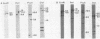Abstract
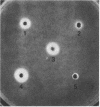
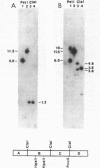
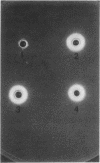
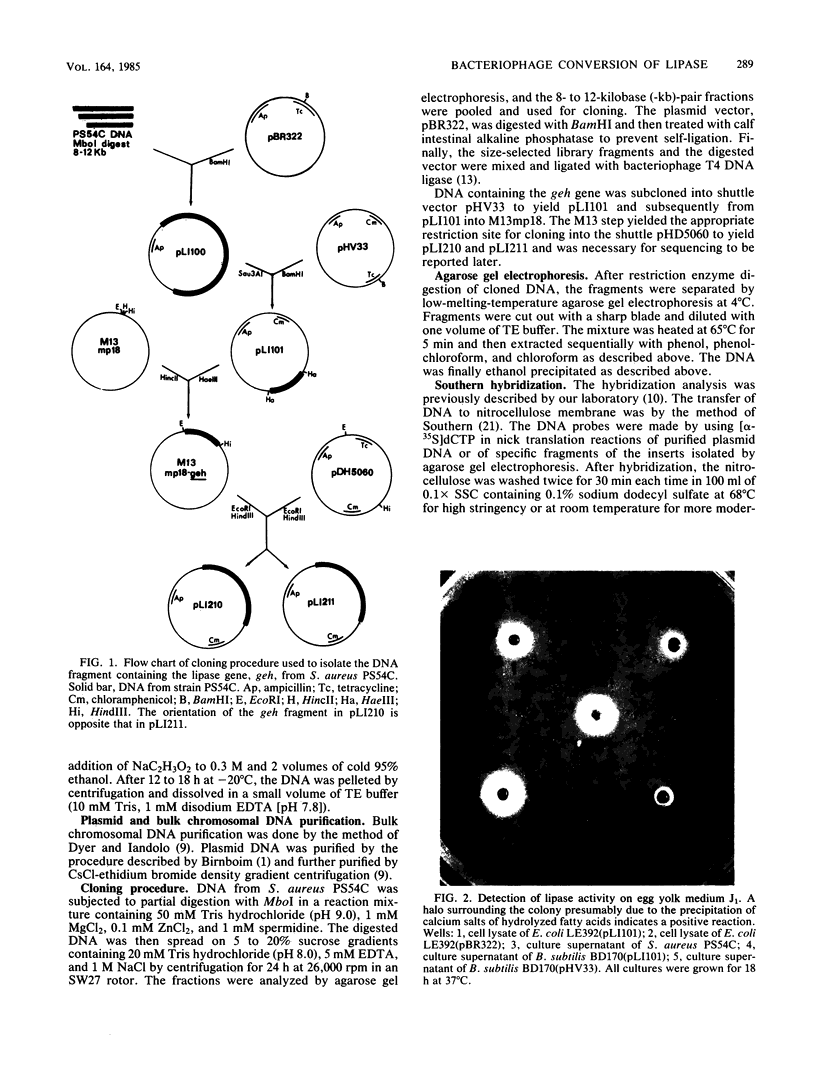
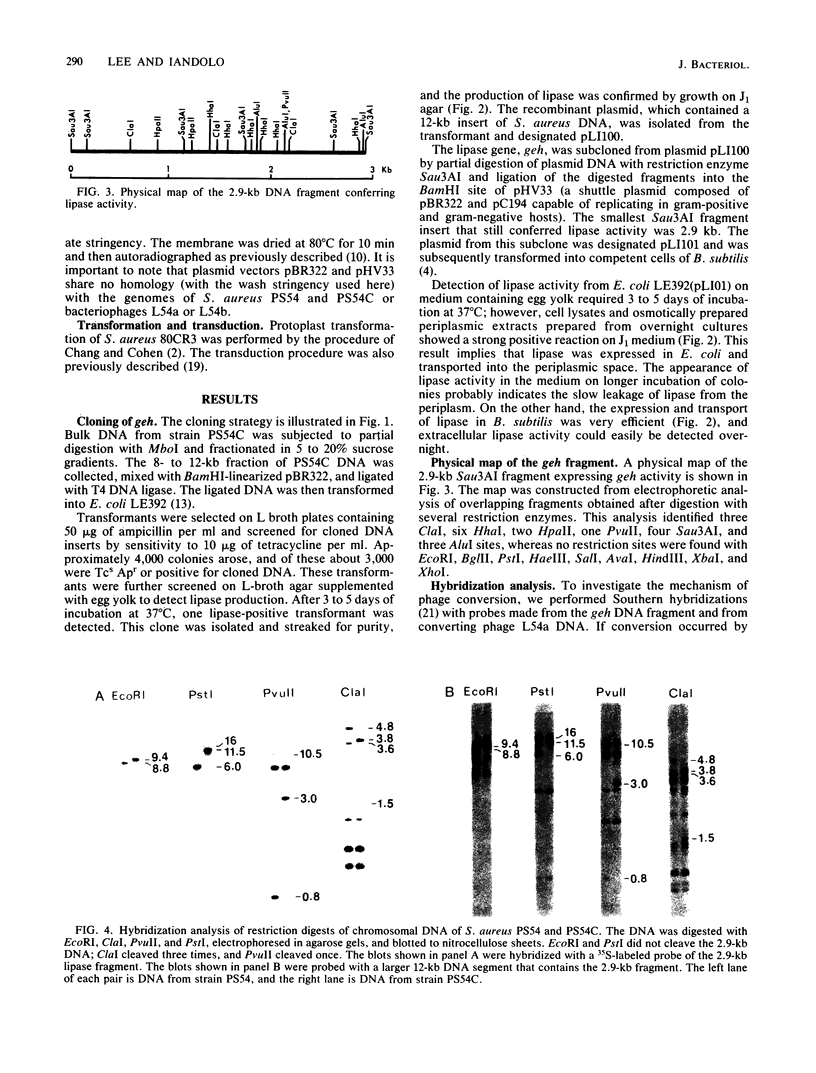
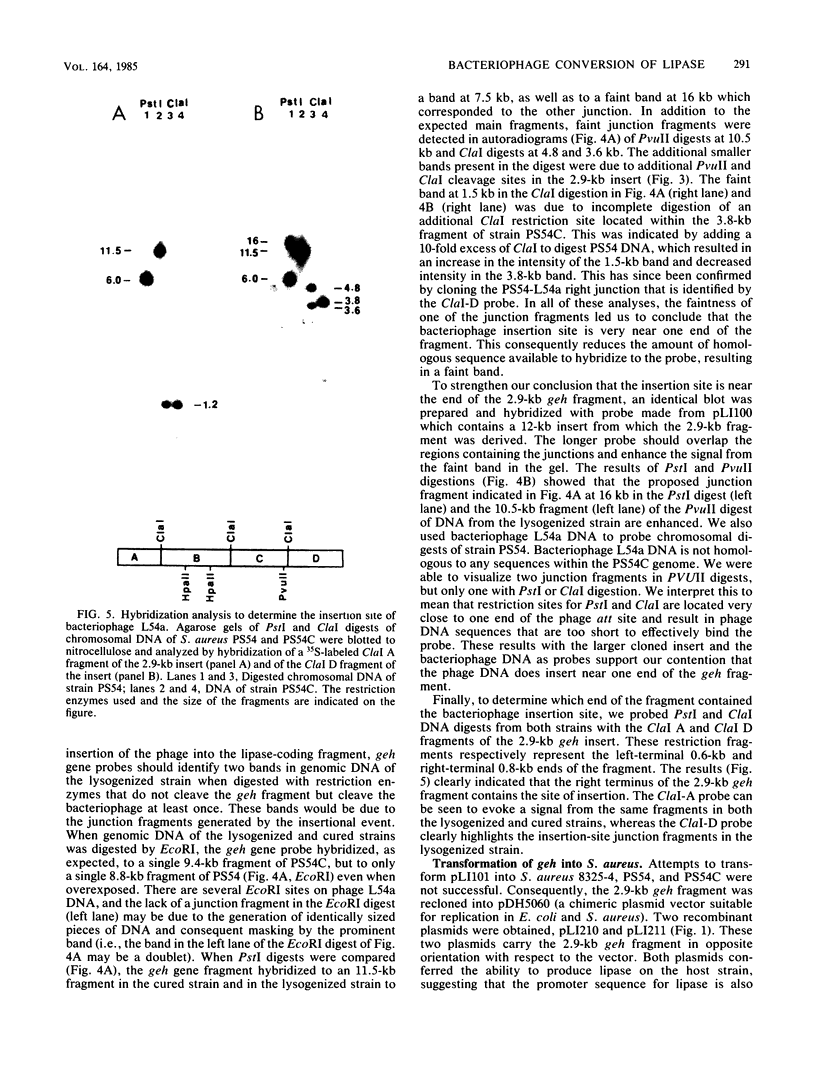
Staphylococcus aureus PS54 harbors two temperate bacteriophages and manifests no lipase activity on egg yolk agar. Curing of one of the resident prophages (L54a) restores lipase activity. To study the mechanism of bacteriophage conversion, the prophage was cured, and the gene encoding lipase activity was cloned into pBR322 in Escherichia coli on a 2.9-kilobase DNA fragment of the chromosome. The fragment was subcloned into a shuttle vector and subsequently transformed into S. aureus and Bacillus subtilis. Lipase activity was expressed in all three genetic backgrounds. Transformation and transductional data indicated that conversion is due to insertional inactivation of the lipase gene. Hybridization analysis with probes made from converting-phage DNA and from the cloned fragment confirmed that the phage insertion site resides within the terminal 0.8 kilobase of the insert.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C. A rapid alkaline extraction method for the isolation of plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:243–255. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00059-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S., Cohen S. N. High frequency transformation of Bacillus subtilis protoplasts by plasmid DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 5;168(1):111–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00267940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clecner B., Sonea S. Acquisition de la propriété hémolytique de type delta par conversion lysogénique chez Staphylococcus aureus. Rev Can Biol. 1966 Sep;25(3):145–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contente S., Dubnau D. Characterization of plasmid transformation in Bacillus subtilis: kinetic properties and the effect of DNA conformation. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 2;167(3):251–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00267416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson A. B., Raibaud P., Mocquot G. Agar medium for the selective enumeration of coagulase-positive Staphylococcus from the rat alimentary tract. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):418–425. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.418-425.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobardzic R., Sonea S. Production d'hémolysines et conversion lysogène chez Staphylococcus aureus. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1971 Jan;120(1):42–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duval-Iflah Y. Lysogenic conversion of the lipase in Staphylococcus pyogenes group 3 strains. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Sep;18(9):1491–1497. doi: 10.1139/m72-228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duval-Iflah Y., Van Heijenoort J., Rousseau M., Raibaud P. Lysogenic conversion for multiple characters in a strain of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1281–1291. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1281-1291.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer D. W., Iandolo J. J. Rapid isolation of DNA from Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):283–285. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.283-285.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer D. W., Rock M. I., Iandolo J. J. Autogenous transduction of phi 11de in Staphylococcus aureus: transfer and genetic properties. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):689–695. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.689-695.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jollick J. D. Evidence for bacteriophage conversion in Staphylococcus. Microbios. 1972 Sep-Oct;6(22):97–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pariza M. W., Iandolo J. J. Base ratio and deoxyribonucleic acid homology studies of six Staphylococcus aureus typing bacteriophages. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Feb;27(2):317–323. doi: 10.1128/am.27.2.317-323.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendal K., Bülow P. Temperate phages influencing lipase production by Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Dec;41(3):349–356. doi: 10.1099/00221287-41-3-349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAH D. B., WILSON J. B. EGG YOLK FACTOR OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. I. NATURE OF THE SUBSTRATE AND ENZYME INVOLVED IN THE EGG YOLK OPACITY REACTION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Mar;85:516–521. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.3.516-521.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sako T., Sawaki S., Sakurai T., Ito S., Yoshizawa Y., Kondo I. Cloning and expression of the staphylokinase gene of Staphylococcus aureus in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;190(2):271–277. doi: 10.1007/BF00330650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer W. M., Iandolo J. J. Genetics of staphylococcal enterotoxin B in methicillin-resistant isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):902–911. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.902-911.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadehra D. V., Harmon L. G. Isolation and purification of staphylococcal lipase. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Mar;15(2):292–295. doi: 10.1128/am.15.2.292-295.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler K. C., de Waart J., Grootsen C. Lysogenic conversion of staphylococci to loss of beta-toxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Jun;39(3):321–333. doi: 10.1099/00221287-39-3-321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]