Abstract
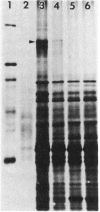
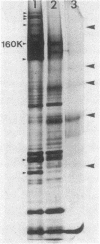
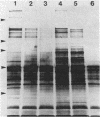
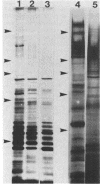
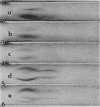
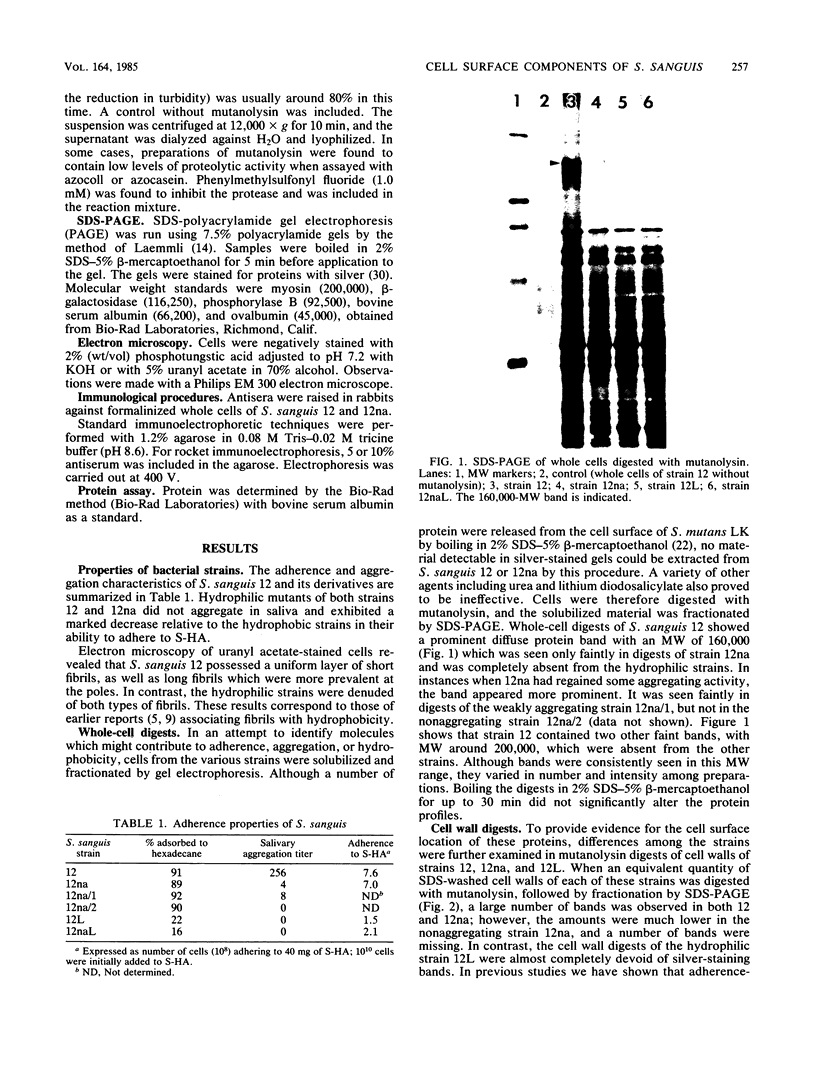
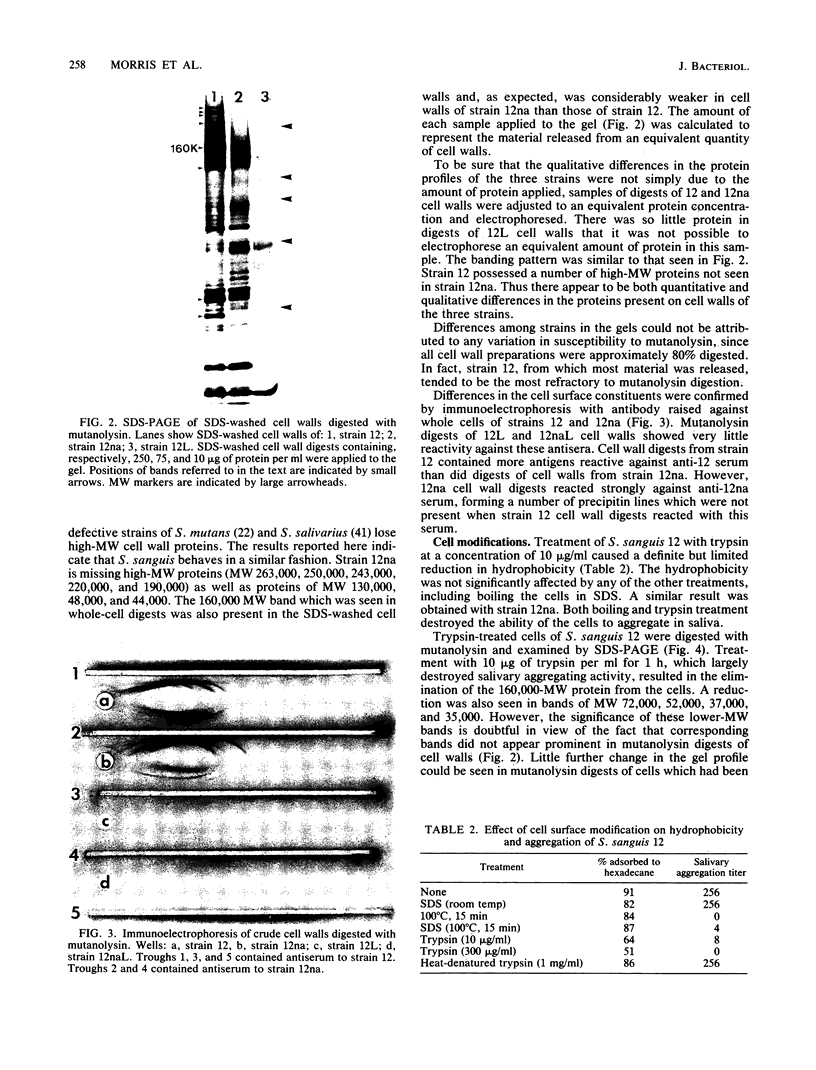
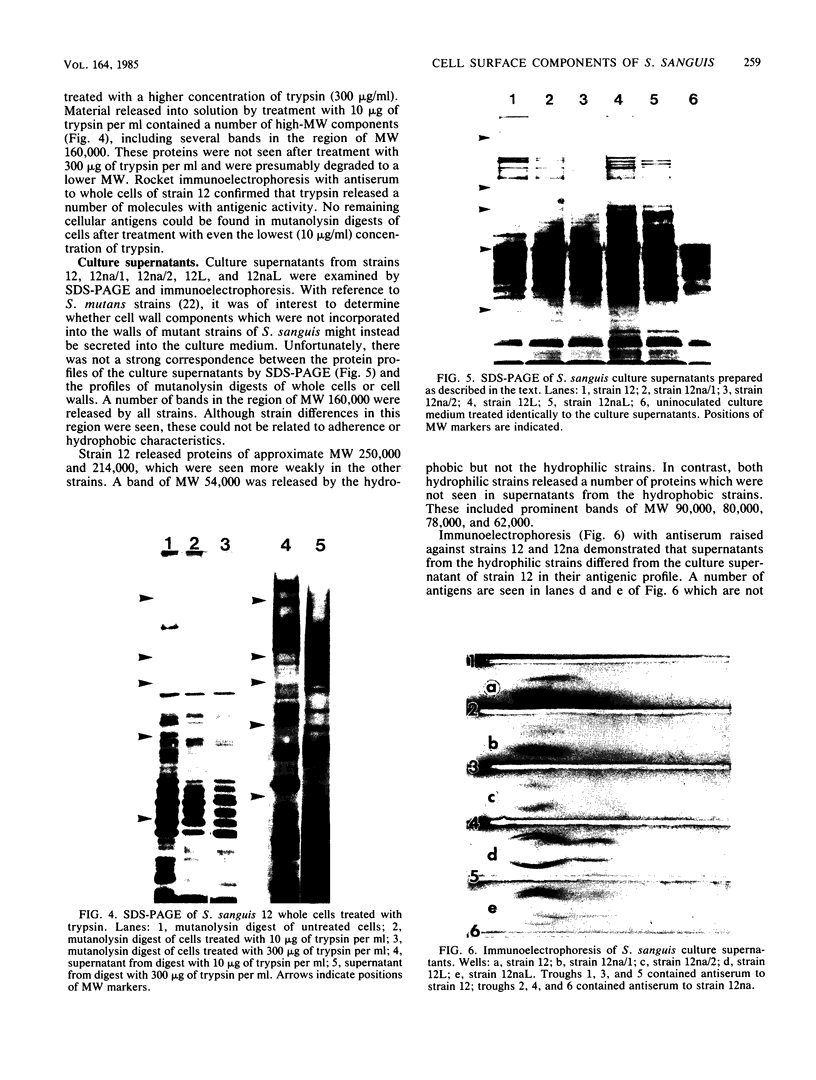
Cell surfaces of aggregation, adherence, and hydrophilic variants of Streptococcus sanguis were compared with cell surfaces of the parent strain with regard to their protein and antigenic constituents. Cell surface molecules were released by digestion with mutanolysin. Extraction with sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) urea, lithium diiodosalicylate, and boiling water did not solubilize any material which stained with AgNO3 in an SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gel. The parent organism S. sanguis 12, which aggregates in saliva, adheres to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite and is hydrophobic, was found to possess a prominently staining 160,000 molecular weight (MW) protein. This protein was almost completely absent from strain 12na, a hydrophobic nonaggregating variant, and was completely absent from the hydrophilic nonaggregating strain 12L. Trypsinization of strain 12 resulted in the coincident loss of the 160,000-MW protein and the ability to aggregate in saliva. Trypsin treatment reduced but did not eliminate the hydrophobic character of the cells. Boiling destroyed their ability to aggregate, but did not alter their hydrophobicity. Cell wall digests of strain 12 contained a number of proteins which were absent from strains 12na and 12L. Mutanolysin digests of cell walls of the hydrophilic strains contained almost no material that was visible in a silver-stained SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gel. Culture supernatants contained a number of proteins which were immunologically cross-reactive with cell surface proteins. The hydrophilic organisms released a number of 60,000- to 90,000-MW proteins not seen in culture supernatants from the parent strain.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appelbaum B., Rosan B. Cell surface proteins of oral streptococci. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):245–250. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.245-250.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Ofek I. Epithelial cell binding of group A streptococci by lipoteichoic acid on fimbriae denuded of M protein. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):759–771. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellen R. P., Gibbons R. J. M protein-associated adherence of Streptococcus pyogenes to epithelial surfaces: prerequisite for virulence. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):826–830. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.826-830.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fachon-Kalweit S., Elder B. L., Fives-Taylor P. Antibodies that bind to fimbriae block adhesion of Streptococcus sanguis to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):617–624. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.617-624.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fives-Taylor P. M., Thompson D. W. Surface properties of Streptococcus sanguis FW213 mutants nonadherent to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):752–759. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.752-759.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Etherden I. Comparative hydrophobicities of oral bacteria and their adherence to salivary pellicles. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1190–1196. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1190-1196.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Etherden I. Enzymatic modification of bacterial receptors on saliva-treated hydroxyapatite surfaces. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):52–58. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.52-58.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Etherden I., Skobe Z. Association of fimbriae with the hydrophobicity of Streptococcus sanguis FC-1 and adherence to salivary pellicles. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):414–417. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.414-417.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Van Houte J., Liljemark W. F. Parameters that effect the adherence of Streptococcus salivarius to oral epithelial surfaces. J Dent Res. 1972 Mar-Apr;51(2):424–435. doi: 10.1177/00220345720510023101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handley P. S., Carter P. L., Wyatt J. E., Hesketh L. M. Surface structures (peritrichous fibrils and tufts of fibrils) found on Streptococcus sanguis strains may be related to their ability to coaggregate with other oral genera. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):217–227. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.217-227.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen S. D., Henrichsen J. Twitching motility and possession of polar fimbriae in spreading Streptococcus sanguis isolates from the human throat. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Apr;83(2):133–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg S. D., Handley P. S., Embery G. Surface fibrils may be responsible for the salivary glycoprotein-mediated aggregation of the oral bacterium Streptococcus sanguis. Arch Oral Biol. 1981;26(11):945–949. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(81)90156-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. J., Herzberg M. C., Levine M. S., Ellison S. A., Stinson M. W., Li H. C., van Dyke T. Specificity of salivary-bacterial interactions: role of terminal sialic acid residues in the interaction of salivary glycoproteins with Streptococcus sanguis and Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):107–115. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.107-115.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Bloomquist C. G. Isolation of a protein-containing cell surface component from Streptococcus sanguis which affects its adherence to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):428–434. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.428-434.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Gibbons R. J. Proportional distribution and relative adherence of Streptococcus miteor (mitis) on various surfaces in the human oral cavity. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):852–859. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.852-859.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Schauer S. V. Studies on the bacterial components which bind Streptococcus sanguis and Streptococcus mutans to hydroxyapatite. Arch Oral Biol. 1975 Sep;20(9):609–615. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(75)90082-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackie E. B., Brown K. N., Lam J., Costerton J. W. Morphological stabilization of capsules of group B streptococci, types Ia, Ib, II, and III, with specific antibody. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):609–617. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.609-617.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride B. C., Gisslow M. T. Role of sialic acid in saliva-induced aggregation of Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):35–40. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.35-40.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride B. C., Song M., Krasse B., Olsson J. Biochemical and immunological differences between hydrophobic and hydrophilic strains of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):68–75. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.68-75.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miörner H., Johansson G., Kronvall G. Lipoteichoic acid is the major cell wall component responsible for surface hydrophobicity of group A streptococci. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):336–343. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.336-343.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris E. J., McBride B. C. Adherence of Streptococcus sanguis to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite: evidence for two binding sites. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):656–663. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.656-663.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouton C., Reynolds H. S., Genco R. J. Characterization of tufted streptococci isolated from the "corn cob" configuration of human dental plaque. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):235–245. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.235-245.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. A., Levine M. J., Tabak L. A., Reddy M. S. Specificity of salivary-bacterial interactions: II. Evidence for a lectin on Streptococcus sanguis with specificity for a NeuAc alpha 2, 3Ga1 beta 1, 3Ga1NAc sequence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 31;106(2):390–396. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91122-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Nakao M., Shibata S., Shizukuishi S., Nakamura R., Tsunemitsu A. Purification and characterization of galactosephilic component present on the cell surfaces of Streptococcus sanguis ATCC 10557. J Periodontol. 1983 Mar;54(3):163–172. doi: 10.1902/jop.1983.54.3.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt W. E., Doyle R. J., Taylor K. G. Hydrophobic interactions and the adherence of Streptococcus sanguis to hydroxylapatite. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):637–644. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.637-644.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Formation of molecular complexes between a structurally defined M protein and acylated or deacylated lipoteichoic acid of Streptococcus pyogenes. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):426–433. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.426-433.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Whitnack E., Beachey E. H. Hydrophobic interactions of group A streptococci with hexadecane droplets. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):139–145. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.139-145.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson J., Odham G. Effect of inorganic ions and surface active organic compounds on the adherence of oral streptococci. Scand J Dent Res. 1978 Mar;86(2):108–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1978.tb00615.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reusch V. M., Jr Isolation and analysis of sacculi from Streptococcus sanguis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1543–1552. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1543-1552.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Judes H., Weiss E. Cell surface hydrophobicity of dental plaque microorganisms in situ. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):831–834. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.831-834.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Rosenberg E. Role of adherence in growth of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus RAG-1 on hexadecane. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):51–57. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.51-57.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLIN E. A., WOLIN M. J., WOLFE R. S. FORMATION OF METHANE BY BACTERIAL EXTRACTS. J Biol Chem. 1963 Aug;238:2882–2886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., Jacobs T. Cell wall-associated protein antigens of Streptococcus salivarius: purification, properties, and function in adherence. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):233–242. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.233-242.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., McBride B. C. Identification of a Streptococcus salivarius cell wall component mediating coaggregation with Veillonella alcalescens V1. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):723–730. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.723-730.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westergren G., Olsson J. Hydrophobicity and adherence of oral streptococci after repeated subculture in vitro. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):432–435. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.432-435.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]