Abstract
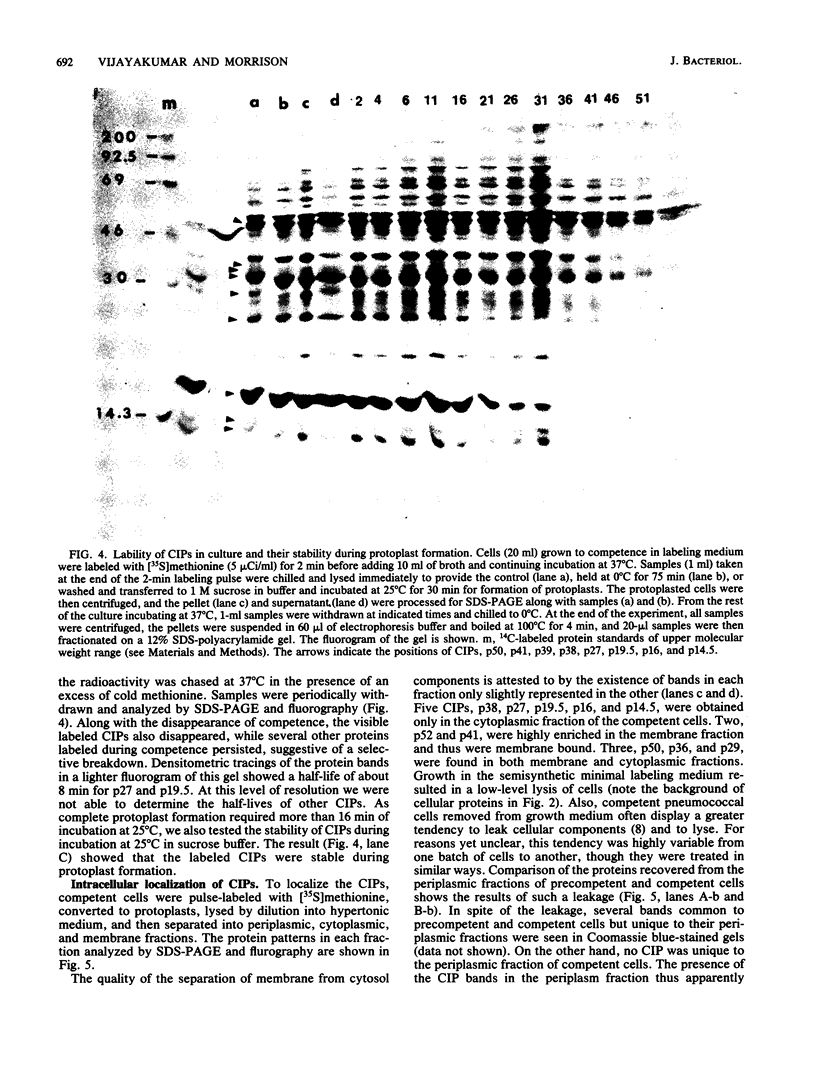
Intracellular locations of 11 proteins associated with the development of competence in Streptococcus pneumoniae were examined by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of subcellular fractions prepared from protoplasts. Controls showed that the competence-induced proteins were stable during the formation of protoplasts at 25 degrees C even though some had a half-life of only 8 min at 37 degrees C. Five competence-induced proteins p38, p27, p19.5, p16, and p14.5, were found in the cytoplasm. Two, p52 and p41, were associated with the membrane, and one, p10, was extracellular. Three others, p50, p36, and p29, were recovered in both cytoplasmic and membrane fractions. No competence-induced protein was detected in the periplasmic fraction except under conditions where leakage of all components was occurring, a phenomenon that was seen in many preparations. Similar fractionation of competent cells soon after uptake of [3H]DNA showed the "eclipse complex" of single-stranded DNA and p19.5 was associated approximately one-third with membranes and two-thirds with cytoplasmic fractions, with almost none in the periplasm. This result suggests strongly that at the time the donor DNA entered the cytosol it was in single-stranded form and it had not yet paired with the recipient DNA.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- LACKS S. Molecular fate of DNA in genetic transformation of Pneumococcus. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:119–131. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80067-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S., Greenberg B., Neuberger M. Role of a deoxyribonuclease in the genetic transformation of Diplococcus pneumoniae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2305–2309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S., Neuberger M. Membrane location of a deoxyribonuclease implicated in the genetic transformation of Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;124(3):1321–1329. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.3.1321-1329.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A., Baker M. F. Competence for genetic transformation in pneumococcus depends on synthesis of a small set of proteins. Nature. 1979 Nov 8;282(5735):215–217. doi: 10.1038/282215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A., Guild W. R. Transformation and deoxyribonucleic acid size: extent of degradation on entry varies with size of donor. J Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;112(3):1157–1168. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1157-1168.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A., Mannarelli B. Transformation in pneumococcus: nuclease resistance of deoxyribonucleic acid in the eclipse complex. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):655–665. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.655-665.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A. Transformation in pneumococcus: existence and properties of a complex involving donor deoxyribonucleate single strands in eclipse. J Bacteriol. 1977 Nov;132(2):576–583. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.2.576-583.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A. Transformation in pneumococcus: protein content of eclipse complex. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):548–557. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.548-557.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raina J. L., Metzer E., Ravin A. W. Translocation of the pre-synaptic complex formed upon DNA uptake by Streptococcus sanguis and its inhibition by ethidium bromide. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Mar 5;170(3):249–259. doi: 10.1007/BF00267058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raina J. L., Ravin A. W. Switches in macromolecular synthesis during induction of competence for transformation of Streptococcus sanguis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6062–6066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow P. Purification and properties of a specific proteolytic enzyme present in spores of Bacillus magaterium. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 25;251(24):7853–7862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto H., Tomasz A. Protoplast formation and leakage of intramembrane cell components: induction by the competence activator substance of pneumococci. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):344–353. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.344-353.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker N. B., Guild W. R. Kinetics of integration of transforming DNA in pneumococcus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3331–3335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Mosser J. L. On the nature of the pneumococcal activator substance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jan;55(1):58–66. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.1.58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Zanati E. ppearance of a protein "agglutinin" on the spheroplast membrane of pneumococci during induction of competence. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):1213–1215. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.1213-1215.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijayakumar M. N., Morrison D. A. Fate of DNA in eclipse complex during genetic transformation in Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):644–648. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.644-648.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]