Abstract
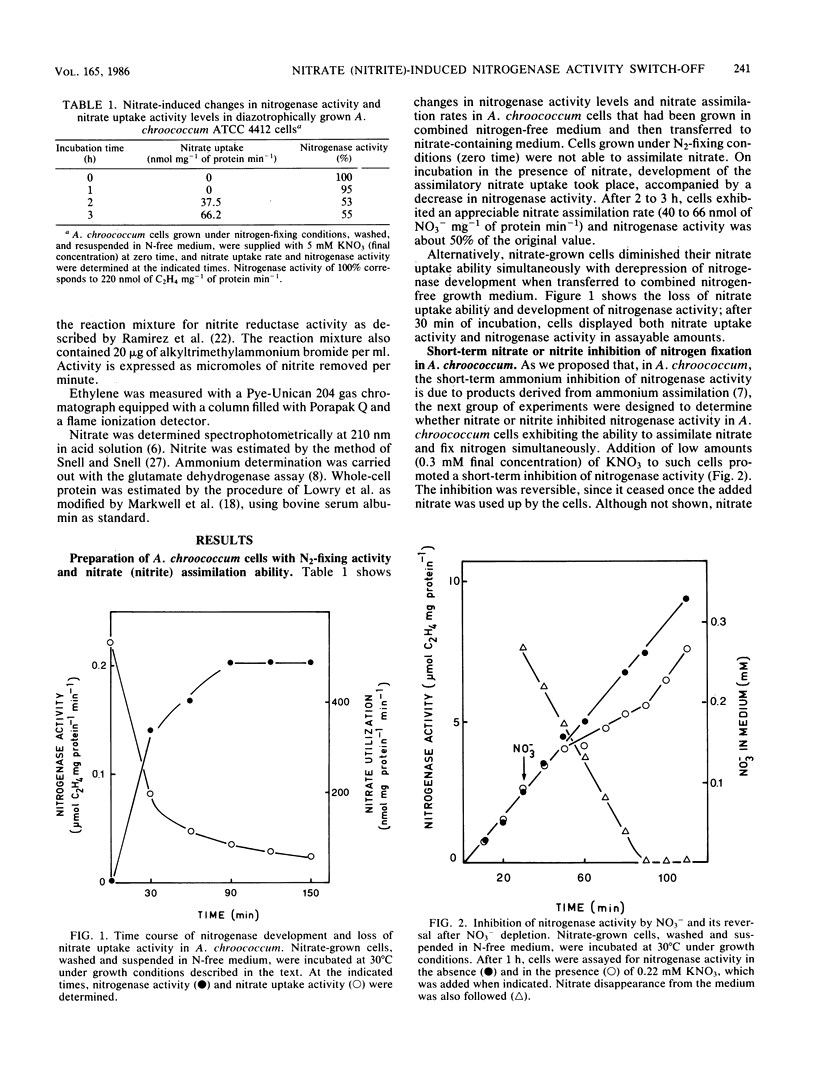
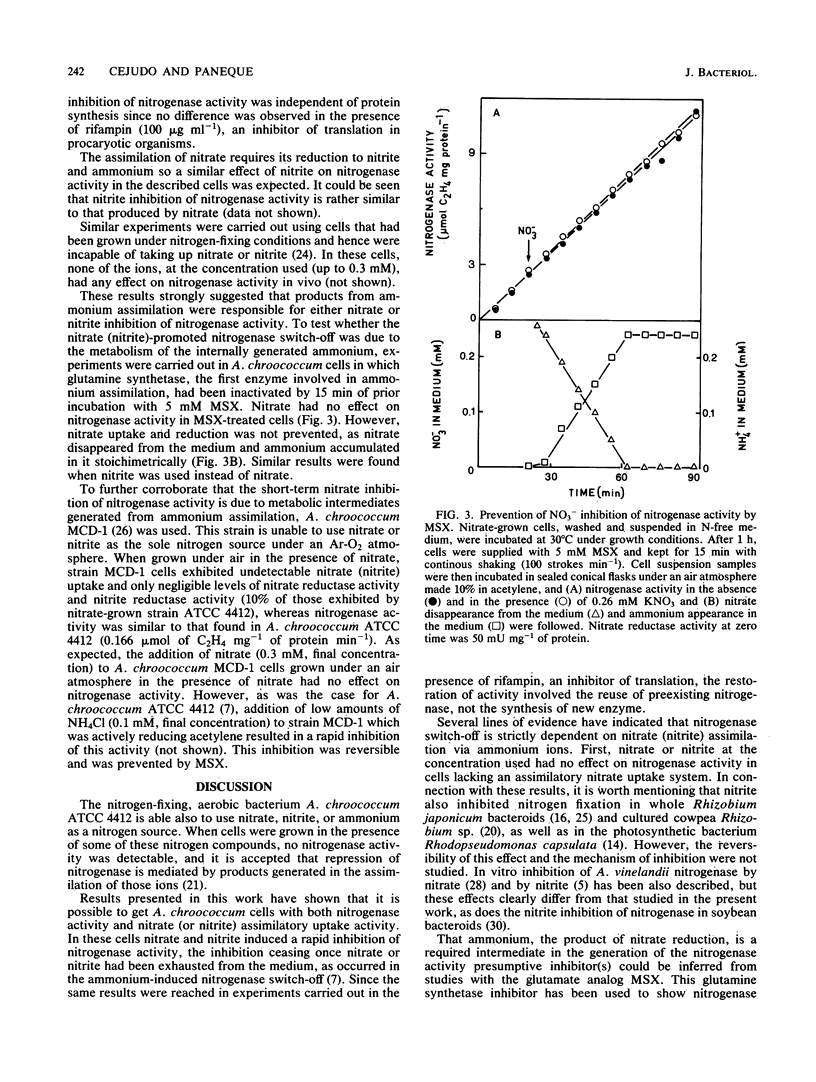
Nitrate-grown Azotobacter chroococcum ATCC 4412 cells lack the ability to fix N2. Nitrogenase activity developed after the cells were suspended in a combined nitrogen-free medium and was paralleled by a concomitant decrease in nitrate assimilation capacity. In such treated cells exhibiting transitory nitrate assimilation and N2-fixation capacity, nitrate or nitrite caused a short-term inhibitory effect on nitrogenase activity which ceased once the anion was exhausted from the medium. The analog L-methionine-DL-sulfoximine, an inhibitor of glutamine synthetase, prevented inhibition of nitrogenase activity by nitrate or nitrite without affecting the uptake of these antions, which were reduced and stoichiometrically released into the external medium as ammonium. Inhibition of nitrogenase by nitrate (nitrite) did not take place in A. chroococcum MCD1, which is unable to assimilate either. We conclude that the short-term inhibitory effect of nitrate (nitrite) on nitrogenase activity is due to some organic product(s) formed during the assimilation of the ammonium resulting from nitrate (nitrite) reduction.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenchley J. E. Effect of methionine sulfoximine and methionine sulfone on glutamate synthesis in Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):666–673. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.666-673.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cejudo F. J., de la Torre A., Paneque A. Short-term ammonium inhibition of nitrogen fixation in Azotobacter. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Sep 17;123(2):431–437. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90248-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drozd J. W., Tubb R. S., Postgate J. R. A chemostat study of the effect of fixed nitrogen sources on nitrogen fixation, membranes and free amino acids in Azotobacter chroococcum. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Nov;73(2):221–232. doi: 10.1099/00221287-73-2-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. K., Brill W. J. Derepression of nitrogenase synthesis in the presence of excess NH4+. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Aug 5;59(3):967–971. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero M. G., Vega J. M., Leadbetter E., Losada M. Preparation and characterization of a soluble nitrate reductase from Azotobacter chroococcum. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973 Jun 25;91(4):287–304. doi: 10.1007/BF00425049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. W., Holsten R. D., Jackson E. K., Burns R. C. The acetylene-ethylene assay for n(2) fixation: laboratory and field evaluation. Plant Physiol. 1968 Aug;43(8):1185–1207. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.8.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy C., Postgate J. R. Expression of Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogen fixation genes in nitrate reductase mutants of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Feb;98(2):551–557. doi: 10.1099/00221287-98-2-551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy I. R., Rigaud J., Trinchant J. C. Nitrate reductase from bacteroides of Rhizobium japonicum: enzyme characteristics and possible interaction with nitrogen fixation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 27;397(1):24–35. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laane C., Krone W., Konings W., Haaker H., Veeger C. Short-term effect of ammonium chloride on nitrogen fixation by Azotobacter vinelandii and by bacteroids of Rhizobium leguminosarum. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jan;103(1):39–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04286.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim J., Marcus L. Correlation of ultrastructure in Azotobacter vinelandii with nitrogen source for growth. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jan;101(1):286–291. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.1.286-291.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagan J. D., Scowcroft W. R., Dudman W. F., Gibson A. H. Nitrogen fixation in nitrate reductase-deficient mutants of cultured rhizobia. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):718–723. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.718-723.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez J. M., Del Campo F. F., Paneque A., Losada M. Ferredoxin-nitrite reductase from spinach. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Apr 12;118(1):58–71. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80144-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson R. L., Chesshyre J. A., Wheeler C., Jones R., Woodley P. R., Postgate J. R. Genome size and complexity in Azotobacter chroococcum. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Jul;130(7):1603–1612. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-7-1603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger G. J. Regulation of nitrogen fixation in Azotobacter vinelandii OP: the role of nitrate reductase. J Bacteriol. 1969 Apr;98(1):56–61. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.1.56-61.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. D., Rowell P. Effects of L-methionine-DL-sulphoximine on the assimilation of newly fixed NH3, acetylene reduction and heterocyst production in Anabaena cylindrica. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Aug 4;65(3):846–856. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80463-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tubb R. S., Postgate J. R. Control of nitrogenase synthesis in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Nov;79(1):103–117. doi: 10.1099/00221287-79-1-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumft W. G., Castillo F. Regulatory properties of the nitrogenase from Rhodopseudomonas palustris. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Apr 27;117(1):53–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00689351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


