Abstract
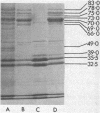
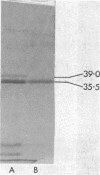
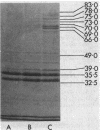
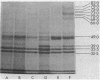
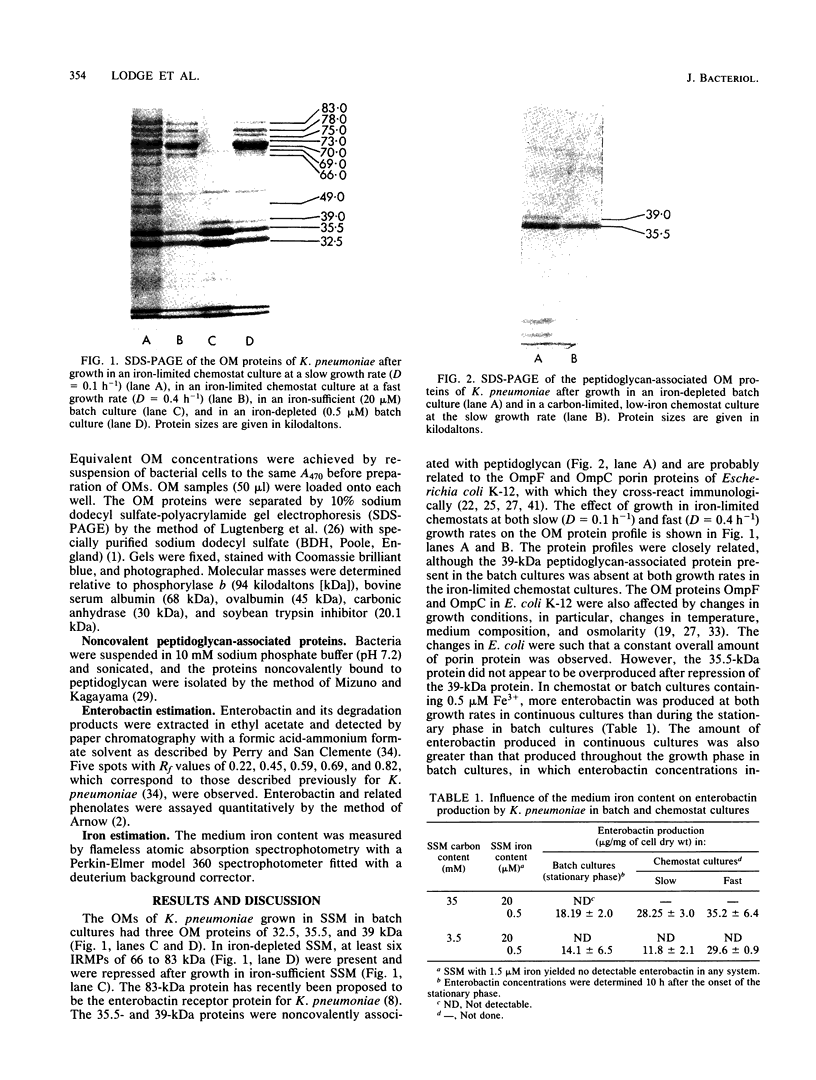
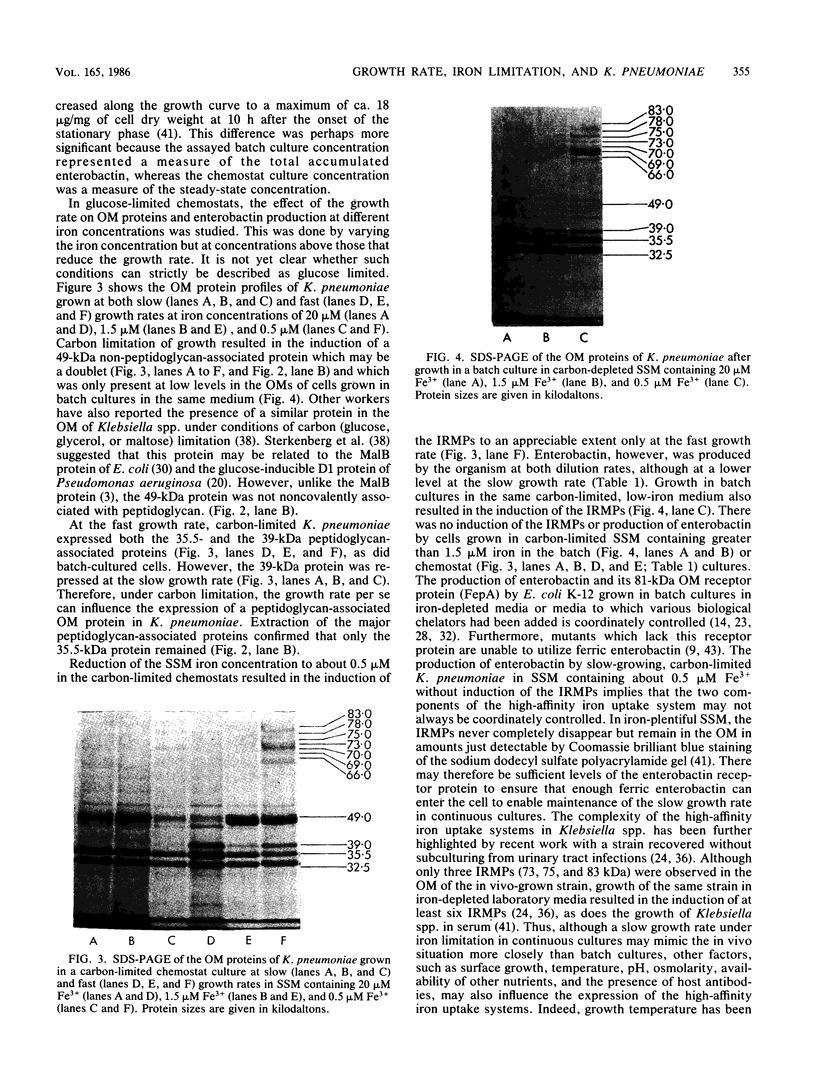
The influence of the growth rate on outer membrane protein composition and enterobactin production was studied with Klebsiella pneumoniae grown under conditions of iron limitation in chemostats. More enterobactin was produced at fast (D = 0.4 h-1) and slow (D = 0.1 h-1) growth rates in continuous cultures than in either logarithmic- or stationary-phase batch cultures. When the growth rate was controlled under conditions of carbon limitation and the iron level was reduced to 0.5 microM, the iron-regulated outer membrane proteins and enterobactin were induced at the fast growth rate. At the slow growth rate, although the iron-regulated outer membrane proteins were barely visible, a significant level of enterobactin was still produced. These results suggest that under conditions of either carbon or iron limitation, the growth rate can influence the induction of the high-affinity iron uptake system of K. pneumoniae. Other outer membrane proteins, including a 39-kilodalton peptidoglycan-associated protein, were found to vary with the growth rate and nutrient limitation.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anwar H., Lambert P. A., Brown M. R. Influence of sodium dodecyl sulphate quality on the electrophoretic mobility of the outer membrane proteins of mucoid and non-mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 13;761(2):119–125. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90220-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Krieger-Brauer H. J. Interrelationship of the phage lambda receptor protein and maltose transport in mutants of Escherichia coli K12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 15;469(1):89–98. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90328-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. D. Microbial growth rates in nature. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Mar;35(1):39–58. doi: 10.1128/br.35.1.39-58.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. R., Williams P. Influence of substrate limitation and growth phase on sensitivity to antimicrobial agents. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jan;15 (Suppl A):7–14. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.suppl_a.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen J. J. The significance of iron in infection. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6):1127–1138. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.6.1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chart H., Griffiths E. Antigenic and molecular homology of the ferric enterobactin receptor protein of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Jun;131(6):1503–1509. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-6-1503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. B., Gibson F., Luke R. K., Newton N. A., O'Brien I. G., Rosenberg H. Mutations affecting iron transport in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):219–226. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.219-226.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eudy W. W., Burrous S. E. Generation times of Proteus mirabilis and Escherichia coli in experimental infections. Chemotherapy. 1973;19(3):161–170. doi: 10.1159/000221451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filip C., Fletcher G., Wulff J. L., Earhart C. F. Solubilization of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli by the ionic detergent sodium-lauryl sarcosinate. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):717–722. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.717-722.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming T. P., Nahlik M. S., McIntosh M. A. Regulation of enterobactin iron transport in Escherichia coli: characterization of ent::Mu d(Apr lac) operon fusions. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1171–1177. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1171-1177.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garibaldi J. A. Influence of temperature on the biosynthesis of iron transport compounds by Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):262–265. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.262-265.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert P. The theory and relevance of continuous culture. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jan;15 (Suppl A):1–6. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.suppl_a.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERBERT D., ELSWORTH R., TELLING R. C. The continuous culture of bacteria; a theoretical and experimental study. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Jul;14(3):601–622. doi: 10.1099/00221287-14-3-601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E. Alterations in outer membrane permeability. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:237–264. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstra H., Dankert J. Antigenic cross-reactivity of major outer membrane proteins in enterobacteriaceae species. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Apr;111(2):293–302. doi: 10.1099/00221287-111-2-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebba P. E., McIntosh M. A., Neilands J. B. Kinetics of biosynthesis of iron-regulated membrane proteins in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):880–888. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.880-888.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Bronstein H., van Selm N., Peters R. Peptidoglycan-associated outer membrane proteins in gammegatine bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 17;465(3):571–578. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90274-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Van Alphen L. Molecular architecture and functioning of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli and other gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):51–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh M. A., Earhart C. F. Coordinate regulation by iron of the synthesis of phenolate compounds and three outer membrane proteins in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jul;131(1):331–339. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.1.331-339.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Kageyama M. Isolation and characterization of major outer membrane proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO with special reference to peptidoglycan-associated protein. J Biochem. 1979 Oct;86(4):979–989. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakae T., Ishii J. Permeability properties of Escherichia coli outer membrane containing, pore-forming proteins: comparison between lambda receptor protein and porin for saccharide permeation. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jun;142(3):735–740. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.3.735-740.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Microbial envelope proteins related to iron. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:285–309. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Microbial iron compounds. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:715–731. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Vaara M. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):1–32. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.1-32.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. D., San Clemente C. L. Siderophore synthesis in Klebsiella pneumoniae and Shigella sonnei during iron deficiency. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):1129–1132. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.1129-1132.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sciortino C. V., Finkelstein R. A. Vibrio cholerae expresses iron-regulated outer membrane proteins in vivo. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):990–996. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.990-996.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shand G. H., Anwar H., Kadurugamuwa J., Brown M. R., Silverman S. H., Melling J. In vivo evidence that bacteria in urinary tract infection grow under iron-restricted conditions. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):35–39. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.35-39.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. Microbial surfaces in relation to pathogenicity. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):475–500. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.475-500.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterkenburg A., Vlegels E., Wouters J. T. Influence of nutrient limitation and growth rate on the outer membrane proteins of Klebsiella aerogenes NCTC 418. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Sep;130(9):2347–2355. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-9-2347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron and infection. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):45–66. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.45-66.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron withholding: a defense against infection and neoplasia. Physiol Rev. 1984 Jan;64(1):65–102. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P., Brown M. R., Lambert P. A. Effect of iron deprivation on the production of siderophores and outer membrane proteins in Klebsiella aerogenes. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Sep;130(9):2357–2365. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-9-2357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worsham P. L., Konisky J. Effect of growth temperature on the acquisition of iron by Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.163-168.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young I. G. Preparation of enterochelin from Escherichia coli. Prep Biochem. 1976;6(2-3):123–131. doi: 10.1080/00327487608061607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]