Abstract
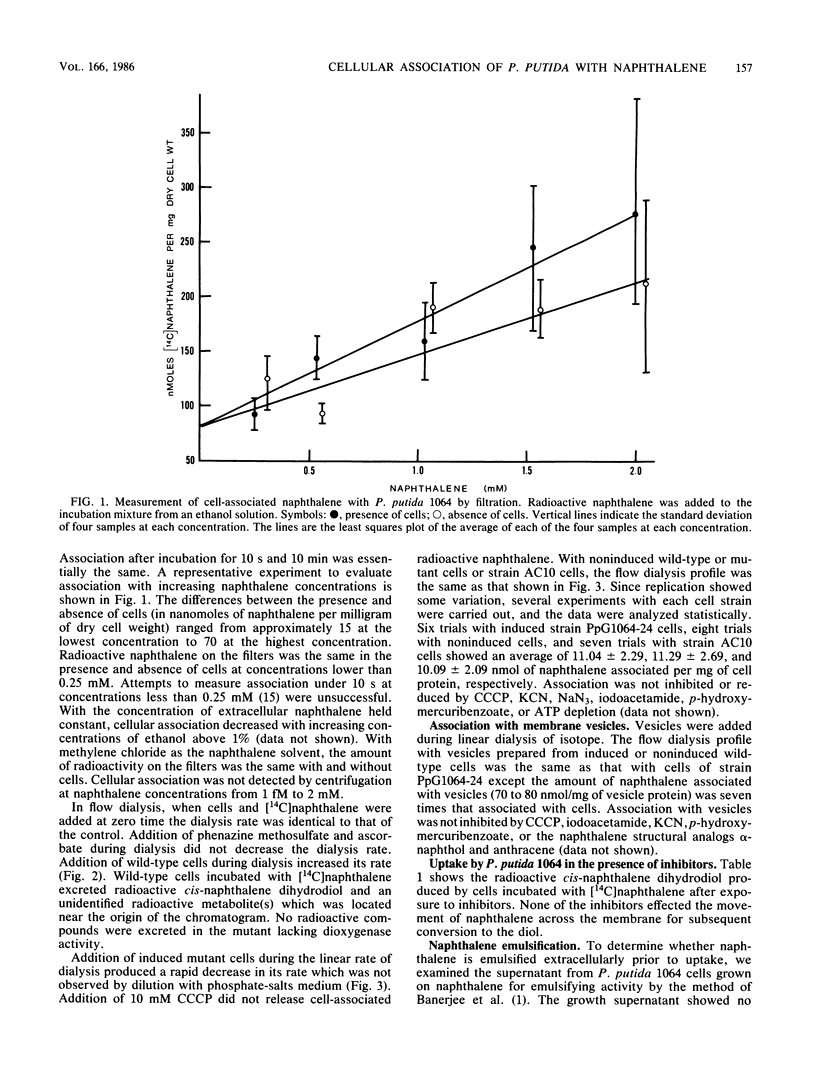
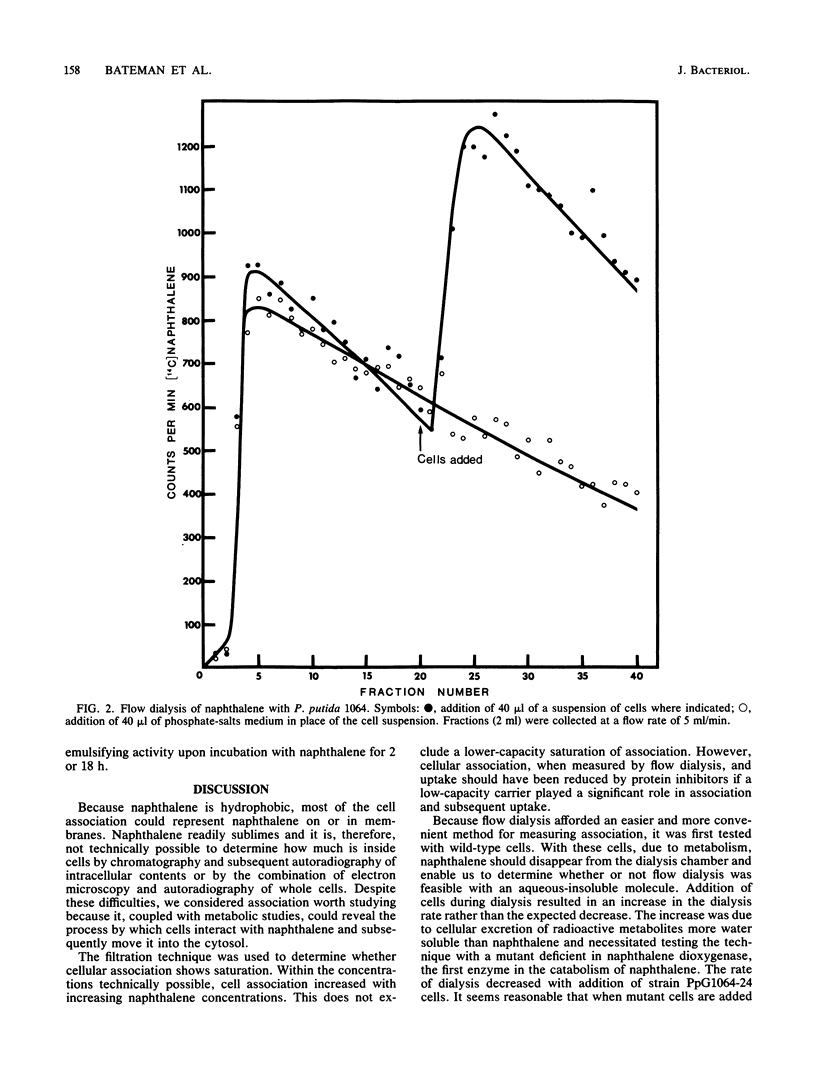
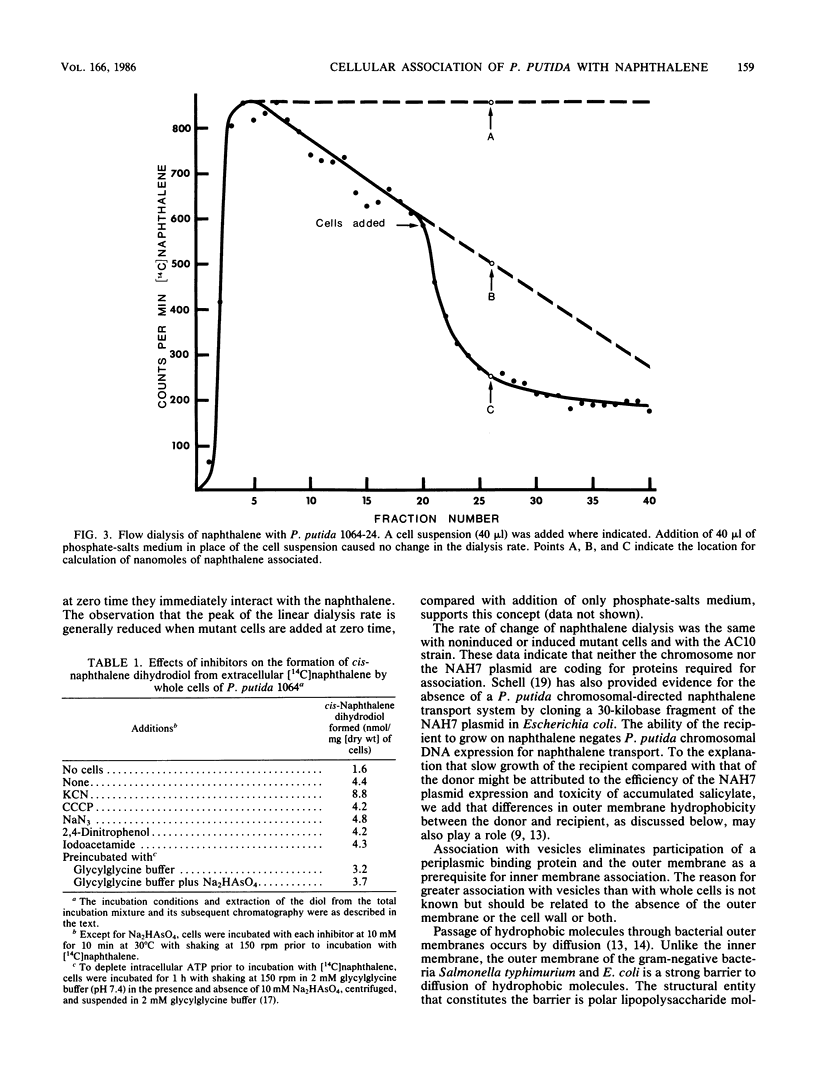
Two methods for bacterial membrane transport, filtration and flow dialysis, were used to study cellular association of Pseudomonas putida with naphthalene. It is not technically possible to determine the exact cellular or vesicular location of the naphthalene, and because it is hydrophobic, it could be at the membrane(s) rather than inside the cells. As an index of naphthalene having crossed the inner membrane we used the intracellular formation of its first catabolite. An energized membrane or ATP was not essential for association or movement into the cell. Evidence for a nonspecific association and a movement into cells by simple diffusion are the lack of saturation of association, an absence of inhibition of association by protein inhibitors and structural analogs, and the passage of naphthalene through cell membranes in the presence of iodoacetamide. Specific naphthalene metabolism gene expression was not required for association.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnsley E. A. Role and regulation of the ortho and meta pathways of catechol metabolism in pseudomonads metabolizing naphthalene and salicylate. J Bacteriol. 1976 Feb;125(2):404–408. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.2.404-408.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty A. M. Genetic basis of the biodegradation of salicylate in Pseudomonas. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):815–823. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.815-823.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. I., Evans W. C. Oxidative metabolism of naphthalene by soil pseudomonads. The ring-fission mechanism. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):251–261. doi: 10.1042/bj0910251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubler R. E., Toscano W. A., Jr, Hartline R. A. Transport of succinate by Pseudomonas putida. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Feb;160(2):422–429. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90416-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards W. V., Sando J. J., Hartline R. A. Transport of C5 dicarboxylate compounds by Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):748–754. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.748-754.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensley B. D., Gibson D. T., Laborde A. L. Oxidation of naphthalene by a multicomponent enzyme system from Pseudomonas sp. strain NCIB 9816. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):948–954. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.948-954.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann K. New devices for flow dialysis and ultrafiltration for the study of protein--ligand interactions. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jul 15;88(1):225–235. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90414-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilleland H. E., Jr, Stinnett J. D., Roth I. L., Eagon R. G. Freeze-etch study of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: localization within the cell wall of an ethylenediaminetetraacetate-extractable. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jan;113(1):417–432. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.1.417-432.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Molecular biology and energetics of membrane transport. J Cell Physiol. 1976 Dec;89(4):575–593. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040890414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labischinski H., Barnickel G., Bradaczek H., Naumann D., Rietschel E. T., Giesbrecht P. High state of order of isolated bacterial lipopolysaccharide and its possible contribution to the permeation barrier property of the outer membrane. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):9–20. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.9-20.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Vaara M. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):1–32. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.1-32.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pekala P. H., Perfetti T., Hartline R. A. Physiological basis for preferential uptake of D-alpha-aminoadipate over the L-isomer by Alcaligenes denitrificans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jun 11;394(1):65–75. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Schuldiner S., Kaback H. R. The use of flow dialysis for determinations of deltapH and active transport. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:680–688. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano A. H., Voytek A., Bruskin A. M. Energization of glucose transport by Pseudomonas fluorescens. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jun;142(3):755–762. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.3.755-762.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala-Trepat J. M., Murray K., Williams P. A. The metabolic divergence in the meta cleavage of catechols by Pseudomonas putida NCIB 10015. Physiological significance and evolutionary implications. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 24;28(3):347–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01920.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schell M. A. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the naphthalene degradation genes from plasmid NAH7. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):822–829. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.822-829.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRECCANI V., WALKER N., WILTSHIRE G. H. The metabolism of naphthalene by soil bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Dec;11(3):341–348. doi: 10.1099/00221287-11-3-341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALKER N., WILTSHIRE G. H. The breakdown of naphthalene by a soil bacterium. J Gen Microbiol. 1953 Apr;8(2):273–276. doi: 10.1099/00221287-8-2-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen K. M., Gunsalus I. C. Plasmid gene organization: naphthalene/salicylate oxidation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):874–878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



