Abstract
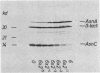
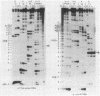
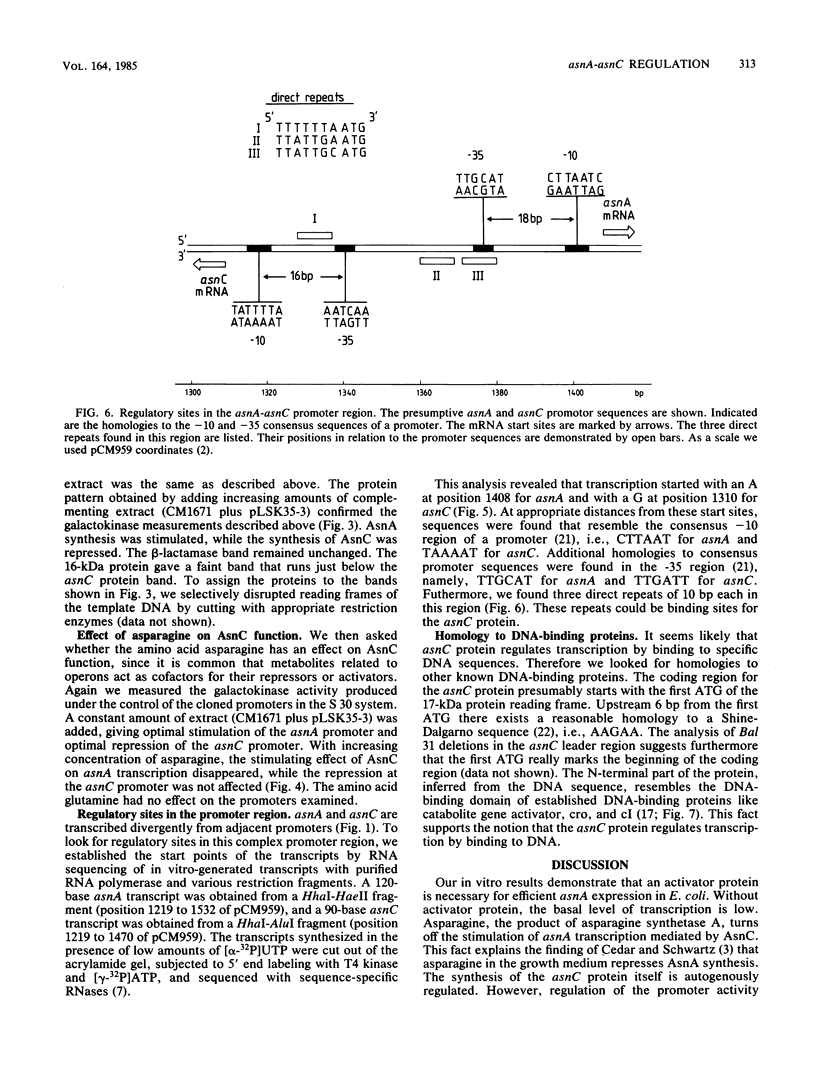
The regulation of the asparagine synthetase A gene of Escherichia coli was studied in vitro with a coupled transcription-translation system. It was shown that the 17-kilodalton gene, which is transcribed divergently from the adjacent asnA gene, codes for an activator of asnA transcription. The synthesis of the 17-kilodalton protein, which we now call AsnC, is autogenously regulated. The stimulating effect of AsnC on asnA transcription is abolished by asparagine, while the autoregulation of asnC is not affected by asparagine. The N-terminal part of the asnC protein, inferred from the DNA sequence, is homologous to the DNA-binding domain of regulatory proteins like catabolite gene activator, cro, and cI. This homology and direct repeats found in the region of the two asn promoters suggest that the asnC protein regulates transcription by binding to DNA. The asn promoters were defined by mapping of the mRNA start sites of in vitro-generated transcripts.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Backman K., Ptashne M., Gilbert W. Construction of plasmids carrying the cI gene of bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4174–4178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhk H. J., Messer W. The replication origin region of Escherichia coli: nucleotide sequence and functional units. Gene. 1983 Oct;24(2-3):265–279. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90087-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedar H., Schwartz J. H. The asparagine synthetase of Escherhic coli. I. Biosynthetic role of the enzyme, purification, and characterization of the reaction products. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 10;244(15):4112–4121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. Cell-free synthesis of proteins coding for mobilisation functions of ColE1 and transposition functions of Tn3. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):29–42. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Casale T., Sollitti P., Chesney R. H. Cytoplasmic L-asparaginase: isolation of a defective strain and mapping of ansA. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):513–515. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.513-515.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiLauro R., Taniguchi T., Musso R., de Crombrugghe B. Unusual location and function of the operator in the Escherichia coli galactose operon. Nature. 1979 Jun 7;279(5713):494–500. doi: 10.1038/279494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felton J., Michaelis S., Wright A. Mutations in two unlinked genes are required to produce asparagine auxotrophy in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Apr;142(1):221–228. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.1.221-228.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Funnell B. E., Kornberg A. The dnaA protein complex with the E. coli chromosomal replication origin (oriC) and other DNA sites. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):889–900. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen F. G., Hansen E. B., Atlung T. The nucleotide sequence of the dnaA gene promoter and of the adjacent rpmH gene, coding for the ribosomal protein L34, of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1043–1048. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01294.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humbert R., Simoni R. D. Genetic and biomedical studies demonstrating a second gene coding for asparagine synthetase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Apr;142(1):212–220. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.1.212-220.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley R. L., Yanofsky C. Trp aporepressor production is controlled by autogenous regulation and inefficient translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3120–3124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lother H., Kölling R., Kücherer C., Schauzu M. dnaA protein-regulated transcription: effects on the in vitro replication of Escherichia coli minichromosomes. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):555–560. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03664.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lother H., Messer W. Promoters in the E. coli replication origin. Nature. 1981 Nov 26;294(5839):376–378. doi: 10.1038/294376a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. W., Ohlendorf D. H., Anderson W. F., Fisher R. G., Takeda Y. Cro repressor protein and its interaction with DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):427–433. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenney K., Shimatake H., Court D., Schmeissner U., Brady C., Rosenberg M. A system to study promoter and terminator signals recognized by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Gene Amplif Anal. 1981;2:383–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M., Yamada M., Hirota Y., Sugimoto K., Oka A., Takanami M. Nucleotide sequence of the asnA gene coding for asparagine synthetase of E. coli K-12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 25;9(18):4669–4676. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.18.4669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rak B., von Reutern M. Insertion element IS5 contains a third gene. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):807–811. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01889.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A., Jakes K. How ribosomes select initiator regions in mRNA: base pair formation between the 3' terminus of 16S rRNA and the mRNA during initiation of protein synthesis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4734–4738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuitje A. R., Meijer M. Maintenance and incompatibility of plasmids carrying the replication origin of the Escherichia coli chromosome: evidence for a control region of replication between oriC and asnA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5775–5791. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubay G. In vitro synthesis of protein in microbial systems. Annu Rev Genet. 1973;7:267–287. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.07.120173.001411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Meyenburg K., Hansen F. G., Riise E., Bergmans H. E., Meijer M., Messer W. Origin of replication, oriC, of the Escherichia coli K12 chromosome: genetic mapping and minichromosome replication. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):121–128. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]