Abstract
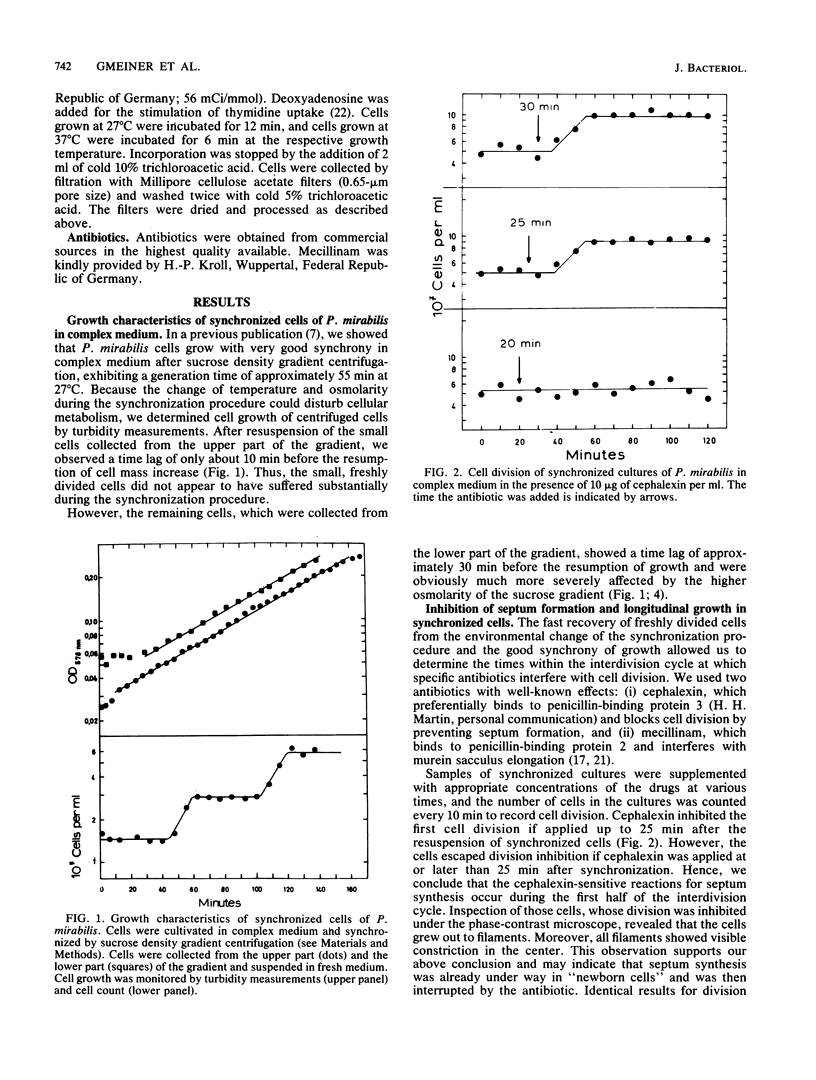
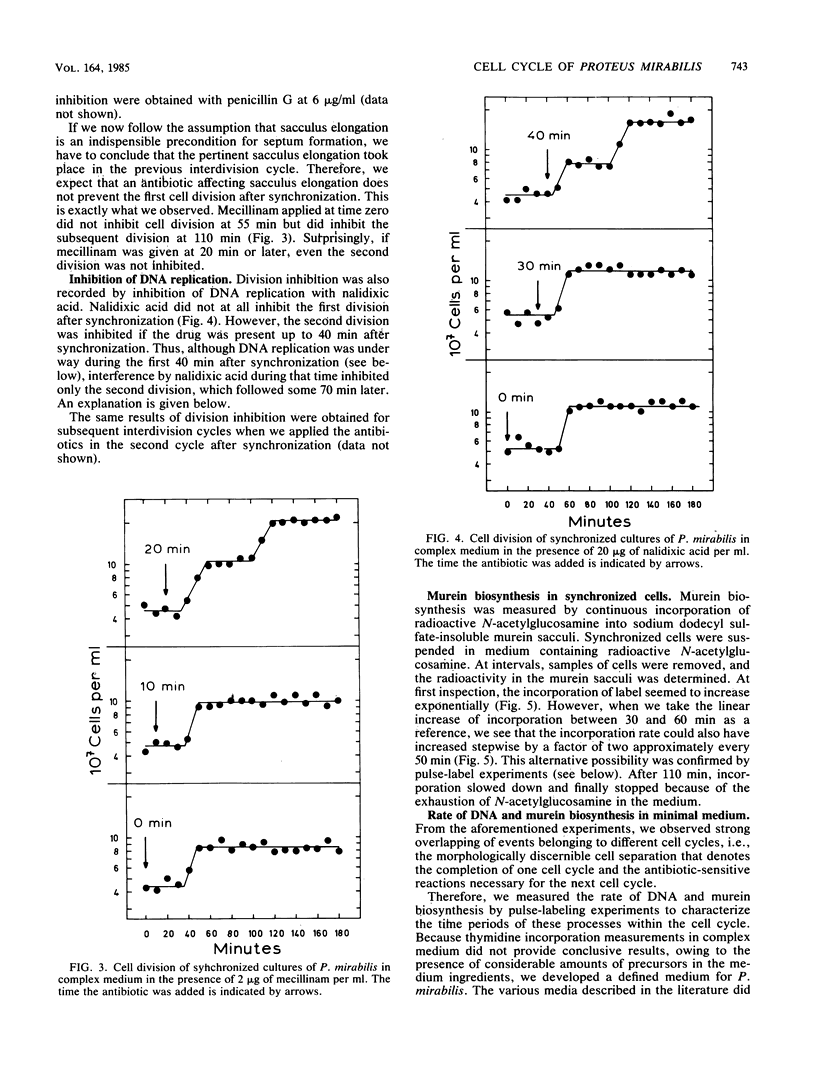
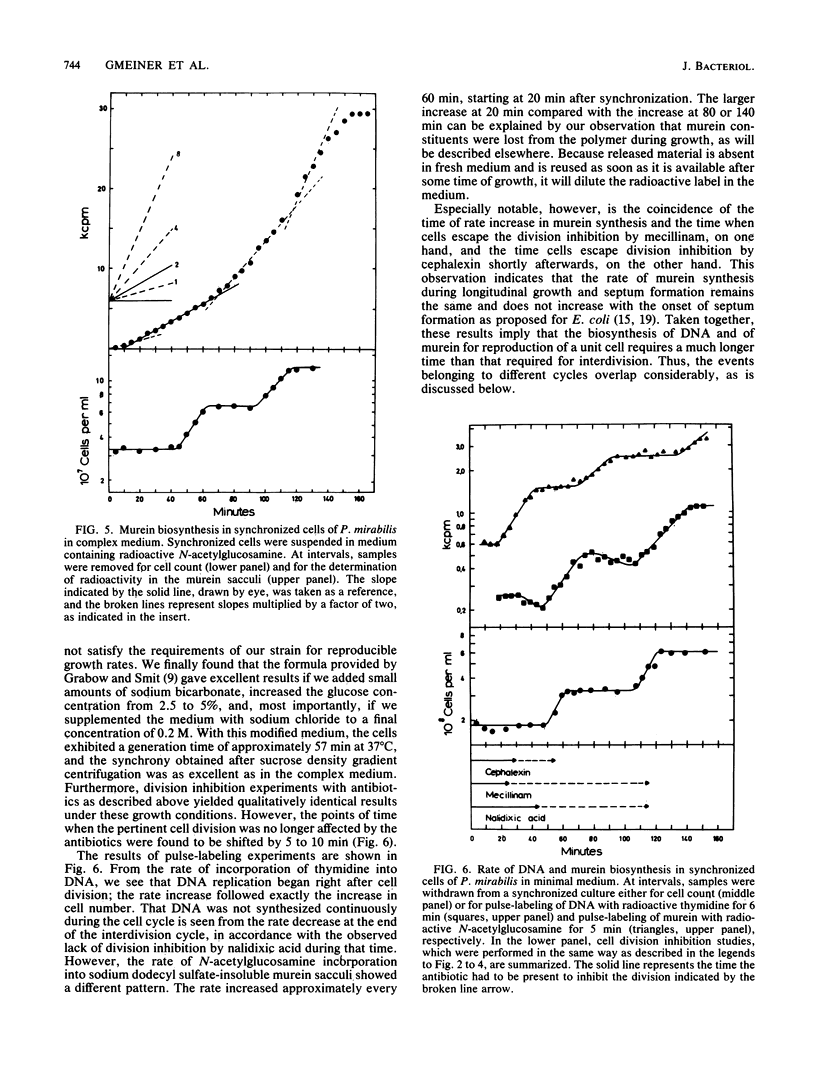
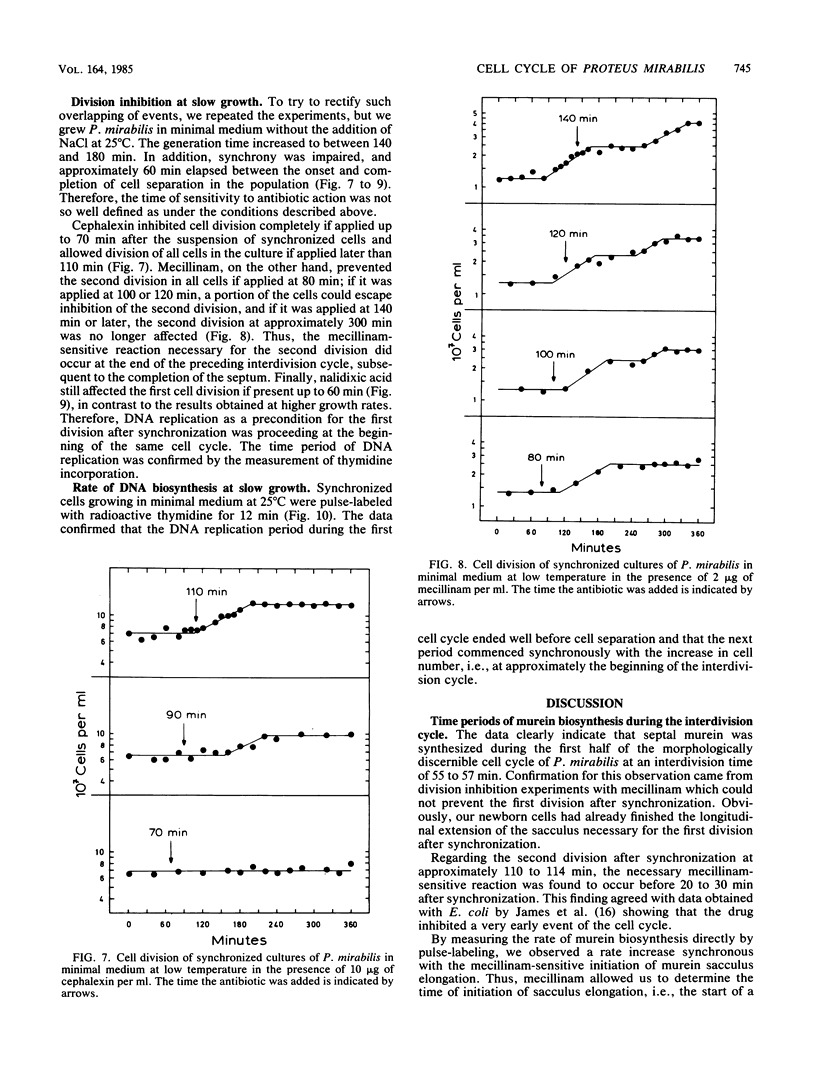
We investigated the time periods of DNA replication, lateral cell wall extension, and septum formation within the cell cycle of Proteus mirabilis. Cells were cultivated under three different conditions, yielding interdivision times of approximately 55, 57, and 160 min, respectively. Synchrony was achieved by sucrose density gradient centrifugation. The time periods were estimated by division inhibition studies with cephalexin, mecillinam, and nalidixic acid. In addition, DNA replication was measured by thymidine incorporation, and murein biosynthesis was measured by incorporation of N-acetylglucosamine into sodium dodecyl sulfate-insoluble murein sacculi. At interdivision times of 55 to 57 min murein biosynthesis for reproduction of a unit cell lasted longer than the interdivision time itself, whereas DNA replication finished within 40 min. Surprisingly, inhibition of DNA replication by nalidixic acid did not inhibit the subsequent cell division but rather the one after that. Because P. mirabilis fails to express several reactions of the recA-dependent SOS functions known from Escherichia coli, the drug allowed us to determine which DNA replication period actually governed which cell division. Taken together, the results indicate that at an interdivision time of 55 to 57 min, the biosynthetic cell cycle of P. mirabilis lasts approximately 120 min. To achieve the observed interdivision time, it is necessary that two subsequent biosynthetic cell cycles be tightly interlocked. The implications of these findings for the regulation of the cell cycle are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braun V., Gnirke H., Henning U., Rehn K. Model for the structure of the shape-maintaining layer of the Escherichia coli cell envelope. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1264–1270. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1264-1270.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton P., Holland I. B. Two pathways of division inhibition in UV-irradiated E. coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;190(2):309–314. doi: 10.1007/BF00330656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S., Helmstetter C. E. Chromosome replication and the division cycle of Escherichia coli B/r. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):519–540. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90425-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Essig P., Martin H. H., Gmeiner J. Murein and lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis in synchronized cells of Escherichia coli K 12 and the effect of penicillin G, mecillinam and nalidixic acid. Arch Microbiol. 1982 Sep;132(3):245–250. doi: 10.1007/BF00407959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gmeiner J., Kroll H. P. Murein biosynthesis and O-acetylation of N-acetylmuramic acid during the cell-division cycle of Proteus mirabilis. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jun;117(1):171–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06317.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabow W. O., Smit J. A. Methionine synthesis in Proteus mirabilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Jan;46(1):47–57. doi: 10.1099/00221287-46-1-47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudas L. J., Pardee A. B. Model for regulation of Escherichia coli DNA repair functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofemeister J., Böhme H. DNA repair in Proteus mirabilis. III.Survival, dimer excision, and UV reactivation in comparison with Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Nov 24;141(2):147–161. doi: 10.1007/BF00267680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofemeister J., Eitner G. Repair and plasmid R46 mediated mutation requires inducible functions in Proteus mirabilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;183(2):369–375. doi: 10.1007/BF00270642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofemeister J., Köhler H., Filippov V. D. DNA repair in Proteus mirabilis. VI. Plasmid (R46-) mediated recovery and UV mutagenesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Oct 3;176(2):265–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann B., Messer W., Schwarz U. Regulation of polar cap formation in the life cycle of Escherichia coli. J Supramol Struct. 1972;1(1):29–37. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James R., Haga J. Y., Pardee A. B. Inhibition of an early event in the cell division cycle of Escherichia coli by FL1060, an amidinopenicillanic acid. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):1283–1292. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.1283-1292.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin H. H., Gmeiner J. Modification of peptidoglycan structure by penicillin action in cell walls of Proteus mirabilis. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Apr;95(3):487–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12988.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olijhoek A. J., Klencke S., Pas E., Nanninga N., Schwarz U. Volume growth, murein synthesis, and murein cross-linkage during the division cycle of Escherichia coli PA3092. J Bacteriol. 1982 Dec;152(3):1248–1254. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.3.1248-1254.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satta G., Fontana R. Characterization of a conditional mutant with altered envelope showing pH-dependent morphology and temperature-dependent division. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jan;80(1):51–63. doi: 10.1099/00221287-80-1-51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G., Pardee A. B. Penicillin-binding proteins and cell shape in E. coli. Nature. 1975 Apr 10;254(5500):516–517. doi: 10.1038/254516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Störl K., Venner H. Einbau von Thymin und Thymidin in die DNS von Proteus mirabilis. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1972;12(6):479–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


