Abstract
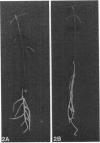
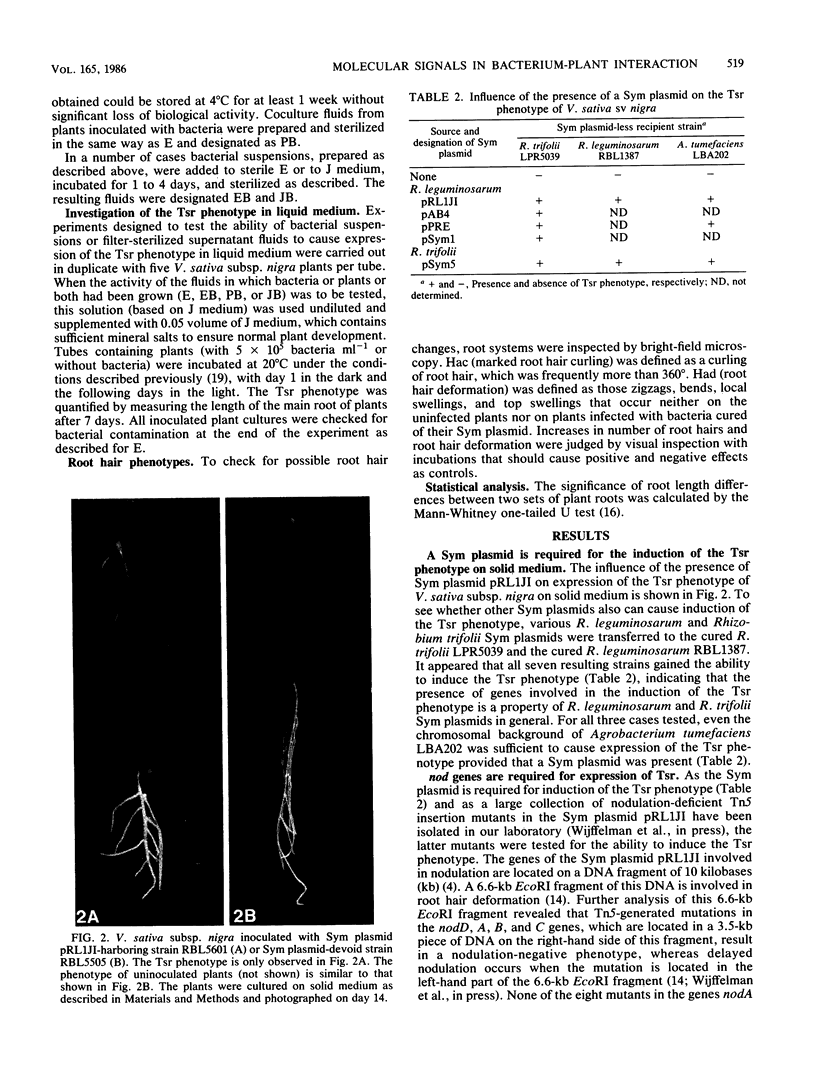
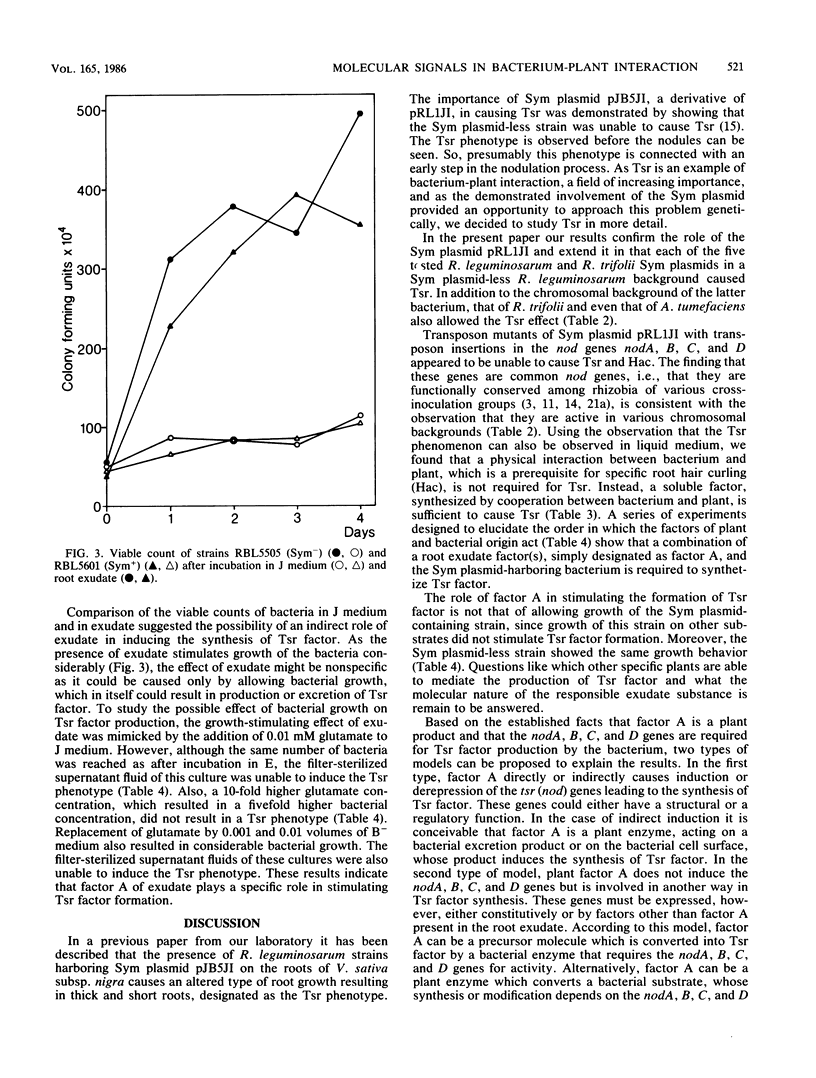
In a previous paper it was shown that cocultivation of Rhizobium leguminosarum with the plant Vicia sativa subsp. nigra on solid medium causes a changed mode of growth of the plant roots, resulting in thick and short roots (Tsr). The Sym plasmid present in the bacterium appeared to be essential for causing Tsr (A. A. N. van Brussel, T. Tak, A. Wetselaar, E. Pees, and C. A. Wijffelman, Plant Sci. Lett. 27:317-325, 1982). In the present paper, we show that a role in causing Tsr is general for Sym plasmids of R. leguminosarum and Rhizobium trifolii. Moreover, mutants with transposon insertions in the Sym plasmid-localized nodulation genes nodA, B, C, and D are unable to cause Tsr, in contrast to nodulation mutants localized in other parts of the Sym plasmid. The observation that Tsr could also be brought about in liquid medium enabled us to show that Tsr is caused by a soluble factor. Experiments in which plants and bacteria were grown separately in the sterile supernatant fluids of each other resulted in establishing the following sequence of events. (i) The plant produces a factor, designated as factor A. (ii) Factor A causes the Sym plasmid-harboring bacteria to produce Tsr factor. (iii) Growth of young plants in the presence of Tsr factor results in the Tsr phenotype. Models explaining this example of molecular signalling between bacteria and plants are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Downie J. A., Ma Q. S., Knight C. D., Hombrecher G., Johnston A. W. Cloning of the symbiotic region of Rhizobium leguminosarum: the nodulation genes are between the nitrogenase genes and a nifA-like gene. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):947–952. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01526.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooykaas P. J., Snijdewint F. G., Schilperoort R. A. Identification of the Sym plasmid of Rhizobium leguminosarum strain 1001 and its transfer to and expression in other rhizobia and Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plasmid. 1982 Jul;8(1):73–82. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90042-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okker R. J., Spaink H., Hille J., van Brussel T. A., Lugtenberg B., Schilperoort R. A. Plant-inducible virulence promoter of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid. Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):564–566. doi: 10.1038/312564a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossen L., Johnston A. W., Downie J. A. DNA sequence of the Rhizobium leguminosarum nodulation genes nodAB and C required for root hair curling. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9497–9508. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schetgens T. M., Bakkeren G., van Dun C., Hontelez J. G., van den Bos R. C., van Kammen A. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of Rhizobium leguminosarum structural nif-genes by site-directed transposon mutagenesis and expression in Escherichia coli minicells. J Mol Appl Genet. 1984;2(4):406–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Török I., Kondorosi E., Stepkowski T., Pósfai J., Kondorosi A. Nucleotide sequence of Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9509–9524. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]