Abstract
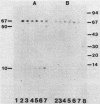
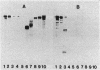
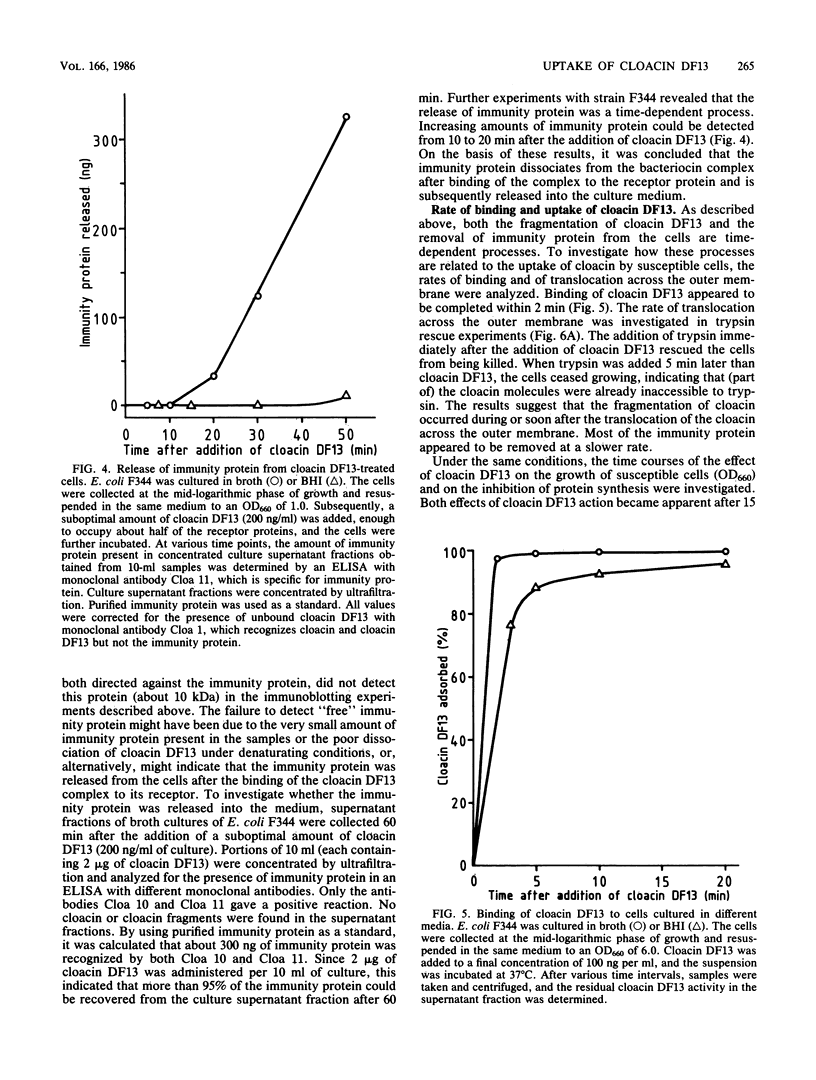
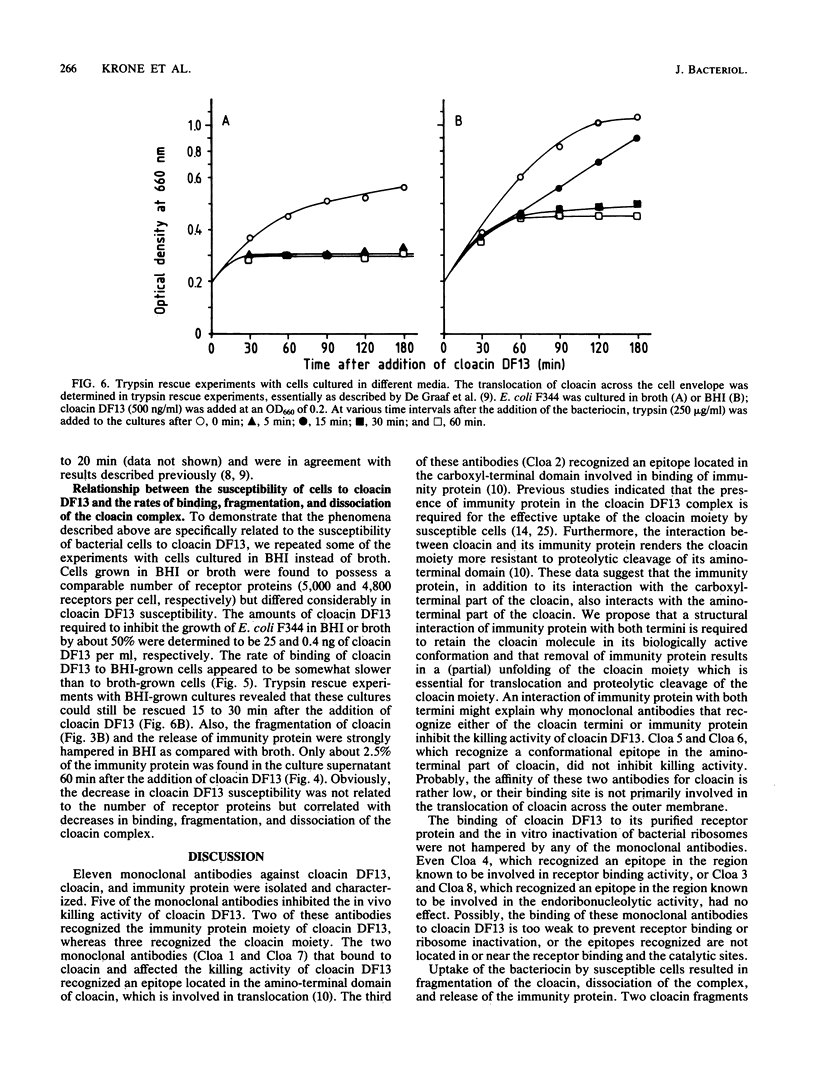
Monoclonal antibodies (MAb) directed against different epitopes on the equimolar complex of cloacin and immunity protein (cloacin DF13) were isolated, characterized, and used to study the uptake of cloacin DF13 by susceptible cells. Four MAbs recognized the amino-terminal part, one MAb recognized the central part, and three MAbs recognized the carboxyl-terminal part of the cloacin molecule. Three MAbs reacted with the immunity protein. Five MAbs inhibited the lethal action of cloacin DF13, but none of the MAbs inhibited the binding of cloacin DF13 to its purified outer membrane receptor protein or the in vitro inactivation of ribosomes. Binding of cloacin DF13 to susceptible cells cultured in broth resulted in a specific, time-dependent dissociation of the complex and a fragmentation of the cloacin molecules. Increasing amounts of immunity protein were detected in the culture medium from about 20 min after the addition of cloacin DF13. Cloacin was fragmented into two carboxyl-terminal fragments with relative molecular masses of 50,000 and 10,000. The larger fragment was detected 5 min after the binding of the bacteriocin complex to the cells. The smaller fragment was detected after 10 min. Both fragments were associated with the cells and could not be detected in the culture supernatant fraction. Cells grown in brain heart infusion were much less susceptible to cloacin DF13 than cells grown in broth, although they possessed a similar number of outer membrane receptor molecules. This decreased susceptibility correlated with a decreased translocation, dissociation, and fragmentation of cloacin DF13.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreoli P. M., Overbeeke N., Veltkamp E., van Embden J. D., Nijkamp H. J. Genetic map of the bacteriocinogenic plasmid CLO DF13 derived by insertion of the transposon Tn901. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Mar 20;160(1):1–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00275113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowles L. K., Konisky J. Cleavage of colicin Ia by the Escherichia coli K-12 outer membrane is not mediated by the colicin Ia receptor. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):668–671. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.668-671.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brey R. N. Fragmentation of colicins A and E1 by cell surface proteases. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):306–315. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.306-315.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavard D., Lazdunski C. Interaction of colicin E4 with specific receptor sites mediates its cleavage into two fragments inactive towards whole cells. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun 1;96(3):525–533. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung C. H., Goldberg A. L. The product of the lon (capR) gene in Escherichia coli is the ATP-dependent protease, protease La. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4931–4935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Graaf F. K., Klaasen-Boor P. Purification and characterization of a complex between cloacin and its immunity protein isolated from Enterobacter cloacae (Clo DF13). Dissociation and reconstitution of the complex. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Feb 15;73(1):107–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaastra W., Koopmans G., de Graaf F. K. Circular dichroism and structure- function relationships in cloacin DF13- immunity protein complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jan 13;80(1):97–103. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91109-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaastra W., Oudega B., de Graaf F. K. The use of mutants in the study of structure-function relationships in cloacin DF13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 3;540(2):301–312. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90143-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Niday E., Gordon J. A dot-immunobinding assay for monoclonal and other antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90677-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krone W. J., Oudega B., Stegehuis F., de Graaf F. K. Cloning and expression of the cloacin DF13/aerobactin receptor of Escherichia coli (ColV-K30). J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):716–721. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.716-721.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooi F. R., de Graaf F. K., van Embden J. D. Cloning, mapping and expression of the genetic determinant that encodes for the K88ab antigen. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Mar;6(3):849–865. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.3.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane P. K., Kawaoi A. Peroxidase-labeled antibody. A new method of conjugation. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1084–1091. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudega B., Klaasen-Boor P., De Graaf F. K. Mode of action of the cloacin DF13-immunity protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 5;392(1):184–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudega B., Klaasen-Boor P., Sneeuwloper G., De Graaf F. K. Interaction of the complex between cloacin and its immunity protein and of cloacin with the outer and cytoplasmic membranes of sensitive cells. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Sep;78(2):445–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11757.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudega B., de Graaf F. K. Enzymatic properties of cloacin DF13 and kinetics of ribosome inactivation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 17;425(3):296–304. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90256-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudega B., van der Molen J., de Graaf F. K. In vitro binding of cloacin DF13 to its purified outer membrane receptor protein and effect of peptidoglycan on bacteriocin-receptor interaction. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):964–970. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.964-970.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbuch M., Audran R. The isolation of IgG from mammalian sera with the aid of caprylic acid. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Nov;134(2):279–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90285-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Tiel-Menkveld G. J., Mentjox-Vervuurt J. M., Oudega B., de Graaf F. K. Siderophore production by Enterobacter cloacae and a common receptor protein for the uptake of aerobactin and cloacin DF13. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):490–497. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.490-497.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. H., Sherratt D. J. In vivo proteolytic cleavage of colicins requires specific receptor binding. Nature. 1979 Mar 22;278(5702):362–364. doi: 10.1038/278362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graaf F. K., Niekus H. G., Klootwijk J. Inactivation of bacterial ribosomes in vivo and in vitro by cloacin DF13. FEBS Lett. 1973 Sep 1;35(1):161–165. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80601-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graaf F. K., Spanjaerdt Speckman E. A., Stouthamer A. H. Mode of action of a bacteriocin produced by Enterobacter cloacae DF13. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1969;35(3):287–306. doi: 10.1007/BF02219150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graaf F. K., Stukart M. J., Boogerd F. C., Metselaar K. Limited proteolysis of cloacin DF13 and characterization of the cleavage products. Biochemistry. 1978 Mar 21;17(6):1137–1142. doi: 10.1021/bi00599a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Haan P., de Jonge A. J., Verbrugge T., Boorsma D. M. Three epitope-specific monoclonal antibodies against the hapten penicillin. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1985;76(1):42–46. doi: 10.1159/000233659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Embden J. D., Veltkamp E., Stuitje T., Andreoli P. M., Nijkamp H. J. Integration of a transposable DNA sequence which mediates ampicillin resistance into Clo DF13 plasmid DNA: determination of the site and orientation of TnA insertions. Plasmid. 1978 Feb;1(2):204–217. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Elzen P. J., Gaastra W., Spelt C. E., de Graaf F. K., Veltkamp E., Nijkamp H. J. Molecular structure of the immunity gene and immunity protein of the bacteriocinogenic plasmid Clo DF13. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 10;8(19):4349–4363. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.19.4349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Elzen P. J., Walters H. H., Veltkamp E., Nijkamp H. J. Molecular structure and function of the bacteriocin gene and bacteriocin protein of plasmid Clo DF13. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2465–2477. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]