Abstract
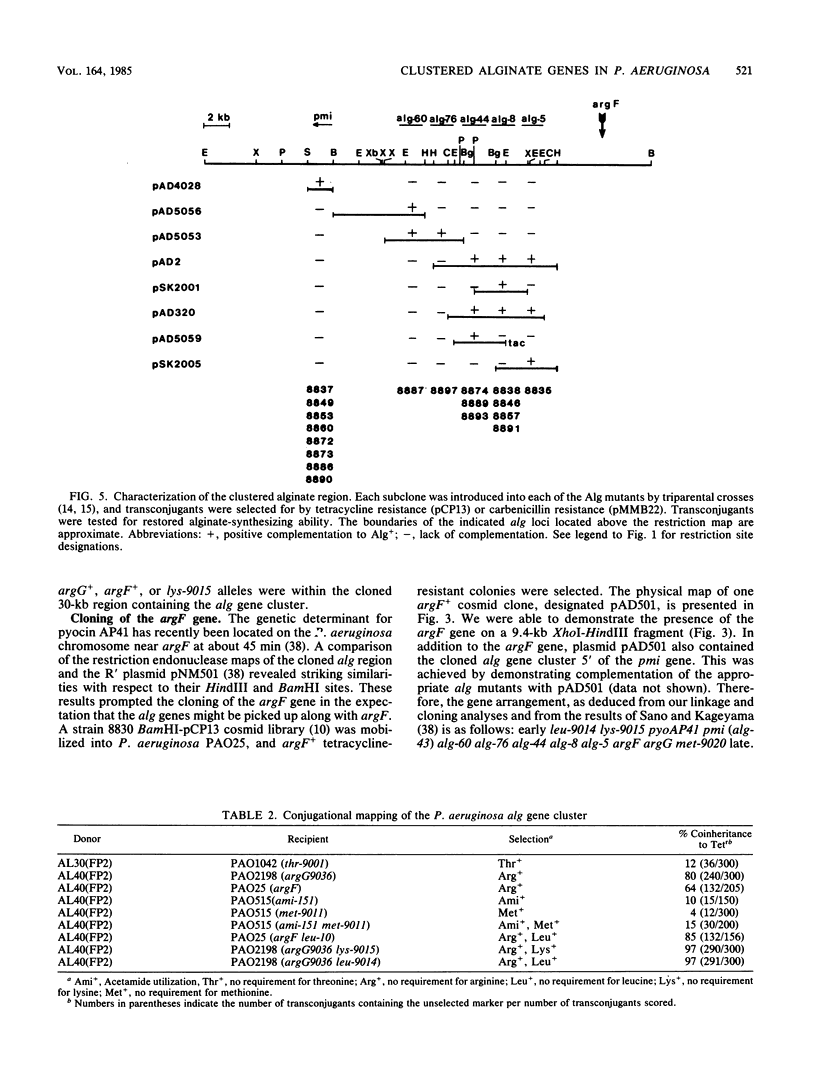
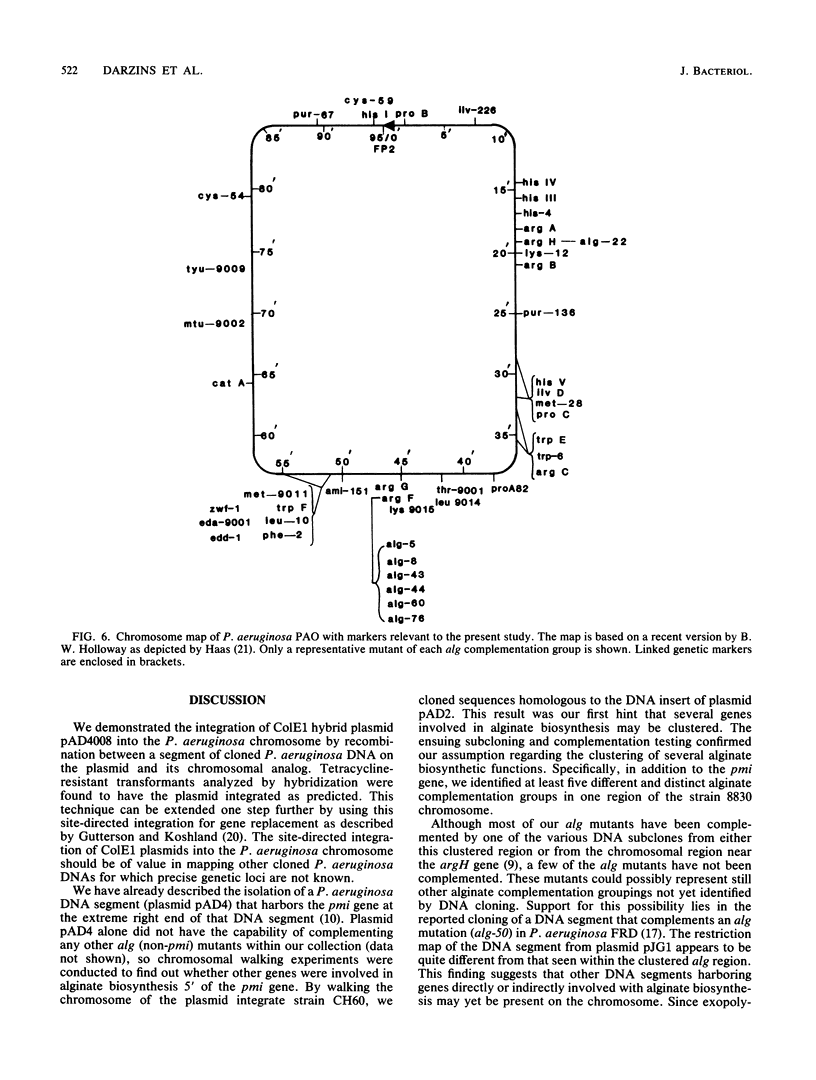
A 10-kilobase DNA fragment previously shown to contain the phosphomannose isomerase gene (pmi) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa was used to construct a pBR325-based hybrid that can be propagated in P. aeruginosa only by the formation of a chromosomal-plasmid cointegrate. This plasmid, designated pAD4008, was inserted into the P. aeruginosa chromosome by recombination at a site of homology between the cloned P. aeruginosa DNA and the chromosome. Mobilization of pAD4008 into P. aeruginosa PAO and 8830 and selection for the stable acquisition of tetracycline resistance resulted in specific and predictable changes in the pattern of endonuclease restriction sites in the phosphomannose isomerase gene region of the chromosomes. Chromosomal DNA from the tetracycline-resistant transformants was used to clone the drug resistance determinant with Bg/II or XbaI, thereby allowing the "walking" of the P. aeruginosa chromosome in the vicinity of the pmi gene. Analysis of overlapping tetracycline-resistant clones indicated the presence of sequences homologous to the DNA insert of plasmid pAD2, a recombinant clone of P. aeruginosa origin previously shown to complement several alginate-negative mutants. Restriction mapping, subcloning, and complementation analysis of a 30-kilobase DNA region demonstrated the tight clustering of several genetic loci involved in alginate biosynthesis. Furthermore, the tetracycline resistance determinant in PAO strain transformed by pAD4008 was mapped on the chromosome by plasmid FP2-mediated conjugation and was found to be located near 45 min.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J., Low K. B., Taylor A. L. Recalibrated linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Mar;40(1):116–167. doi: 10.1128/br.40.1.116-167.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagdasarian M. M., Amann E., Lurz R., Rückert B., Bagdasarian M. Activity of the hybrid trp-lac (tac) promoter of Escherichia coli in Pseudomonas putida. Construction of broad-host-range, controlled-expression vectors. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90197-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee P. C., Vanags R. I., Chakrabarty A. M., Maitra P. K. Alginic acid synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants defective in carbohydrate metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):238–245. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.238-245.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee P. C., Vanags R. I., Chakrabarty A. M., Maitra P. K. Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase activity is essential for synthesis of alginate from glucose by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):458–460. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.458-460.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz J. L., Brown J. E., Clarke P. H., Day M. Genetic analysis of amidase mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Genet Res. 1974 Jun;23(3):335–359. doi: 10.1017/s001667230001497x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler P. M., Krishnapillai V. Isolation and properties of recombination-deficient mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mutat Res. 1974 Apr;23(1):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(74)90155-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford I. P. Gene rearrangements in the evolution of the tryptophan synthetic pathway. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Jun;39(2):87–120. doi: 10.1128/br.39.2.87-120.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzins A., Chakrabarty A. M. Cloning of genes controlling alginate biosynthesis from a mucoid cystic fibrosis isolate of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):9–18. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.9-18.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzins A., Nixon L. L., Vanags R. I., Chakrabarty A. M. Cloning of Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa phosphomannose isomerase genes and their expression in alginate-negative mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):249–257. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.249-257.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doggett R. G., Harrison G. M., Carter R. E. Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with chronic illnesses. Lancet. 1971 Jan 30;1(7692):236–237. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90973-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARGIE B., HOLLOWAY B. W. ABSENCE OF CLUSTERING OF FUNCTIONALLY RELATED GENES IN PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA. Genet Res. 1965 Jul;6:284–299. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300004158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figurski D. H., Helinski D. R. Replication of an origin-containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. M., Long S. R., Brown S. E., Buikema W. J., Ausubel F. M. Construction of a broad host range cosmid cloning vector and its use in the genetic analysis of Rhizobium mutants. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyfe J. A., Govan J. R. Alginate synthesis in mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a chromosomal locus involved in control. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Aug;119(2):443–450. doi: 10.1099/00221287-119-2-443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg J. B., Ohman D. E. Cloning and expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa of a gene involved in the production of alginate. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1115–1121. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1115-1121.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govan J. R., Fyfe J. A., McMillan C. The instability of mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa: fluctuation test and improved stability of the mucoid form in shaken culture. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Jan;110(1):229–232. doi: 10.1099/00221287-110-1-229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govan J. R. Mucoid strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: the influence of culture medium on the stability of mucus production. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Nov;8(4):513–522. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-4-513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutterson N. I., Koshland D. E., Jr Replacement and amplification of bacterial genes with sequences altered in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4894–4898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas D. Genetic aspects of biodegradation by pseudomonads. Experientia. 1983 Nov 15;39(11):1199–1213. doi: 10.1007/BF01990357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas D., Holloway B. W. R factor variants with enhanced sex factor activity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Mar 30;144(3):243–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00341722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessie T. G., Phibbs P. V., Jr Alternative pathways of carbohydrate utilization in pseudomonads. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:359–388. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.002043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T. Y., Hassid W. Z. Pathway of algnic acid synthesis in the marine brown alga, Fucus gardneri Silva. J Biol Chem. 1966 Nov 25;241(22):5284–5297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linker A., Jones R. S. A new polysaccharide resembling alginic acid isolated from pseudomonads. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 25;241(16):3845–3851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynn A. R., Sokatch J. R. Incorporation of isotope from specifically labeled glucose into alginates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1161–1162. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1161-1162.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto H., Nakazawa T., Ohta S., Terawaki Y. Chromosomal locations of catA, pobA, dcu and chu genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Genet Res. 1981 Dec;38(3):251–266. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300020590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mee B. J., Lee B. T. A map order for his I, one of the genetic regions controlling histidine biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa, using the transducing phage F116. Genetics. 1969 Jul;62(3):687–696. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mian F. A., Jarman T. R., Righelato R. C. Biosynthesis of exopolysaccharide by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1978 May;134(2):418–422. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.2.418-422.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman D. E., Chakrabarty A. M. Genetic mapping of chromosomal determinants for the production of the exopolysaccharide alginate in a Pseudomonas aeruginosa cystic fibrosis isolate. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):142–148. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.142-148.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pindar D. F., Bucke C. The biosynthesis of alginic acid by Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;152(3):617–622. doi: 10.1042/bj1520617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roehl R. A., Feary T. W., Phibbs P. V., Jr Clustering of mutations affecting central pathway enzymes of carbohydrate catabolism in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1123–1129. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1123-1129.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roehl R. A., Phibbs P. V., Jr Characterization and genetic mapping of fructose phosphotransferase mutations in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):897–905. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.897-905.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvkun G. B., Ausubel F. M. A general method for site-directed mutagenesis in prokaryotes. Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):85–88. doi: 10.1038/289085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Hartman P. E. Linkage map of Salmonella typhimurium, edition V. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Jun;42(2):471–519. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.2.471-519.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano Y., Kageyama M. Genetic determinant of pyocin AP41 as an insert in the Pseudomonas aeruginosa chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):562–570. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.562-570.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanisich V., Holloway B. W. Conjugation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Genetics. 1969 Feb;61(2):327–339. doi: 10.1093/genetics/61.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Torrontegui G., Diaz R., Wheelis M. L., Cánovas J. L. Supra-operonic clustering of genes specifying glucose dissimilation in Pseudomonas putida. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Mar 30;144(3):307–311. doi: 10.1007/BF00341729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]