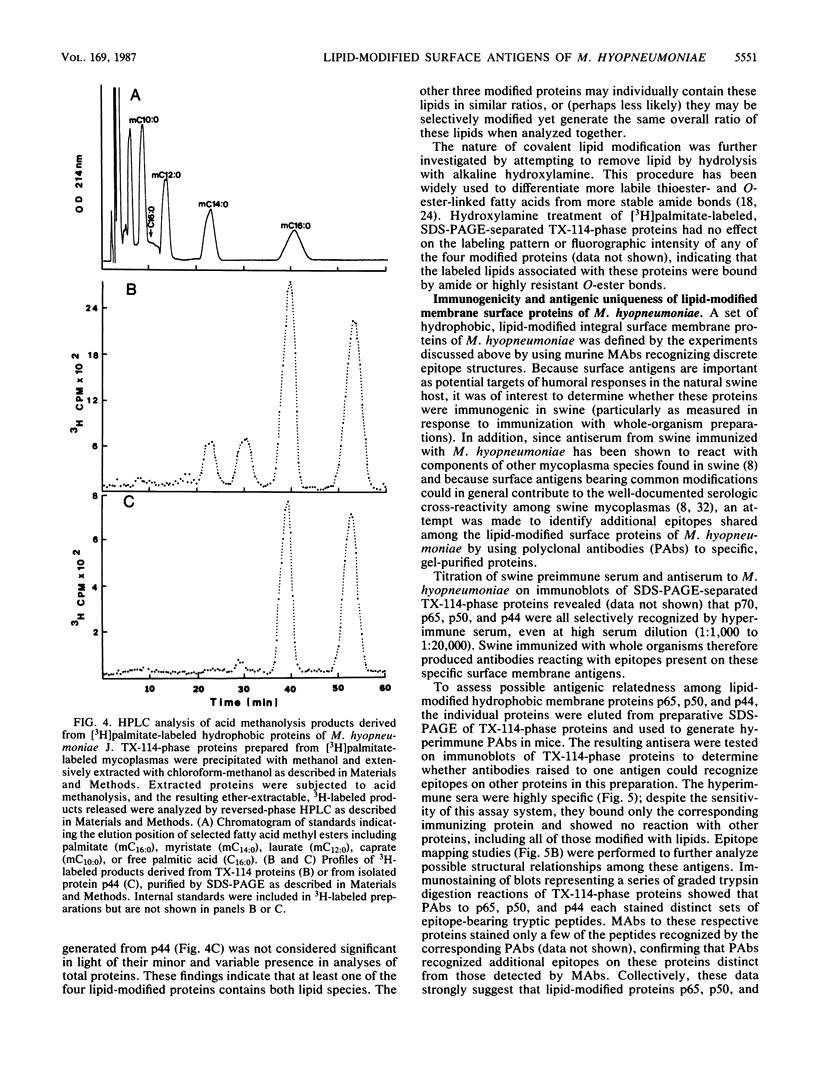
Surface protein antigens of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae were identified by direct antibody-surface binding or by radioimmunoprecipitation of surface 125I-labeled proteins with a series of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs). Surface proteins p70, p65, p50, and p44 were shown to be integral membrane components by selective partitioning into the hydrophobic phase during Triton X-114 (TX-114)-phase fractionation, whereas p41 was concomitantly identified as a surface protein exclusively partitioning into the aqueous phase. Radioimmunoprecipitation of TX-114-phase proteins from cells labeled with [35S]methionine, 14C-amino acids, or [3H] palmitic acid showed that proteins p65, p50, and p44 were abundant and (with one other hydrophobic protein, p60) were selectively labeled with lipid. Covalent lipid attachment was established by high-performance liquid chromatography identification of [3H]methyl palmitate after acid methanolysis of delipidated proteins. An additional, unidentified methanolysis product suggested conversion of palmitate to another form of lipid also attached to these proteins. Alkaline hydroxylamine treatment of labeled proteins indicated linkage of lipids by amide or stable O-linked ester bonds. Proteins p65, p50, and p44 were highly immunogenic in the natural host as measured by immunoblots of TX-114-phase proteins with antisera from swine inoculated with whole organisms. These proteins were antigenically and structurally unrelated, since hyperimmune mouse antibodies to individual gel-purified proteins were monospecific and gave distinct proteolytic epitope maps. Intraspecies size variants of one surface antigen of M. hyopneumoniae were revealed by a MAb to p70 (defined in strain J, ATCC 25934), which recognized a larger p73 component on strain VPP11 (ATCC 25617). In addition, MAb to internal, aqueous-phase protein p82 of strain J failed to bind an analogous antigen in strain VPP11. These studies establish that a highly restricted set of distinct, lipid-modified hydrophobic membrane proteins are major surface antigens of M. hyopneumoniae and that structural variants of surface antigens occur within this species.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Eukaryotic protein modification and membrane attachment via phosphatidylinositol. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):179–181. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90419-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl C. E., Dahl J. S., Bloch K. Proteolipid formation in Mycoplasma capricolum. Influence of cholesterol on unsaturated fatty acid acylation of membrane proteins. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11814–11818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl C. E., Dahl J. S. Phospholipids as acyl donors to membrane proteins of Mycoplasma capricolum. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10771–10776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl C. E., Sacktor N. C., Dahl J. S. Acylated proteins in Acholeplasma laidlawii. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):445–447. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.445-447.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman M. J., Armstrong C. H., Sands-Freeman L. L., Lopez-Osuna M. Serological cross-reactivity of porcine reference antisera to Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae, M. flocculare, M. hyorhinis and M. hyosynoviae indicated by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, complement fixation and indirect hemagglutination tests. Can J Comp Med. 1984 Apr;48(2):202–207. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gois M., Kuksa F., Franz J., Taylor-Robinson D. The antigenic differentiation of seven strains of Mycoplasma hyorhinis by growth-inhibition, metabolism-inhibition, latex-agglutination, and polyacrylamide-gel-electrophoresis tests. J Med Microbiol. 1974 Feb;7(1):105–115. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-1-105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Lujan E., Ostrander F., Hood L. E. Isolation of microgram quantities of proteins from polyacrylamide gels for amino acid sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:227–236. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinkert M. Q., Herrmann R., Schaller H. Surface proteins of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae identified from an Escherichia coli expression plasmid library. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):329–335. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.329-335.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee A. I., Courtneidge S. A. Two classes of fatty acid acylated proteins exist in eukaryotic cells. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1137–1144. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03751.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A. A new solid-state reagent to iodinate proteins. I. Conditions for the efficient labeling of antiserum. Anal Biochem. 1982 Sep 15;125(2):427–432. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyström S., Johansson K. E., Wieslander A. Selective acylation of membrane proteins in Acholeplasma laidlawii. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Apr 1;156(1):85–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09552.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Towler D. A., Glaser L. Specificity of fatty acid acylation of cellular proteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3784–3790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riethman H. C., Boyer M. J., Wise K. S. Triton X-114 phase fractionation of an integral membrane surface protein mediating monoclonal antibody killing of Mycoplasma hyorhinis. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1094–1100. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1094-1100.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers M. J., Simmons J., Walker R. T., Weisburg W. G., Woese C. R., Tanner R. S., Robinson I. M., Stahl D. A., Olsen G., Leach R. H. Construction of the mycoplasma evolutionary tree from 5S rRNA sequence data. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1160–1164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger M. J. Proteolipids. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:193–206. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. F. Fatty acid binding: a new kind of posttranslational modification of membrane proteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;102:101–129. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68906-2_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonis S., Cullen S. E. Fatty acylation of murine Ia alpha, beta, and invariant chains. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):2962–2967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R., Oliphant J. C. Immunogenic variation among the so-called LC strains of Mycoplasma mycoides subspecies mycoides. J Hyg (Lond) 1983 Jun;90(3):441–449. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400029089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajima M., Yagihashi T. Interaction of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae with the porcine respiratory epithelium as observed by electron microscopy. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1162–1169. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1162-1169.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. A., Ferrell R. V., Wise K. S., McIntosh M. A. Identification of a repetitive genomic sequence that is distributed among a select group of mycoplasmas. Isr J Med Sci. 1987 May;23(5):368–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. A., McIntosh M. A., Robbins J., Wise K. S. Cloned genomic DNA sequences from Mycoplasma hyorhinis encoding antigens expressed in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4154–4158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. A., Wise K. S., McIntosh M. A. Selective detection of Mycoplasma hyorhinis using cloned genomic DNA fragments. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):827–830. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.827-830.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegmann W., Bertschinger H. U., Keller H. Die enzootische Pneumonie der Schweine. Eine elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchung mit Erregernachweis im Gewebe. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1969 Jul;16(5):428–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise K. S., Kim M. F. Identification of intrinsic and extrinsic membrane proteins bearing surface epitopes of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae. Isr J Med Sci. 1987 May;23(5):469–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise K. S., Minion F. C., Cheung H. C. Translocation of Thy-1 antigen and a fluorescent lipid probe during lymphoblastoid cell interaction with Mycoplasma hyorhinis. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 May-Jun;4 (Suppl):S210–S218. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.supplement_1.s210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise K. S., Watson R. K. Monoclonal antibodies to Mycoplasma hyorhinis surface antigens: tools for analyzing mycoplasma-lymphoid cell interactions. Yale J Biol Med. 1983 Sep-Dec;56(5-6):623–629. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise K. S., Watson R. K. Mycoplasma hyorhinis GDL surface protein antigen p120 defined by monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1332–1339. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1332-1339.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Stackebrandt E., Ludwig W. What are mycoplasmas: the relationship of tempo and mode in bacterial evolution. J Mol Evol. 1984;21(4):305–316. doi: 10.1007/BF02115648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wroblewski H., Blanchard A., Nyström S., Wieslander A., Thomas D. Amphiphilic properties of spiralin, the major surface antigen of spiroplasmas. A preliminary report. Isr J Med Sci. 1987 May;23(5):439–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. C., Tokunaga M. Biogenesis of lipoproteins in bacteria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;125:127–157. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71251-7_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]