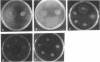
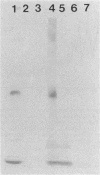
Abstract
In vivo and in vitro methylation, methanol production assays, and the use of specific antibodies raised against the sensory transducing protein Tar in Escherichia coli all failed to demonstrate the presence of methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins (MCPs) in the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodobacter sphaeroides, although such proteins did exist in another photosynthetic bacterium, Rhodospirillum rubrum. The range of chemicals to which Rhodobacter sphaeroides responds, the lack of an all-or-none response, and the lack of true repellents indicate an alternative chemosensory pathway. The existence of MCPs in Rhodospirillum rubrum means that the lack of MCPs is not the result of a phototrophic metabolism, but may be connected to the unidirectional flagellar motor of Rhodobacter sphaeroides.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F., Niakido K. In vivo methylation of prokaryotic elongation factor Tu. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):9947–9950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson B., Anderson J. M., Ryrie I. J. Transbilayer organization of the chlorophyll-proteins of spinach thylakoids. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr 1;123(2):465–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb19790.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armitage J. P., Evans M. C. Membrane potential changes during chemotaxis of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jun 1;102(1):143–146. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80946-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armitage J. P., Ingham C., Evans M. C. Role of proton motive force in phototactic and aerotactic responses of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):967–972. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.967-972.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armitage J. P., Macnab R. M. Unidirectional, intermittent rotation of the flagellum of Rhodobacter sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):514–518. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.514-518.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. B., Adler J., Dahl M. M. Nonchemotactic mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):390–398. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.390-398.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittner M., Kupferer P., Morris C. F. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins and nucleic acids from slab gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl cellulose or nitrocellulose sheets. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):459–471. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess-Cassler A., Ordal G. W. Functional homology of Bacillus subtilis methyltransferase II and Escherichia coli cheR protein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12835–12838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAYTON R. K. The induced synthesis of catalase in Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jan 29;37:503–512. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90507-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engström P., Hazelbauer G. L. Multiple methylation of methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins during adaptation of E. coli to chemical stimuli. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90244-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBSON K. D., NEUBERGER A., TAIT G. H. STUDIES ON THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF PORPHYRIN AND BACTERIOCHLOROPHYLL BY RHODOPSEUDOMONAS SPHEROIDES. 4. S-ADENOSYLMETHIONINEMAGNESIUM PROTOPORPHYRIN METHYLTRANSFERASE. Biochem J. 1963 Aug;88:325–334. doi: 10.1042/bj0880325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulbourne E. A., Jr, Greenberg E. P. A voltage clamp inhibits chemotaxis of Spirochaeta aurantia. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):916–920. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.916-920.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham C. J., Armitage J. P. Involvement of transport in Rhodobacter sphaeroides chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5801–5807. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5801-5807.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehry M. R., Doak T. G., Dahlquist F. W. Stimulus-induced changes in methylesterase activity during chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11828–11835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kort E. N., Goy M. F., Larsen S. H., Adler J. Methylation of a membrane protein involved in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3939–3943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengeler J., Auburger A. M., Mayer R., Pecher A. The phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent carbohydrate: phosphotransferase system enzymes II as chemoreceptors in chemotaxis of Escherichia coli K 12. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;183(1):163–170. doi: 10.1007/BF00270156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muskavitch M. A., Kort E. N., Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Attraction by repellents: an error in sensory information processing by bacterial mutants. Science. 1978 Jul 7;201(4350):63–65. doi: 10.1126/science.351803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowlin D. M., Nettleton D. O., Ordal G. W., Hazelbauer G. L. Chemotactic transducer proteins of Escherichia coli exhibit homology with methyl-accepting proteins from distantly related bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):262–266. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.262-266.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordal G. W. Bacterial chemotaxis: biochemistry of behavior in a single cell. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1985;12(2):95–130. doi: 10.3109/10408418509104426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postma P. W., Lengeler J. W. Phosphoenolpyruvate:carbohydrate phosphotransferase system of bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):232–269. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.232-269.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repaske D. R., Adler J. Change in intracellular pH of Escherichia coli mediates the chemotactic response to certain attractants and repellents. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1196–1208. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1196-1208.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J., Kersulis G., Koshland D. E., Jr Neither methylating nor demethylating enzymes are required for bacterial chemotaxis. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):683–690. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90125-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger T. C., Bogonez E., Wang E. A., Koshland D. E., Jr Sites of methyl esterification on the aspartate receptor involved in bacterial chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9608–9611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso W. W., Adler J. Negative chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):560–576. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.560-576.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullah A. H., Ordal G. W. In vivo and in vitro chemotactic methylation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):958–965. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.958-965.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]