Abstract
Polygalacturonase (PG) is one of the most important enzymes associated with plant cell wall degradation. It has been proposed to participate in the early steps of the Rhizobium–legume interaction. We have identified two classes of cDNA fragments corresponding to two classes of PG genes in the Medicago genome. One of this class, represented by E2 in M. truncatula and Pl1 in M. sativa, seems to be related to previously characterized plant PG genes expressed in pollen. We have isolated the genomic clone containing the entire gene corresponding to the second class (E3). We showed that MsPG3 is a single gene in the Medicago genome coding for PG. By reverse transcription-PCR, MsPG3 expression was detected in roots 1 day after Rhizobium inoculation. The early induction of the MsPG3, as also seen by in situ hybridization experiments, supports its involvement in the early stages of the Rhizobium-legume infection process. In addition, by analyzing the expression of a MsPG3 promoter-gus construct in Vicia hirsuta-transgenic root nodules, we showed that MsPG3 was expressed in all cells of nodule primordia and in the cells of the invasion zone. By Northern blot, MsPG3 transcripts are not detected in various Medicago tissues, indicating that the function of this gene is related closely to symbiosis. Thus, our results strongly suggest the involvement of MsPG3 gene during meristem formation and/or in the infection process, probably by facilitating cell wall rearrangement, penetration of the bacteria through the root hair wall, or infection thread formation and release of bacteria in plant cells. MsPG3 represents a class of PG genes, distinct from the pollen-specific genes, and it is the first pectic encoded enzyme demonstrated to be involved in Rhizobium-legume symbiosis.
Keywords: infection process/symbiosis/noduline/pectic gene
Soil bacteria known as rhizobia have the capacity to induce the formation of nodules on the root of their leguminous host plants. When the bacteria are released into the plant cells, they differentiate into bacteroids fixing the atmospheric nitrogen. The early stages of the interaction are controlled by signals exchanged between the two symbiotic partners, resulting in spatially and temporally regulated expression of specific genes (1). The mechanisms controlling the bacterial entry, the initial formation of infection threads, the directional growth and passage through root hair and cortical cell walls of these structures, and the release of the bacteria in the infected cells are still poorly understood. Nutman (2) proposed that a redirection of root hair tip growth by bacterial action resulted in an invagination of the hair wall forming the infection thread. Fahraeus and Ljunggren (3) proposed that legume roots produce the enzyme polygalacturonase induced by the homologous Rhizobium strain. The ability to induce polygalacturonase production by the root may be controlled by a resident plasmid of the Rhizobium (4). Electron microscopic studies have demonstrated that rhizobia penetrate a degraded region of the plant cell wall at a very localized site (5). These studies support the involvement of cell wall degrading enzymes in the infection process allowing the penetration of the bacteria. In addition, the production of cellulolytic and pectolytic enzymes by Rhizobium has been demonstrated (6). However, conclusive experiments demonstrating the role of these enzymes in the infection and nodulation phenomena have not been reported yet.
Polygalacturonase (PG) is one of the most important enzymes associated with cell wall degradation. This enzyme, in conjunction with other secreted cell wall-degrading enzymes such as pectin esterase and pectate lyase are involved largely in several biological processes. Endopolygalacturonase activity has been identified in ripening fruits, and it has been implicated as the primary agent of polyuronide degradation and hence implicated as the enzyme responsible for fruit softening that accompany ripening (7). Brown and Crouch (8) proposed that PG may function by depolymerizing pectin in the cell wall of the pistil during pollination to allow penetration by the pollen tubes and/or to provide wall precursors for the growing tube. This enzyme is also among those which are secreted by invasive plant pathogens to degrade the host cell wall (9).
We have characterized a Medicago sativa polygalacturonase gene (MsPG3) specifically expressed during symbiosis with R. meliloti. Our expression studies suggest that this enzyme may play multiple roles during the symbiotic interaction.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Growth Conditions for Plants and Bacteria.
Alfalfa seeds sterilization and plant growth under aeroponic conditions were done accordingly to Bauer et al. (10). To generate root nodules, the roots were inoculated with wild-type R. meliloti strain 41 and the non-nodulating mutant derivative ZB138 as described (10).
Nucleic Acid Manipulations.
Genomic DNA of M. sativa ssp. sativa cv. Nagyszénàsi and M. truncatula cv. Jemalong was prepared according to Dellaporta et al. (11). Restriction enzyme digestions were performed under standard conditions. Total RNA was isolated from different organs of M. sativa ssp. varia or M. sativa ssp. sativa using the guanidinium thiocyanate method and subsequent cesium chloride gradient centrifugation according to Sambrook et al. (12). Poly(A+) RNA were prepared according to Sambrook et al. (12). Transfer of the nucleic acids to Hybond-N nylon membranes (Amersham) and subsequent hybridization were carried out by using the manufacturer’s instructions.
Polygalacturonase Gene Isolation.
Two oligonucleotide primers named 370: 5′-GGTGATGATTGTAT(T/C)TCA- AT-3′ and 389: 5′-GTCTTGATCCTAACTCC-3′ corresponding respectively to the conserved amino acid sequences GDDCISI and GVRIKT present in different plant PG genes were used to PCR amplify several partial Medicago DNA fragments homologous to PG. Then 100 ng of genomic DNA or one-tenth of the cDNA synthesis reaction mix were used as templates for amplification in 100 μl of Taq polymerase buffer without Mg2+ (10 mM Tris⋅HCl, pH 9.0/50 mM KCl/0.1% Triton X-100), 6 mM MgCl2, 0.12 mM dNTP, 70 pmol of 370 and 389 primers, and 1.5 units of Taq polymerase, (Promega). Amplification was performed by using 30 cycles of 1-min denaturation at 94°C, 1-min primer annealing at 48°C, and 1-min elongation at 72°C. The PCR products were size-fractionated on a 1.5% agarose gel, transferred to nylon filters, and hybridized to a radiolabeled tomato PG cDNA clone (13). A 186-bp PCR product that hybridized was blunt-ended by using T4 DNA polymerase and cloned into the EcoRV site of pBluescript IIKS (Stratagene). To isolate the entire alfalfa MsPG3 gene, the E3 fragment (see Results) was used as a probe to screen a genomic library prepared from M. sativa ssp. sativa cv. Nagyszénàsi genomic DNA cloned into the λEMBL-4 vector by using standard procedures (12). Inserts of the purified phages were subcloned into pBluescript IIKS (Stratagene).
Reverse Transcription–PCR (RT-PCR).
The technical aspects of the RT-PCR assay and the necessary controls were described previously (10). Based on the nucleotide sequence alignment of fragments E3, E2 and Pl1, specific primers were designed. Primer 427 (5′-CCATTGTCAGTATTTG(A/T)- GT-3′) is specific for E3 and primer 428 (5′-CATTGTCG- GTTG(T/C)TGTCAG-3′) for E2 and Pl1. The amplification rate was in a linear range for all PCR products. One-tenth of the PCR products were electrophoresed and transferred to Hybond-N nylon membrane. The membrane was first hybridized at high stringency conditions to either the Msc27 or Rhe2 PCR fragments for quantification. The blot was stripped and rehybridized to either the E2 or E3 PCR fragments.
DNA Sequence Analysis.
DNA sequencing analysis was carried out by the dideoxy chain-terminating method (12). For fragments longer than 0.5 kb, deletion derivatives were obtained by using the Erase-a-Base System Kit (Promega). Computer analyses of sequence information was performed by using the software package of the University of Wisconsin Genetics Computer Group.
In Situ Hybridization.
For preparing antisense and sense RNA fragments of the alfalfa MsPG3 gene, a cDNA fragment of 833 bp, obtained by RT-PCR from alfalfa nodule RNA, was cloned into pBluescript IISK vector (Stratagene) giving plasmid pCJ3. For this RT-PCR amplification, two primers corresponding to genomic PG sequence were synthesized. The 5′ primer (primer 420) is 5′-CTTAATGATGCTTATCAA- TGG-3′ and the 3′ primer (primer 1751) is 5′-ACACATTT- AGCGTTTACTGG-3′. The probes were digoxigenin-labeled by using the DIG RNA-labeling Kit from Boehringer Mannheim and degraded to ≈150 nucleotides long before hybridization. Alfalfa nodules and nodule primordia induced by wild-type R. meliloti strain 41 were fixed, dehydrated, and finally infiltrated and embedded into paraffin. Sections (9 μm thick) were hybridized to digoxigenin-labeled antisense or sense RNA probes according to a procedure derived from Bochenek and Hirsch (14). Sections were photographed with a POLYVAR Reichert-Jung microscope by using T-160 Ektachrome Kodak film.
V. hirsuta Transformation and Analysis of Transgenic Root Nodules.
A fragment containing the 2.7 kb-promoter sequence, ending 3 bp upstream of the ATG codon of MsPG3 gene, was subcloned into the binary vector pPR97 (15) to construct a transcriptional fusion to gusA-int. V. hirsuta transformation was performed as described (16) using Agrobacterium rhizogenes A4Tc24 containing the new plasmid named pPG97. Composite V. hirsuta plants were transferred to fresh nitrogen-free medium and inoculated with an overnight culture of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae. Histochemical β-glucuronidase (GUS) staining of plant material was performed as described (17). Semithin sections (100 μm) of fresh unfixed nodules were cut by using a Micro-Cut H1200 (Bio-Rad) and photographed with a POLYVAR Reichert-Jung microscope by using T-160 Ektachrome Kodak film.
RESULTS
Isolation of PCR Products from Medicago cDNA and Genomic DNA Hybridizing to a Tomato Polygalacturonase cDNA Clone.
To determine the presence of PG genes in the Medicago or Rhizobium genome, we first used heterologous probes. When Southern blots containing genomic DNA obtained from alfalfa, clover, Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii, and Rhizobium meliloti were probed with a tomato PG cDNA clone (13) under low stringency conditions, hybridizing bands were observed only with the alfalfa genomic DNA (data no shown). To clone a homologous gene probe, we used a PCR approach.
The plant PG genes described so far contain a conserved region in the middle of the coding sequence including a histidine residue at position 293 of the tomato amino acid sequence, which may be part of the active site of the enzyme (18). Two oligonucleotide primers (370 and 389) expected to amplify a cDNA fragment of ≈180 bp corresponding to this conserved domain, were synthesized. Using these primers, fragments of this size were amplified from maize total DNA, M. sativa ssp. sativa genomic DNA, M. sativa ssp. sativa pollen cDNA as well as from M. truncatula genomic DNA. All of these PCR fragments hybridized to the tomato PG cDNA clone (data not shown).
Two classes of fragments, distinguishable by the presence of a HindIII restriction site, were cloned from the PCR products obtained from the genomic DNA of the diploid M. truncatula 108–1. One representative of each class was analyzed. The fragment containing a HindIII restriction site was named E3 and the other one E2. A third clone was obtained from the M. sativa ssp. sativa pollen cDNA, named Pl1. This clone did not contain a HindIII restriction site. Comparison of the nucleotide sequences and the predicted amino acid sequences from these PCR products with the already published sequences revealed a high degree of homology with PGs from different organisms (data not shown). Interestingly, analysis of the nucleotide sequences of these partial putative PG genes revealed that fragment Pl1 and E2 were more closely related to each other (96% similarity) than to fragment E3 (71% and 69% similarity respectively), despite the fact that Pl1 and E2 were cloned from different Medicago species. In addition, the peptides encoded by E2 and Pl1 exhibited 73.7% identity with the pollen PG of Zea mays (19) whereas E3 showed only 63.9% identity. These different degrees of homology, together with the fact that the Pl1 fragment was isolated from pollen cDNA, suggested that at least two classes of PG genes are present in Medicago. One class, represented by E2 in M. truncatula and Pl1 in M. sativa, seems to be closer related to the previously characterized genes, which are expressed in pollen. Using Southern blot experiments or the PCR based approach described above, we were unable to detect PG-related sequences in Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii and Rhizobium meliloti.
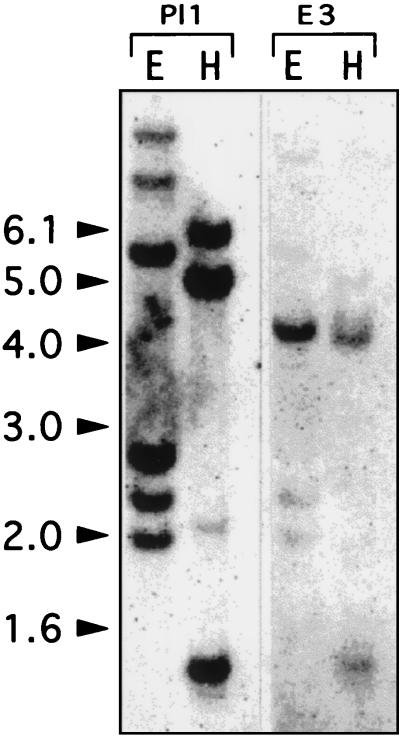
To estimate the number of PG genes in Medicago, genomic DNA from the diploid M. truncatula was digested with EcoRI and HindIII and subsequently hybridized to Pl1 and E3 clones, using the same moderate stringency conditions in both cases. Fig. 1 shows the results of the M. truncatula genomic DNA gel blot analysis. Despite the 68,6% sequence identity between the two probes, distinct hybridizing patterns were obtained. Pl1 probe hybridized strongly to four fragments when the DNA was digested with EcoRI and to three fragments when the DNA was digested with HindIII. E3 probe hybridized strongly to one fragment when the DNA was digested with EcoRI and to two fragments with the same intensity (but lesser than for EcoRI) when the DNA was digested with HindIII (in agreement with the fact that E3 contains an internal HindIII restriction site). Similar results were obtained by using DNA from the tetraploid M. sativa ssp. varia cv. A2 plant (data not shown).
Figure 1.
Southern blot analysis of Medicago plants. M. truncatula genomic DNA was digested with EcoRI (E) and HindIII (H) and hybridized with the Pl1 and E3 probes. The sizes of the molecular mass markers are indicated in kb at the left.
Genes Corresponding to the E3 and E2 Fragments Are Differentially Expressed.
The E3 and E2 PCR fragments were used to successively probe the same RNA gel blot made of poly(A)+ RNA isolated from various plant tissues of M. sativa ssp. varia cv A2 (data not shown). The E2 fragment hybridized to an RNA transcript of ≈1.5 kb present at high level in mature flowers. The transcript was detectable at lower level in flower buds and was not detectable in callus, leaves, nodules, or roots, confirming the previous hypothesis that the E2 fragment may correspond to a Medicago PG gene expressed in pollen. When the same RNA gel blot was probed with E3, no PG transcript was detected. These differential expression data are in agreement with the Southern blot study, suggesting that there are at least two classes of PG genes in Medicago.
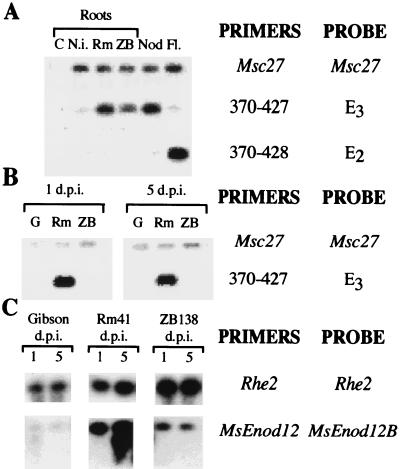
Because of the possible low level or transient expression of the PG gene corresponding to the E3 fragment, the expression pattern was investigated by using a RT-PCR approach. This method, in addition to being more sensitive, allowed us to examine the expression of the two genes independently, despite their high sequence homology, through the use of specific oligonucleotide primers. Alignment of the nucleotide sequences of the E3 and E2/Pl1 PCR fragments, as well as their predicted amino acid sequences, revealed a region which was not conserved at the 3′ end of the PCR product. This region was chosen for designing new specific primers that, in combination with primer 370, represented gene-specific primer pairs (370-427 for E3 and 370-428 for E2/Pl1). After quantification, cDNA was amplified with the E3-specific primers and the PCR products were hybridized to E3. The cDNA also was amplified with the E2-specific primers and then the PCR products hybridized to E2. Fig. 2 A shows that the gene corresponding to E2 (PG-E2) was expressed in flowers but not in roots or nodules (in agreement with the Northern study). The gene corresponding to E3 (PG-E3) was expressed in nodules and in roots harvested 5 days after inoculation either with the wild-type strain R. meliloti Rm41 or the Nod− derivative ZB138 but not in uninoculated roots. The PG-E3 transcripts were present at higher levels in R. meliloti 41-inoculated roots than in roots inoculated with the non-nodulating mutant ZB138. No hybridizing band appeared in the flower cDNA, which hybridized with the E3 fragment, indicating that the designed primers were each highly specific for only one PG clone. The coamplification of the constitutively expressed alfalfa gene Msc27 was used as internal control in the RT-PCR reactions.
Figure 2.
RT-PCR expression studies of PG genes corresponding to the E3 and E2 DNA fragments in different plant tissues. (A) Expression study using complete root, nodules, and flowers. Medicago PGs and the control Msc27 sequences were coamplified during 25 cycles from RNA of various plant tissues of M. sativa ssp. sativa cv. Sitel: H2O (C), noninoculated roots (N.i.), roots harvested 5 days after R. meliloti 41 inoculation (Rm), roots harvested 5 days after inoculation with strain ZB138 (ZB) (in these cases plants were inoculated 3 days after germination), 21-day-old wild-type nodules (Nod) and flowers (Fl.). The PCR products were subjected to electrophoresis on 1% agarose gel, blotted, and hybridized to the corresponding probe. The amount and quality of loaded cDNA was checked by amplification with Msc27-specific oligonucleotides, followed by probing with an Msc27 probe. E3 and E2 sequences were amplified with the oligonucleotide primers 370-427 and 370-428 pairs respectively and each Southern blot was subsequently hybridized to E3 and E2 probes. (B) Expression study using spot innoculated roots. Three-day-old alfalfa seedlings of M. sativa ssp. sativa cv. Sitel were inoculated with Gibson plant medium (G), R. meliloti 41 (Rm), or the non-nodulating mutant ZB138 (ZB). RNA from root samples harvested 1 day (1 d.p.i.) and 5 days (5 d.p.i.) after inoculation were used for RT-PCR. The PCR products were subjected to electrophoresis on 1% agarose gel, blotted, and hybridized to the corresponding probe. cDNAs were coamplified by PCR by using Msc27 specific primers and 370-427 primers, and the PCR products were successively hybridized to an Msc27 or E3 probe. (C) Analysis of MsEnod12 expression: The same cDNA sample were used as in B. Rhe2 was used as constitutive control instead of Msc27 in this experiment. cDNA was coamplified by PCR using Rhe2 specific primers and MsEnod12 primers and the PCR products were successively hybridized to the Rhe2 or MsEnod12B probe (10).
The expression of MsPG3 in all roots inoculated with the strain ZB138 could be caused by a specific response to the Rhizobium or alternatively to a nonspecific response of the roots to the bacteria. Peretto et al. (20) also have shown that PG can be expressed during growth of lateral root primordium. Therefore, to be able to study the specific response to the Nod factor treatment, the expression of the MsPG3 gene at the site of Rhizobium infection was studied by using the spot inoculation technique (10). Three-day-old alfalfa seedlings were spot-inoculated with the wild-type strain 41 and its nod mutant derivative ZB138. Root sections corresponding to the inoculated regions were harvested 1 and 5 days after inoculation, and MsPG3 expression was studied by RT-PCR by using the combination of specific primers 370 and 427. The highest level of the MsPG3 transcript was detected in roots collected 1 day after treatment with the wild-type strain R. meliloti 41 (the earliest time point tested; Fig. 2B), which agree with the results of the previous experiment (Fig. 2A). At 5 days after innoculation, the amount of transcript was reduced in the Rm41 treated roots. No transcripts were detectable in the noninoculated or in the ZB138 inoculated roots. Simultaneously, the RNA samples used were checked by comparing the MsPG3 expression pattern with that of the MsEnod12 gene (Fig. 2C), one of the best characterized early nodulin genes associated with the early stages of nodule development. MsEnod12A and MsEnod12B were amplified by using specific oligonucleotide primers giving two bands corresponding to the expected 239- and 299-bp sizes. According to Bauer et al. (10), the expression of MsEnod12A was detectable 5 days after inoculation with R. meliloti 41, when nodules became visible and MsEnod12B transcripts were found in both root samples. These results indicated that the PG-E3 gene behaves as an early nodulin by expressing at very early stages of nodules development.
Isolation and Structure of the Medicago PG Gene Corresponding to the E3 Fragment.
To further characterize the alfalfa PG gene corresponding to the E3 fragment, we isolated the entire gene. For this, a M. sativa ssp. sativa cv. Nagyszénàsi EMBL-4 genomic library was screened by using the E3 fragment as a probe. Two types of hybridizing phage clones were isolated. One group hybridized strongly to E3, and two hybridizing bands appeared when the DNA was HindIII-digested. The other group hybridized weakly to E3 and only one HindIII-hybridizing band was present, suggesting that these phages may contain pollen-related PG genes. A λ10 clone belonging to the first group was chosen to characterize the entire alfalfa PG gene expressed in symbiosis. This gene was designated MsPG3.
The nucleotide and the deduced amino acid sequences of the MsPG3 gene are deposited in European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL data bank, accession no. Y11118). Analysis of the PG sequence using the test code program (Genetics Computer Group, Madison, WI) indicated the presence of four regions with high coding probability and three others with low coding probability corresponding respectively to the conserved and nonconserved regions. This result suggested the presence of introns in the MsPG3 genomic sequence. The exact position of the predicted introns was determined by comparison with the consensus-splicing sites of dicotyledoneous plants (21). This analysis revealed that the three introns followed the general exon/GT … intron … AG/exon rule. They are 278-, 427-, and 94-bp long, beginning at positions 127, 717, and 1663, respectively. The second and third intron-splicing sites were later confirmed by sequencing the PCR product obtained by amplification from nodule cDNA using oligonucleotide primers 420 and 1751. In the region of MsPG3 corresponding to the E3 PCR fragment, there was no intron as expected. Analysis of the deduced coding sequence revealed the presence of an ORF coding for a putative protein of 395 aa with a predicted molecular mass of 42,673 Da and an isoelectric point of 8.15. The sequence around the proposed start codon (AACATGGA) was very similar to the consensus sequence of the translation start site of the dicotyledoneous plant genes Aa(A/C)ATGGC) (22). The homology to other PG genes suggested that this ATG may be the start codon used in vivo. The protein encoded by the MsPG3 gene contains three potential N-linked glycosilation sites according to the consensus sequence Asp-X-Ser/Thr at amino acid positions 138, 178, and 263. It also contains 14 cysteine residues, and 12 of these residues are conserved among plant PGs. By using the hydrophaty plot, it was shown that the predicted protein is relatively hydrophilic. The N-terminal region is hydrophobic displaying the properties of a signal peptide (23) and strongly suggest post-translational cleavage releasing a 22-aa signal peptide and a mature product.
The deduced ORF displayed 52.1, 48.2, 47.0, 36.8, 36.0, and 31.9% identity and 71.9, 69.2, 67.0, 59.0, 57.4, and 54.7% similarity at the amino acid level to the predicted PG proteins of Oenothera organensis (8), tobacco (24), Brassica napus (25), tomato abscission-specific (26), maize (19), and tomato (27), respectively. The highest conservation was found between amino acids 191 and 277. In this region, the isolated MsPG3-genomic clone showed 91.3% identity at the nucleotide level to the E3 fragment and only 76.7% identity to the Pl1. These data strongly suggest that the MsPG3 gene is the gene expressed in nodules and Rhizobium-inoculated roots in alfalfa. To further support this conclusion, we sequenced the PCR product obtained by the amplification of phage λ3 by using the unspecific primers (370–389) and belonging to the group giving only one hybridizing band after HindIII digestion. This fragment showed 98.9% identity to the pollen-related Pl1 fragment and only 76.2% identity to the corresponding region in the MsPG3-genomic clone studied here. A M. sativa pollen cDNA coding for PG has been recently included in EMBL data bank (EMBL accession no. U20431; X. Qiu and L. Erickson, personal communication). Amino acid sequence comparison with the predicted MsPG3 gene product gave 79.0% similarity and 64.7% identity but 96.7% similarity and 93.4% identity when compared with the PCR Pl1 fragment.
Spatial Expression of MsPG3 During Root Nodule Development.
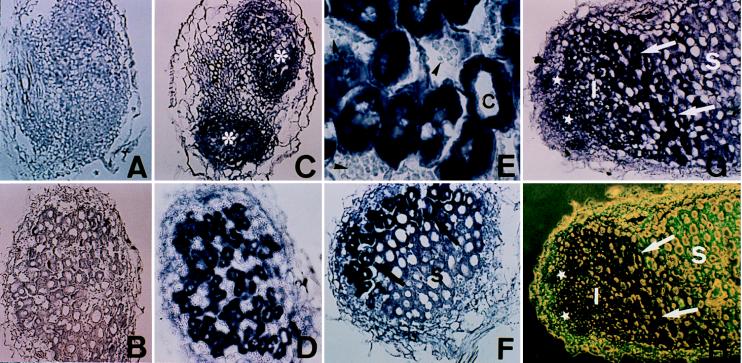
To further analyze the pattern of expression of the MsPG3 gene during nodule development, the spatial localization of MsPG3 transcripts in wild-type nodules was studied by in situ hybridization. As shown in Fig. 3, serial sections of 4-day-old nodule primordia, 7-day-old nodules, and 20 day-old nodules from alfalfa plants were hybridized against an 833-bp antisense MsPG3 RNA probe. Transversal sections of roots harvested 4 days after inoculation and containing nodule primordia also were hybridized to MsPG3 antisense RNA. The MsPG3 mRNA was present in all cells of nodule primordia (Fig. 3C). Sense RNA probes did not yield hybridization signals above background levels (Fig. 3 A and B). In young nodules, PG transcripts were present in the cells of the meristem and of the invasion zone or zone II (Fig. 3F–H) directly adjacent to the meristem where infection thread growth and release of bacteria occur and in the interzone II-III containing amyloplasts, where bacterial proliferation and enlargement of infected cells take place. Once differentiated into cells of the symbiotic zone (zone III), the MsPG3 transcripts were no longer present (Fig. 3 F–H). The PG transcripts were detectable in the infected cells but not in the highly vacuolated noninfected cells of young nodules (Fig. 3 D and E).
Figure 3.
Localization of MsPG3 expression in root nodule primordia and nodules. In situ hybridization was performed on transversal sections of 4-day-old nodule primordia (A and C), transversal sections of 7-day-old nodules (B, D, and E), and longitudinal sections of 7-day-old (F) and 20-day-old nodules (G and H). Digoxigenin-labeled MsPG3 sense (A and B) and antisense (C–H) probes were used. (E) A higher magnification of the bottom part of D. (H) The same section in G photographed under combination of light and fluorescence microscopy. Asterisks, nodule primordia; stars, meristematic zone; I, invasion zone; S, symbiotic zone; C, infected cells; arrows, interzone II-III; arrow heads, starch grains in noninfected cells.
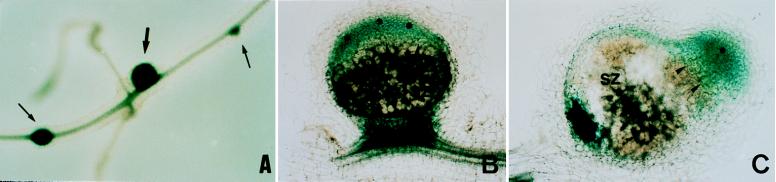
To further confirm the spatial expression pattern of MsPG3, we used another legume plant, V. hirsuta, which also forms indeterminate-type root nodules and for which transgenics roots can rapidly be obtained (16). After transformation with plasmid pPG97 containing a fusion of a 2.7-kb fragment of the MsPG3 gene upstream of the ATG codon to the gusA-int gene, composite V. hirsuta plants harboring “hairy roots” induced by Agrobacterium rhizogenes carrying pPG97 were obtained. The hairy roots were inoculated with Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae, and the spatial distribution of the GUS activity was studied in the nodules formed, as shown in Fig. 4. GUS activity was detected in nodule primordia and in young transgenic nodules (Fig. 4A). In mature nodules, GUS activity was visualized in the cells of the invasion zone, whereas it was never observed in cells of the symbiotic zone (Fig. 4B and C). GUS activity also was detected in vascular tissues and at the junction between nodules and roots. Nontransgenic root nodules did not show any GUS staining (data not shown). The GUS activity pattern observed in these transgenic nodules revealed that the 2.7-kb MsPG3 upstream sequence was sufficient to direct the spatial and temporal expression of the reporter gene that coincided with the expression pattern observed in the in situ experiment on M. sativa.
Figure 4.
GUS activity observation in transgenic V. hirsuta roots and nodules. The activity of the GUS gene directed by the MsPG3-promoter region was visualized in complete young nodules and nodule primordia (A) and longitudinal cuts of mature nodules (B and C). Thick arrow, young nodule; thin arrows, nodule primordium; asterisks, meristematic zone; arrow heads, infection zone; SZ, symbiotic zone.
DISCUSSION
We have isolated and characterized a genomic clone in M. sativa (MsPG3) encoding polygalacturonase (PG). We showed that this single gene represents a class of PG genes that is specifically expressed in roots and nodules induced by R. meliloti and that based on sequence and expression data, is distinct from the pollen specific PG genes.
Sequence analysis of the complete MsPG3 gene revealed a deduced ORF that displayed 64.7, 52.1, 48.2, 47.0, 36.8, 36.0, and 31.9% identity and 79.0, 71.9, 69.2, 67.0, 59.0, 57.4, and 54.7% similarity at the amino acid level to the predicted PG proteins of M. sativa, Oenothera organensis, tobacco, Brassica napus, tomato abscission-specific, maize, and tomato fruit, respectively. The highest conservation was found with a M. sativa pollen cDNA coding for PG (U20431). The predicted protein shows, in addition to 12 cysteines highly conserved among plant PG enzymes, four domains conserved in the bacterial, fungal, and plant polygalacturonase genes (24). The highest homology is present between amino acids 191 and 277. This sequence contains three of four conserved domains and includes a histidine residue, which has been hypothetized to be part of the catalytic site. The encoded peptide also contains a N-terminal-hydrophobic domain displaying the properties of a signal peptide, present in all reported PGs, and involved in the transport of the protein across membranes (23).
Southern blot experiments showed that the E2 and E3 fragments displayed a different hybridizing patterns against M. truncatula DNA as well as M. sativa spp. sativa genomic DNA, supporting the idea that there are at least two different PG genes in the Medicago genome. Expression of MsPG3 was not detected in various Medicago tissues by Northern blot, neither in nodules nor in Rhizobium inoculated roots, indicating that this gene may be expressed at a very low level, if any, or expressed only transiently. This is consistent with the hypothesis that, if this gene is involved in symbiosis, the production of PG should be finely regulated to avoid a defense reaction induced by the enzyme production and subsequent abortion of the infection process (9, 28).
By using RT-PCR analysis, we showed that the E2-related gene was expressed in flowers but not in roots or nodules, in agreement with our early Northern results, whereas MsPG3 was expressed in nodules and roots inoculated with Rhizobium but not in uninoculated roots nor in nonfunctional spontaneous nodules, strongly suggesting its role in Rhizobium-legume symbiosis. The expression studies restricted to the spot-inoculated zone of the alfalfa roots showed that the MsPG3 gene was expressed as early as 1 day after inoculation with the wild-type R. meliloti strain, but no expression was observed in uninoculated roots or roots inoculated with the Nod− mutant strain ZB138, in contrast to the experiment performed with the complete root system. Because the strain ZB138 is not able to produce Nod factors as well as some superficial components, other molecules like polysaccharides or lipopolysaccharides might be involved in inducing MsPG3 expression in addition to the Nod factor. These data together confirm our hipothesys by which MsPG3 is produced by the host plant and induced by the microsymbiont, although the bacterial signal involved in this induction had not been determined yet.
By using in situ hybridization, we showed that MsPG3 is expressed very early during the infection process coinciding with the expression pattern of other early nodulin genes like Enod12 and Enod5 in indeterminate nodules (10, 29). This expression pattern is consistent with a role of the pectic enzymes in meristem maintenance, infection thread directional growth, and cell wall disolution, for bacterial release during the infection process, and constitute the first molecular evidence supporting the hypothesis of Fahraeus and Ljunggren (3) and van Spronsen et al. (30) who suggested a role for plant cell wall degrading enzymes in the infection process, allowing the penetration of the bacteria. The action of these enzymes is probably required in conjunction with the Nod factors to conduct an efficient nodule development.
The analysis of GUS activity directed by the MsPG3-promoter region of transgenic root nodules induced by Rhizobium onto composite V. hirsuta plants confirmed the spatial and temporal pattern of expression obtained by the in situ experiment. In addition, uninoculated transgenic roots of the composite plants showed low level of reporter gene activity in lateral root primordia and emerging lateral roots, in agreement with the PG activity associated to root growth detected in Allium (20). This latter phenomenon could account for the basal expression level observed with RNA isolated from the entire root of alfalfa. These data demonstrated that the promoter region of MsPG3 gene fused to gusA-int gene is sufficient to correctly conduct GUS activity in the heterologous system. Therefore, the reporter fusion in combination with immunological studies, will represent a useful tool to study the role of MsPG3 during symbiosis in M. truncatula transgenic plants, as well as to unravel the bacterial factors involved in the signal transduction pathway leading to its expression.
Acknowledgments
D. Grierson is acknowledged for providing the tomato PG probe. E. Kondorosi is gratefully acknowledged for providing the M. sativa genomic library. We thank M. Crespi and T. Coba for their help with the in situ hybridization experiments and P. Bauer for help with the MsEnod12 expression experiment. Research support was provided by Comision Interministerial de Ciencia y Tecnologia Grants BIO93-0427 and PB95-1268. J.A.M., C.C., and J.P.H. were supported by the Spanish Ministry of Education. J.P.H. also was the recipient of a Short- Term European Molecular Biology Organization fellowship.
ABBREVIATIONS
- RT-PCR
reverse transcription—PCR
- PG
polygalacturonase
- GUS
β-glucuronidase
Footnotes
Data deposition: The sequence reported in this paper has been deposited in the GenBank database (accession no. Y11118).
References
- 1.Nap J P, Bisseling T. Science. 1990;250:948–950. doi: 10.1126/science.250.4983.948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Nutman P S. Biol Rev Biol Proc Cambridge Philos Soc. 1956;31:109–151. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fahraeus G, Ljunggren H. Physiol Plant. 1959;12:145–154. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Palomares A, Montoya E, Olivares J. Microbios. 1978;21:33–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Callaham D A, Torrey J G. Can J Bot. 1981;59:1647–1664. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mateos P F, Jiménez-Zurdo J I, Chen J, Squartini A S, Haack S K, Martínez-Molina E, Hubbell D H, Dazzo F B. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992;58:1816–1822. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.6.1816-1822.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fischer R L, Bennett A B. Plant Mol Biol. 1991;42:675–703. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Brown S M, Crouch M L. Plant Cell. 1990;2:263–274. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.3.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Collmer A, Keen N T. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 1986;24:383–409. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bauer P, Crespi M D, Szécsi J, Allison L A, Schultze M, Ratet P, Kondorosi E, Kondorosi A. Plant Physiol. 1994;105:585–592. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.2.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dellaporta S L, Wood J, Hicks J B. Plant Mol Biol Rep. 1983;4:19–21. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sambrook K J, Fritsch E F, Maniatis T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. 2nd Ed. Plainview, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Lab. Press; 1989. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Slater A, Maunders M J, Edwards K, Schuch W, Grierson D. Plant Mol Biol. 1985;5:137–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00015677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bochenek B, Hirsch A M. Plant Mol Biol Rep. 1990;8:237–248. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Szabados L, Charrier B, Kondorosi A, Bruijn F J, Ratet P. Mol Breeding. 1995;1:419–423. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Quandt H-J, Pühler A, Broer Y. Mol Plant–Microb Interact. 1993;6:699–706. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Jefferson R A, Kavanagh T A, Bevan M W. EMBO J. 1987;13:3901–3907. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02730.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Caprari C, Mattei B, Basile M L, Salvi G, Crescenzi V, De Lorenzo G, Cervone F. Mol Plant–Microb Interact. 1996;9:617–624. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-9-0617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Niogret M F, Dubald M, Mandaron P, Mache R. Plant Mol Biol. 1991;17:1155–1164. doi: 10.1007/BF00028732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Peretto R, Favaron F, Bettini V, de Lorenzo G, Marini S, Alghisi P, Cervone F, Bonfante P. Planta. 1992;188:164–172. doi: 10.1007/BF00216810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Brown J. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986;14:9549–9559. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.9549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Caverer D R, Ray S C. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991;19:3185–3192. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Verner K, Schatz G. Science. 1988;241:1307–1312. doi: 10.1126/science.2842866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tebbutt S J, Rogers H J, Lonsdale D L. Plant Mol Biol. 1994;25:283–297. doi: 10.1007/BF00023244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Robert L S, Allard S, Gerster J L, Cass L, Simmonds J. Plant Mol Biol. 1993;23:1273–1278. doi: 10.1007/BF00042360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kalaitzis P, Koehler S M, Tucker M L. Plant Mol Biol. 1995;28:647–656. doi: 10.1007/BF00021190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bird C R, Smith C J S, Ray J A, Moreau P, Bevan M W, Bird A S, Hughes S, Morris P C, Grierson D, Schuch W. Plant Mol Biol. 1988;11:651–662. doi: 10.1007/BF00017465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Dazzo F, Hubbell D. In: Nitrogen Fixation. Broughton W, editor. Oxford: Clarendon; 1982. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Pichon M, Journet E P, Dedieu A, de Billy F, Truchet G, Barker D G. Plant Cell. 1992;4:1199–1211. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.10.1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Van Spronsen P C, Bakhuizen R, van Brussel A A N, Kijne J W. Eur J Cell Biol. 1994;64:88–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]