Abstract
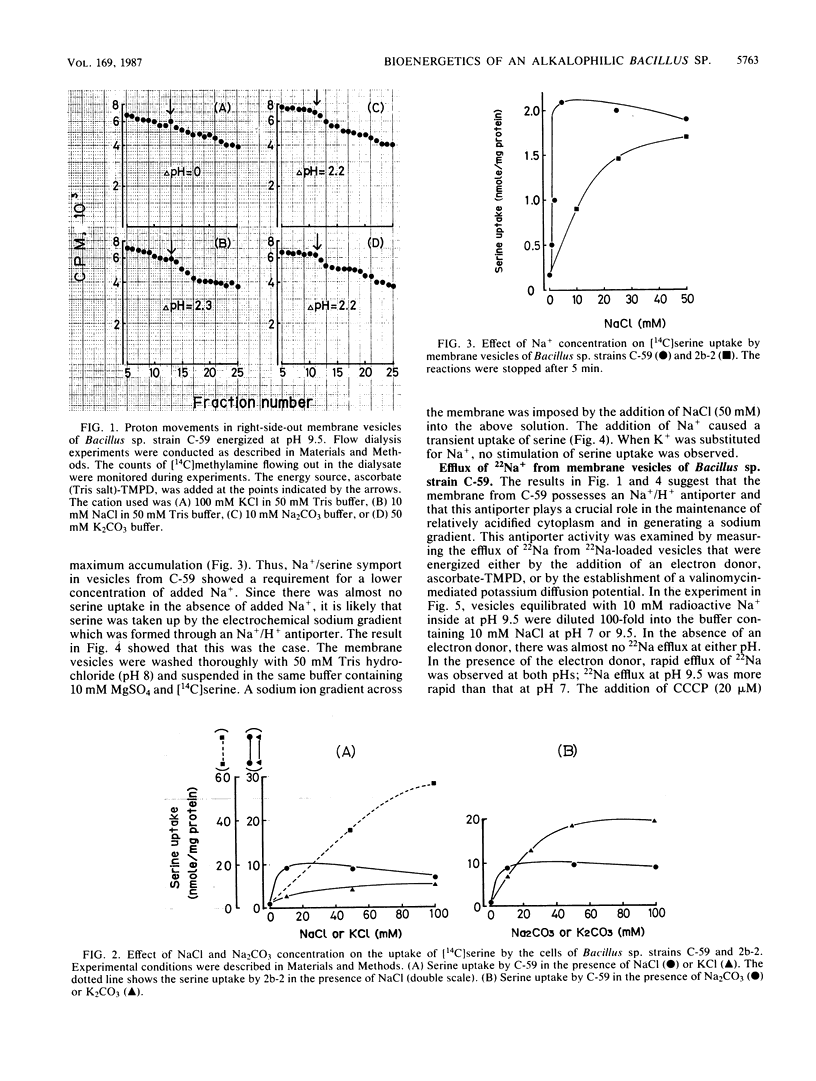
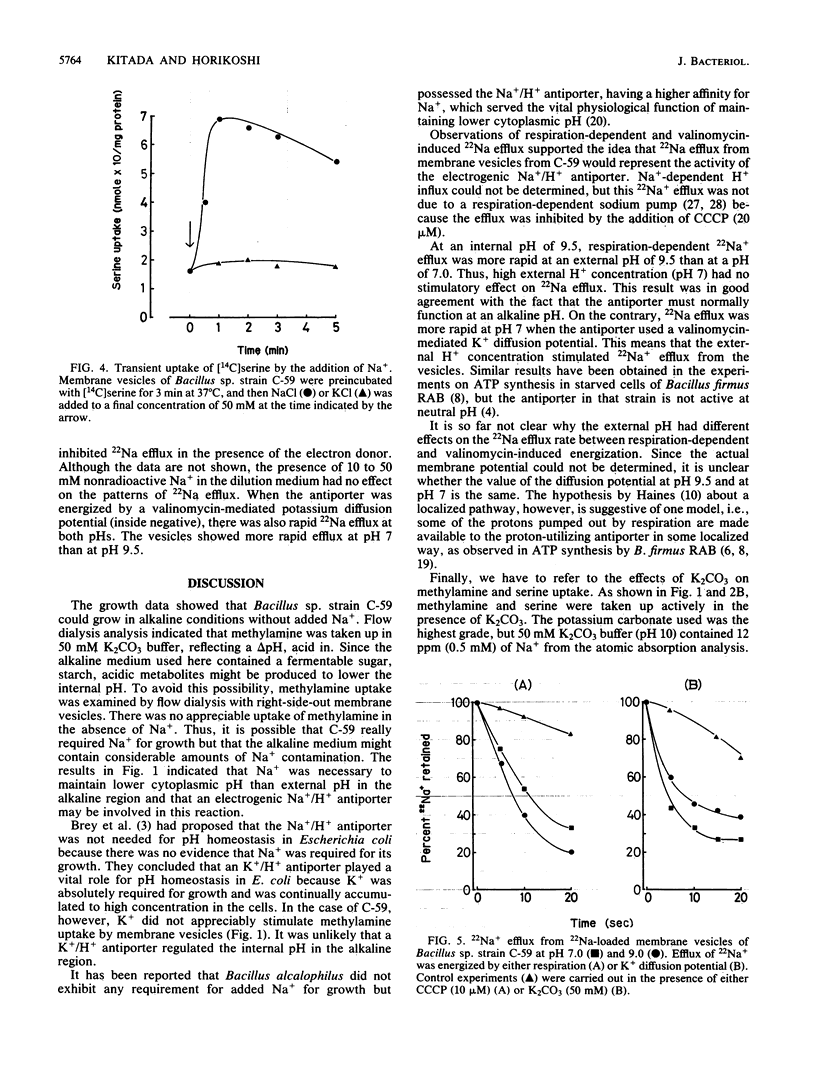
Alkalophilic Bacillus sp. strain C-59 could grow well on an alkaline medium containing K2CO3, as well as Na2CO3, but did not grow on K+-depleted medium. Right-side-out membrane vesicles, energized in the absence of Na+, however, could not take up [14C]methylamine actively, while vesicles equilibrated with 10 mM NaCl actively took up [14C]methylamine. The uptake of [14C]serine was also stimulated by the addition of Na+, and the imposition of a sodium gradient caused transient uptake. These results indicated that an Na+/H+ antiporter was involved in pH homeostasis and generation of an electrochemical sodium gradient in strain C-59 even though a growth requirement for Na+ was not evident. The efflux of 22Na+ from 22Na+-loaded vesicles was more rapid at pH 9.5 than at pH 7 in the presence of an electron donor. On the other hand, vesicles at pH 7 showed more rapid efflux than at pH 9.5 when the antiporter was energized by a valinomycin-mediated K+ diffusion potential (inside negative).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brey R. N., Rosen B. P., Sorensen E. N. Cation/proton antiport systems in Escherichia coli. Properties of the potassium/proton antiporter. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):39–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia M. L., Guffanti A. A., Krulwich T. A. Characterization of the Na+/H+ antiporter of alkalophilic bacilli in vivo: delta psi-dependent 22Na+ efflux from whole cells. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1151–1157. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1151-1157.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guffanti A. A., Bornstein R. F., Krulwich T. A. Oxidative phosphorylation by membrane vesicles from Bacillus alcalophilus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 May 13;635(3):619–630. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(81)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guffanti A. A., Cohn D. E., Kaback H. R., Krulwich T. A. Relationship between the Na+/H+ antiporter and Na+/substrate symport in Bacillus alcalophilus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1481–1484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guffanti A. A., Fuchs R. T., Schneier M., Chiu E., Krulwich T. A. A transmembrane electrical potential generated by respiration is not equivalent to a diffusion potential of the same magnitude for ATP synthesis by Bacillus firmus RAB. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):2971–2975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guffanti A. A., Susman P., Blanco R., Krulwich T. A. The protonmotive force and alpha-aminoisobutyric acid transport in an obligately alkalophilic bacterium. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):708–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haines T. H. Anionic lipid headgroups as a proton-conducting pathway along the surface of membranes: a hypothesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):160–164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitada M., Guffanti A. A., Krulwich T. A. Bioenergetic properties and viability of alkalophilic Bacillus firmus RAB as a function of pH and Na+ contents of the incubation medium. J Bacteriol. 1982 Dec;152(3):1096–1104. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.3.1096-1104.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitada M., Horikoshi K. Further properties of sodium ion-stimulated alpha-[1-14C]aminoisobutyric acid uptake in alkalophilic Bacillus species. J Biochem. 1980 May;87(5):1279–1284. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitada M., Horikoshi K. Sodium ion-stimulated alpha-[1-14C]aminoisobutyric acid uptake in alkalophilic Bacillus species. J Bacteriol. 1977 Sep;131(3):784–788. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.3.784-788.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitada M., Horikoshi K. Sodium-ion stimulated amino acid uptake in membrane vesicles of alkalophilic Bacillus no. 8-1. J Biochem. 1980 Dec;88(6):1757–1764. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyama N., Kiyomiya A., Nosoh Y. Na+-dependent uptake of amino acids by an alkalophilic Bacillus. FEBS Lett. 1976 Dec 15;72(1):77–78. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80816-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A. Bioenergetics of alkalophilic bacteria. J Membr Biol. 1986;89(2):113–125. doi: 10.1007/BF01869707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A., Guffanti A. A., Bornstein R. F., Hoffstein J. A sodium requirement for growth, solute transport, and pH homeostasis in Bacillus firmus RAB. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1885–1889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A., Mandel K. G., Bornstein R. F., Guffanti A. A. A non-alkalophilic mutant of Bacillus alcalophilus lacks the Na+/H+ antiporter. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Nov 14;91(1):58–62. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90582-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A. Na+/H+ antiporters. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 30;726(4):245–264. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(83)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel K. G., Guffanti A. A., Krulwich T. A. Monovalent cation/proton antiporters in membrane vesicles from Bacillus alcalophilus. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7391–7396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Schuldiner S., Kaback H. R. The use of flow dialysis for determinations of deltapH and active transport. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:680–688. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Unemoto T. A respiration-dependent primary sodium extrusion system functioning at alkaline pH in the marine bacterium Vibrio alginolyticus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Sep 16;102(1):265–271. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91516-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Unemoto T. Characterization of the respiration-dependent Na+ pump in the marine bacterium Vibrio alginolyticus. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10007–10014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WADDELL W. J., BUTLER T. C. Calculation of intracellular pH from the distribution of 5,5-dimethyl-2,4-oxazolidinedione (DMO); application to skeletal muscle of the dog. J Clin Invest. 1959 May;38(5):720–729. doi: 10.1172/JCI103852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein D., Agmon V., Schuldiner S., Padan E. The sodium/proton antiporter is part of the pH homeostasis mechanism in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3687–3691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


