Abstract
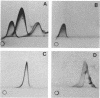
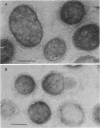
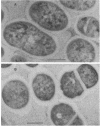
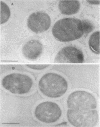
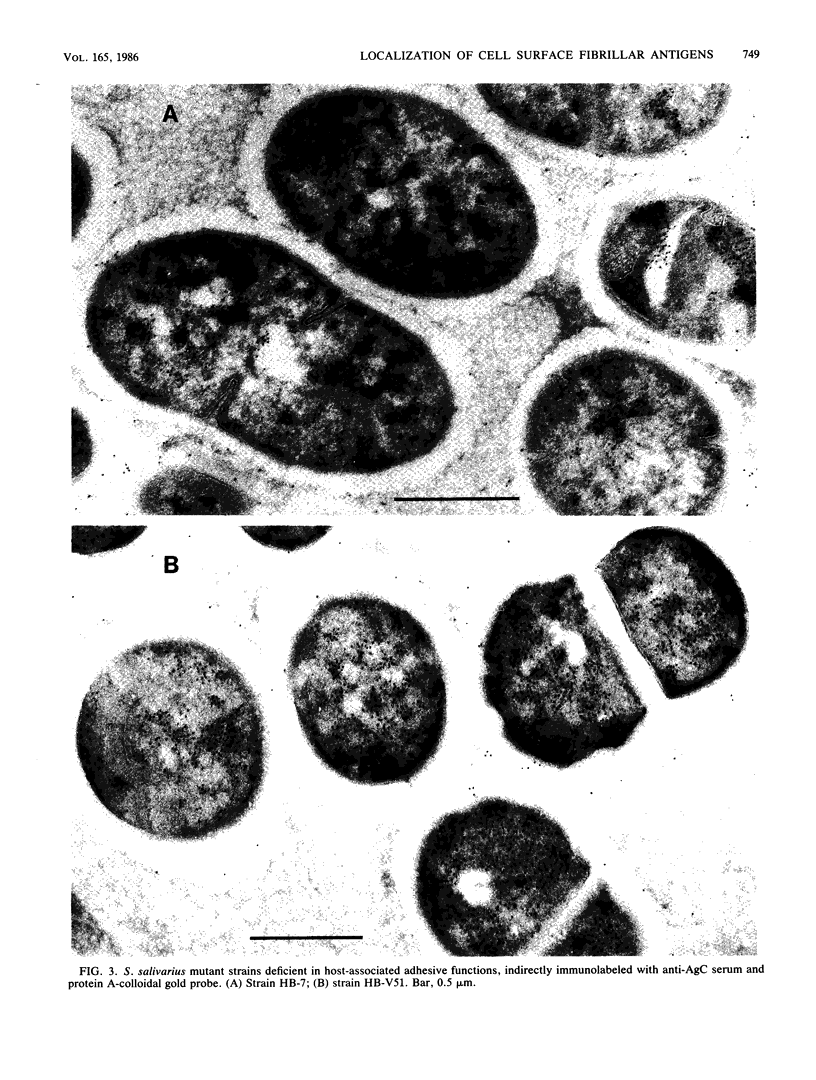
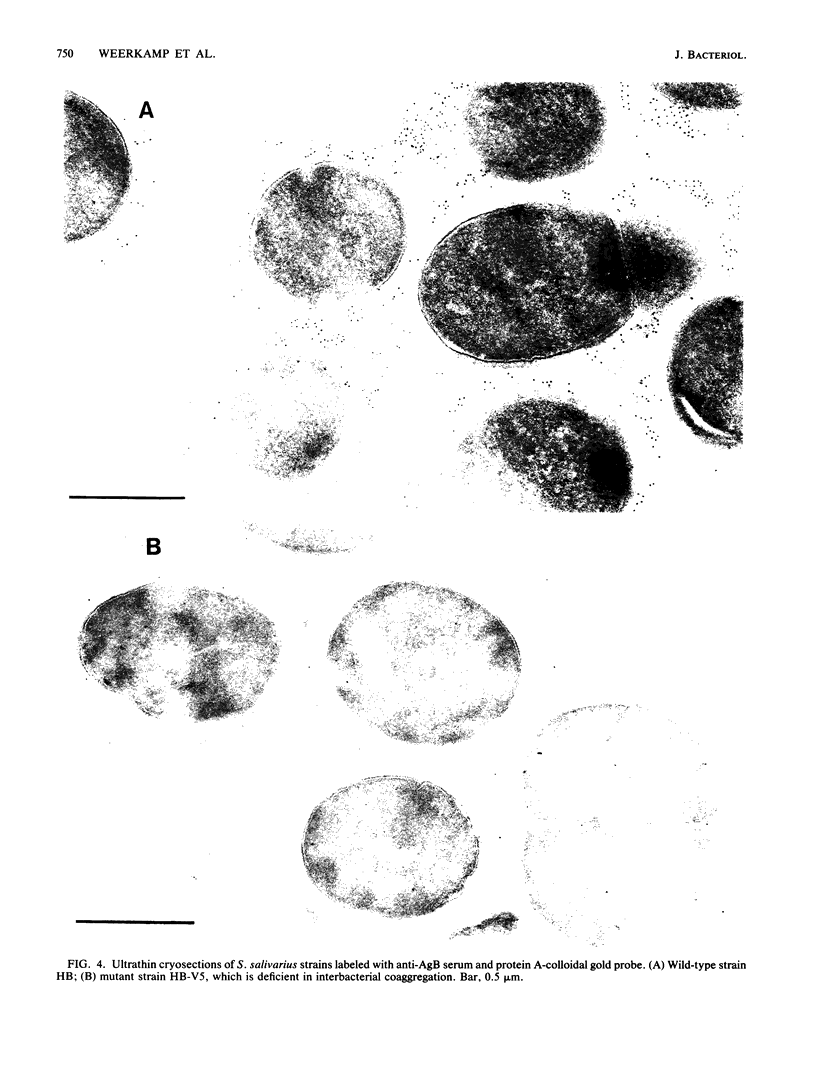
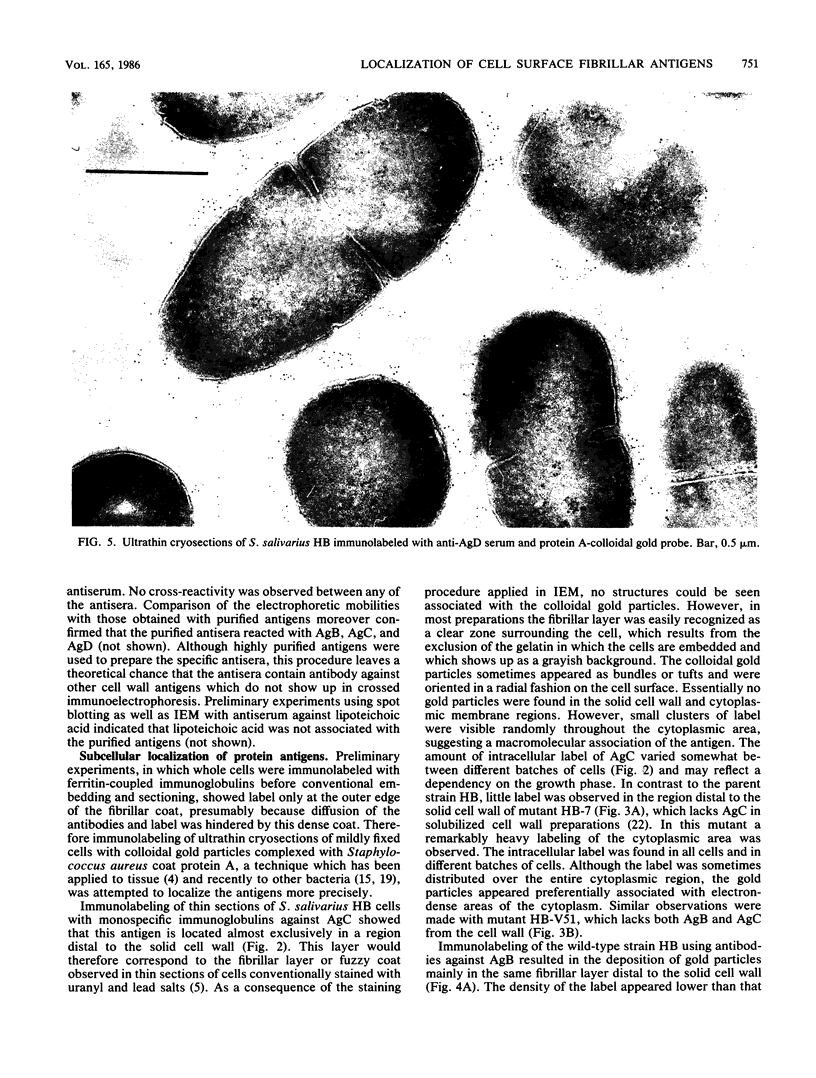
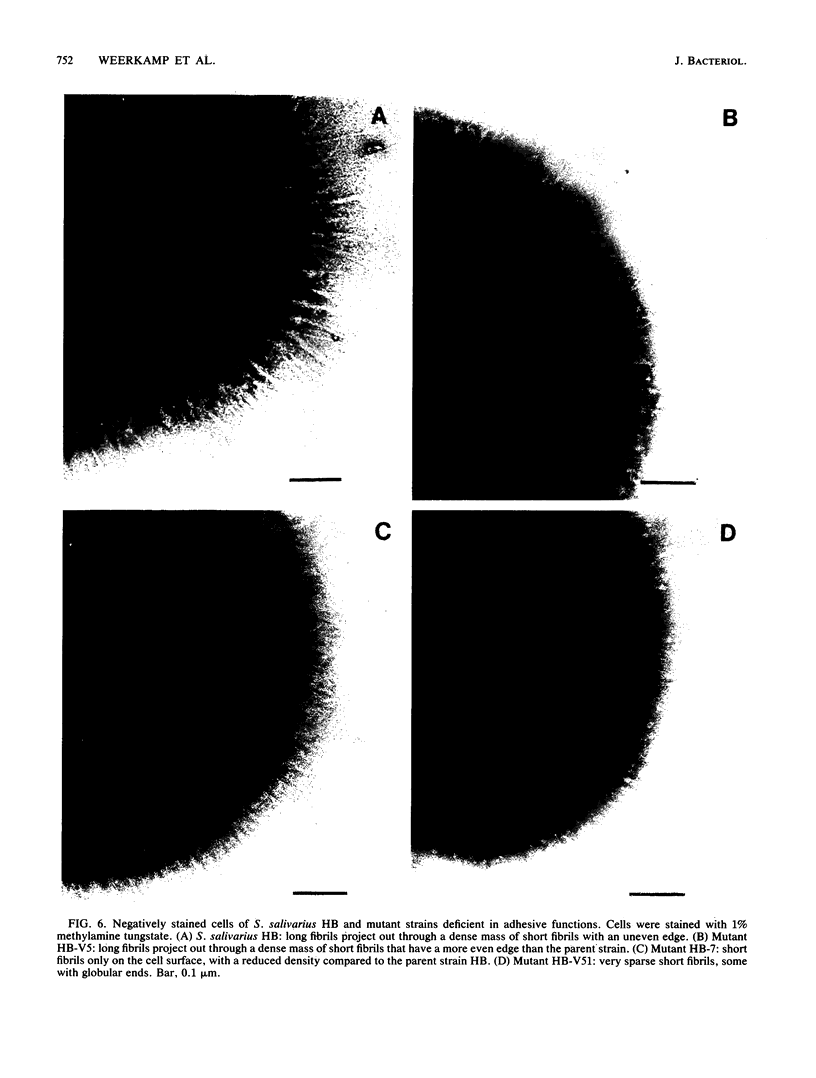
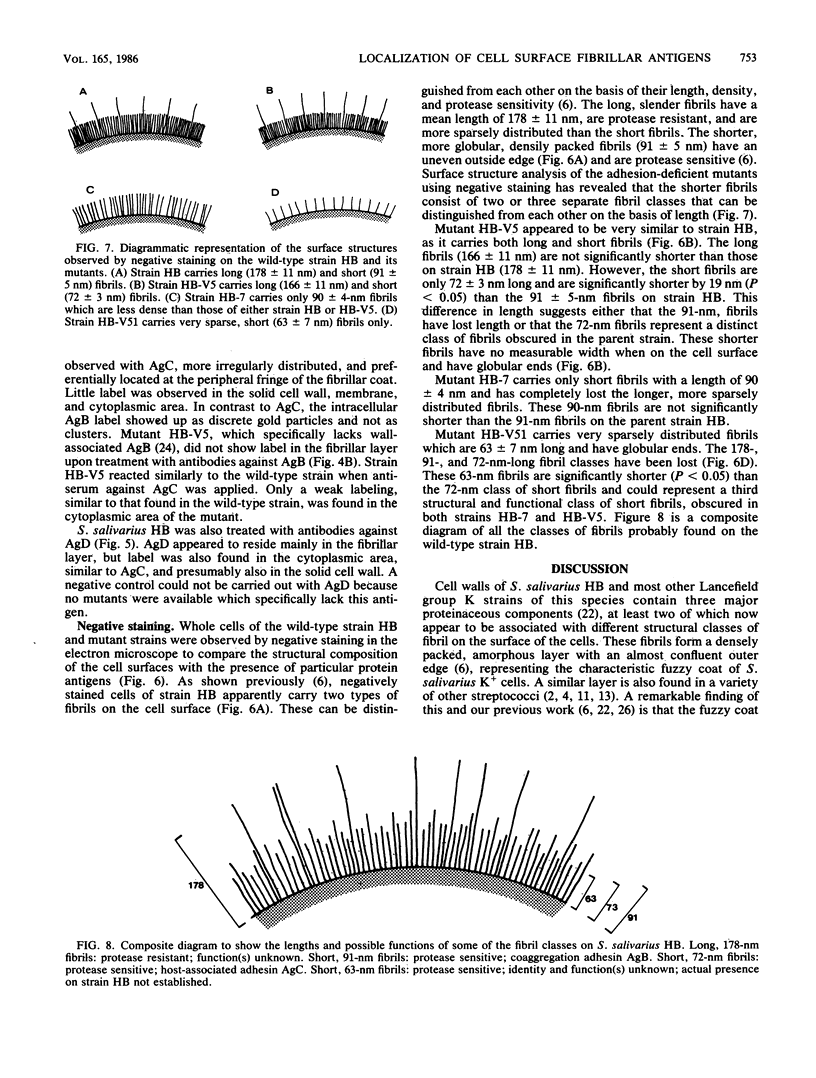
The subcellular distribution of the cell wall-associated protein antigens of Streptococcus salivarius HB, which are involved in specific adhesive properties of the cells, was studied. Mutants which had lost the adhesive properties and lacked the antigens at the cell surface were compared with the parent strain. Immunoelectron microscopy of cryosections of cells labeled with affinity-purified, specific antisera and colloidal gold-protein A complexes was used to locate the antigens. Antigen C (AgC), a glycoprotein involved in attachment to host surfaces, was mainly located in the fibrillar layer outside the cell wall. A smaller amount of label was also found throughout the cytoplasmic area in the form of small clusters of gold particles, which suggests a macromolecular association. Mutant HB-7, which lacks the wall-associated AgC, accumulated AgC reactivity intracellularly. Intracellular AgC was often found associated with isolated areas of increased electron density, but sometimes seemed to fill the entire interior of the cell. Antigen B (AgB), a protein responsible for interbacterial coaggregation, was also located in the fibrillar layer, although its distribution differed from that of the wall-associated AgC since AgB was found predominantly in the peripheral areas. A very small amount of label was also found in the cytoplasmic area as discrete gold particles. Mutant HB-V5, which lacks wall-associated AgB, was not labeled in the fibrillar coat, but showed the same weak intracellular label as the parent strain. Immunolabeling with serum against AgD, another wall-associated protein but of unknown function, demonstrated its presence in the fibrillar layer of strain HB. Negatively stained preparations of whole cells of wild-type S. salivarius and mutants that had lost wall-associated AgB or AgC revealed that two classes of short fibrils are carried on the cell surface at the same time. AgB and AgC are probably located on separate classes of short, protease-sensitive fibrils 91 and 72 nm in length, respectively. A third class of only very sparsely distributed short fibrils (63 nm) was observed on mutant HB-V51, which lacks both wall-associated AgB and AgC antigens. The identity of these fibrils and whether they are present on the wild type are not clear. The function of long, protease-resistant fibrils of 178 nm, which are also present on the wild-type strain, remains unknown.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cisar J. O., Barsumian E. L., Curl S. H., Vatter A. E., Sandberg A. L., Siraganian R. P. Detection and localization of a lectin on Actinomyces viscosus T14V by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1318–1322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellen R. P., Gibbons R. J. M protein-associated adherence of Streptococcus pyogenes to epithelial surfaces: prerequisite for virulence. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):826–830. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.826-830.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fives-Taylor P. M., Thompson D. W. Surface properties of Streptococcus sanguis FW213 mutants nonadherent to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):752–759. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.752-759.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geuze H. J., Slot J. W., van der Ley P. A., Scheffer R. C. Use of colloidal gold particles in double-labeling immunoelectron microscopy of ultrathin frozen tissue sections. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;89(3):653–665. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.3.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Van Houte J., Liljemark W. F. Parameters that effect the adherence of Streptococcus salivarius to oral epithelial surfaces. J Dent Res. 1972 Mar-Apr;51(2):424–435. doi: 10.1177/00220345720510023101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handley P. S., Carter P. L., Fielding J. Streptococcus salivarius strains carry either fibrils or fimbriae on the cell surface. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):64–72. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.64-72.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handley P. S., Carter P. L., Wyatt J. E., Hesketh L. M. Surface structures (peritrichous fibrils and tufts of fibrils) found on Streptococcus sanguis strains may be related to their ability to coaggregate with other oral genera. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):217–227. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.217-227.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. H., Simpson W. A., Dale J. B., Ofek I., Beachey E. H. Lipoteichoic acid-binding and biological properties of T protein of group A streptococcus. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):791–798. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.791-798.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Isaacson R. E. Proteinaceous bacterial adhesins and their receptors. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1983;10(3):229–260. doi: 10.3109/10408418209113564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Gibbons R. J. Proportional distribution and relative adherence of Streptococcus miteor (mitis) on various surfaces in the human oral cavity. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):852–859. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.852-859.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Nakao M., Shibata S., Shizukuishi S., Nakamura R., Tsunemitsu A. Purification and characterization of galactosephilic component present on the cell surfaces of Streptococcus sanguis ATCC 10557. J Periodontol. 1983 Mar;54(3):163–172. doi: 10.1902/jop.1983.54.3.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalbandian J., Freedman M. L., Tanzer J. M., Lovelace S. M. Ultrastructure of Mutants of Streptococcus mutans with Reference to Agglutination, Adhesion, and Extracellular Polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1170–1179. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1170-1179.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R. Wall-associated protein antigens of Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Sep;114(1):109–115. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-1-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilstra M. J., Slot J. W., van der Meide P. H., Posthuma G., Cremers A. F., Bosch L. Immunocytochemical localization of the elongation factor Tu in E. coli cells. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jan 9;165(2):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80164-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklavounou A., Germaine G. R. Adherence of oral streptococci to keratinized and nonkeratinized human oral epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):686–689. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.686-689.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slot J. W., Geuze H. J. A new method of preparing gold probes for multiple-labeling cytochemistry. Eur J Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;38(1):87–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Hsu K. C., Gotschlich E. C. Electron microscopic studies on streptococci. I. M antigen. J Exp Med. 1969 Nov 1;130(5):1063–1091. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.5.1063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinglu G., Ghosh A., Ghosh B. K. Subcellular localization of alkaline phosphatase in Bacillus licheniformis 749/C by immunoelectron microscopy with colloidal gold. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):668–677. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.668-677.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuyasu K. T. Immunochemistry on ultrathin frozen sections. Histochem J. 1980 Jul;12(4):381–403. doi: 10.1007/BF01011956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., Jacobs T. Cell wall-associated protein antigens of Streptococcus salivarius: purification, properties, and function in adherence. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):233–242. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.233-242.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., McBride B. C. Characterization of the adherence properties of Streptococcus salivarius. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):459–468. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.459-468.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., McBride B. C. Identification of a Streptococcus salivarius cell wall component mediating coaggregation with Veillonella alcalescens V1. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):723–730. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.723-730.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., van der Mei H. C., Liem R. S. Structural properties of fibrillar proteins isolated from the cell surface and cytoplasm of Streptococcus salivarius (K+) cells and nonadhesive mutants. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):756–762. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.756-762.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]